This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Atropine
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='2bg9' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption=''> | ||
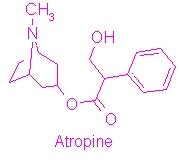
[[Image:Atropine structure.jpg|thumb|right|1000px|Structure of Atropine]][[Atropine]] is an alkaloid drug derived from levohyscocyamine, a plant compound found in the family Solanaceae<ref> Atropine. Encyclopedia Brittanica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/42015/atropine</ref>. It's chemical name is 8-methyl-8-azabicycolo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl) 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate, and the most common medicinal form of atropine is atrophine sulfate ((C17H23NO3)2·H2SO4·H2O)<ref> Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine </ref>. It is a competitive antagonist of both acetylcholine receptors and phospholipase 2A and has a variety of effects on both humans and animals. | [[Image:Atropine structure.jpg|thumb|right|1000px|Structure of Atropine]][[Atropine]] is an alkaloid drug derived from levohyscocyamine, a plant compound found in the family Solanaceae<ref> Atropine. Encyclopedia Brittanica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/42015/atropine</ref>. It's chemical name is 8-methyl-8-azabicycolo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl) 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate, and the most common medicinal form of atropine is atrophine sulfate ((C17H23NO3)2·H2SO4·H2O)<ref> Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine </ref>. It is a competitive antagonist of both acetylcholine receptors and phospholipase 2A and has a variety of effects on both humans and animals. | ||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| - | <applet load='2bg9' size='400' frame='true' align='right' Acetylcholine Receptor='' /> | ||
=== Function and Basic Mechanism === | === Function and Basic Mechanism === | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
Atropine is also a good antidote for poisoning by organophosphates and nerve gases, prime agents in bioterrorism<ref> Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine </ref>, because Atropine blocks acetylcholine at muscscarininc receptors. Atropine, however, has side effects that include nausea, dizziness, blurred visions, tachycardia, and hallucinations, and due to these side effects it has recently become more popular as a recreational drug. | Atropine is also a good antidote for poisoning by organophosphates and nerve gases, prime agents in bioterrorism<ref> Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine </ref>, because Atropine blocks acetylcholine at muscscarininc receptors. Atropine, however, has side effects that include nausea, dizziness, blurred visions, tachycardia, and hallucinations, and due to these side effects it has recently become more popular as a recreational drug. | ||
| - | [[Image:atropine.jpg|thumb| | + | [[Image:atropine.jpg|thumb|left|350px|Atropine Tablets]] <ref>Atropine Diphenoxylate. http://www.everydayhealth.com/drugs/atropine-diphenoxylate </ref> |
==== Uses in Veterinary Medicine ==== | ==== Uses in Veterinary Medicine ==== | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
== '''Interaction of Atropine with Phospholipase 2A''' == | == '''Interaction of Atropine with Phospholipase 2A''' == | ||
| - | < | + | |
| - | [[Image:Phospholipase A2.gif|thumb| | + | <scene name='42/420811/Cv/1'>Atropine in complex with phospholipase A2</scene> ([[1th6]]). |
| + | |||
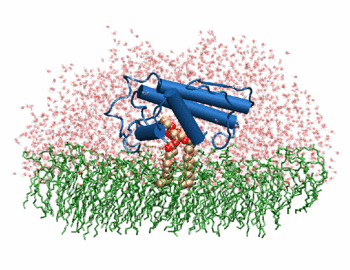
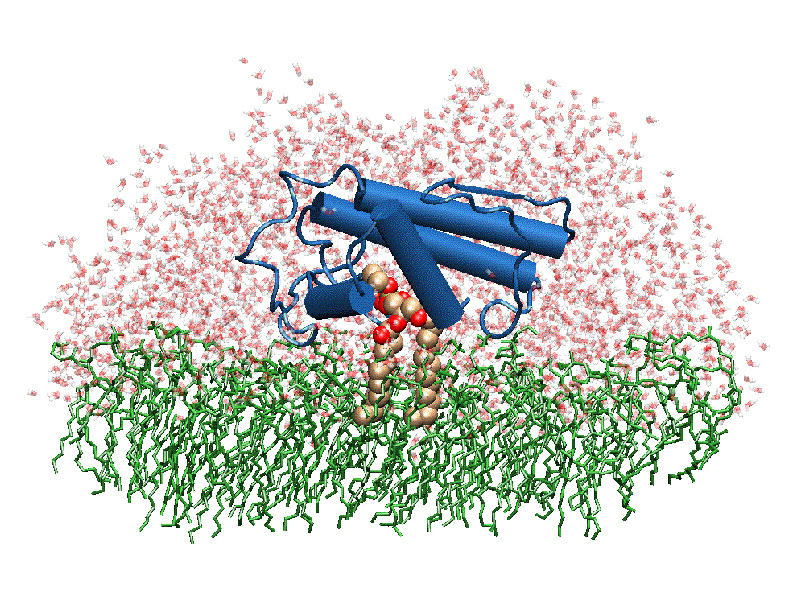
| + | [[Image:Phospholipase A2.gif|thumb|left|350px|Phospholipase 2A in complex with cell membrane]] | ||
In addition to its ability to form complexes with acetylcholine receptors, atropine can also complex with phospholipase A2. Phospholipase A2 is a category of heat-stable enzymes which are involved in cell signaling processes, such as the inflammatory response. <ref>Kumar, Jainendra; Bala, Priti; Vihwal, Preeti. ''Analysis of Interaction of atropine with phospholipase A2 (1th6.pdb)''. Department of Botany and Biotechnlogy, College of Commerce, Patna, India.</ref>. Phospholipase 2A is an upstream regulator of inflammatory processes, and more specifically, it recognizes the sn-2 acyl bond of phospholipids and catalytically hydrolyzes the bond, releasing lysophospholipids <ref> Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2 </ref>. | In addition to its ability to form complexes with acetylcholine receptors, atropine can also complex with phospholipase A2. Phospholipase A2 is a category of heat-stable enzymes which are involved in cell signaling processes, such as the inflammatory response. <ref>Kumar, Jainendra; Bala, Priti; Vihwal, Preeti. ''Analysis of Interaction of atropine with phospholipase A2 (1th6.pdb)''. Department of Botany and Biotechnlogy, College of Commerce, Patna, India.</ref>. Phospholipase 2A is an upstream regulator of inflammatory processes, and more specifically, it recognizes the sn-2 acyl bond of phospholipids and catalytically hydrolyzes the bond, releasing lysophospholipids <ref> Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2 </ref>. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 67: | ||
Removing the labels, atropine can be seen making contact with the atoms emphasized by the space filling model, interacting with the <scene name='Sandbox_53/Phospholipase2a_interactions/1'>active site</scene> of phospholipase 2A through white as-tricks. | Removing the labels, atropine can be seen making contact with the atoms emphasized by the space filling model, interacting with the <scene name='Sandbox_53/Phospholipase2a_interactions/1'>active site</scene> of phospholipase 2A through white as-tricks. | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
== '''References''' == | == '''References''' == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 07:10, 15 September 2013
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Atropine. Encyclopedia Brittanica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/42015/atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Gnagey, Ann L; Seidenberg, Margret; Ellis, John; Site-directed mutagenesis reveals two epitopes involved in the subtype selectivity of the allosteric interactions of gallamine at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Molecular Pharmocology, 56:1245-1253, 1999
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Parker, Julie C; Sarkar, Deboshree; Quick, Michael W; Lester, Robin A. Interactions of Atropine with heterologously expressed and native alpha3 subunit-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. British Journal of Pharmacology. 138:5. p801-810. 2009.
- ↑ Image from: http://www.neurevolution.net/category/history/page/2/
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine. New World Encyclopedia. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Atropine
- ↑ Atropine Diphenoxylate. http://www.everydayhealth.com/drugs/atropine-diphenoxylate
- ↑ Riviere, Jim E. Papich, Mark G. Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 9th Edition. John Wiley and Sons, 2009.
- ↑ ATROPINE- ORAL. http://www.medicinenet.com/atropine-oral/article.htm
- ↑ ATROPINE- ORAL. http://www.medicinenet.com/atropine-oral/article.htm
- ↑ Atropine. http://www.rxlist.com/atropine-drug.htm
- ↑ Kumar, Jainendra; Bala, Priti; Vihwal, Preeti. Analysis of Interaction of atropine with phospholipase A2 (1th6.pdb). Department of Botany and Biotechnlogy, College of Commerce, Patna, India.
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ pla2.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Lindsey Hayes, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel, OCA