Single stranded binding protein
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===Sandbox Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein (SSB)=== | ===Sandbox Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein (SSB)=== | ||
| - | ==Introduction== | ||
'''Single-stranded DNA-binding protein''', or SSB, binds to single-stranded regions of DNA in order to prevent premature annealing, to protect the single-stranded DNA from being digested by nucleases, and to remove secondary structure from the DNA to allow other enzymes to function effectively upon it. Single-stranded DNA is produced during all aspects of DNA metabolism: replication, recombination and repair. As well as stabilizing this single-stranded DNA, SSB proteins bind to and modulate the function of numerous proteins involved in all of these processes. | '''Single-stranded DNA-binding protein''', or SSB, binds to single-stranded regions of DNA in order to prevent premature annealing, to protect the single-stranded DNA from being digested by nucleases, and to remove secondary structure from the DNA to allow other enzymes to function effectively upon it. Single-stranded DNA is produced during all aspects of DNA metabolism: replication, recombination and repair. As well as stabilizing this single-stranded DNA, SSB proteins bind to and modulate the function of numerous proteins involved in all of these processes. | ||
| + | ==Introduction== | ||
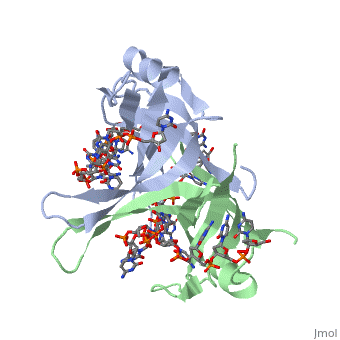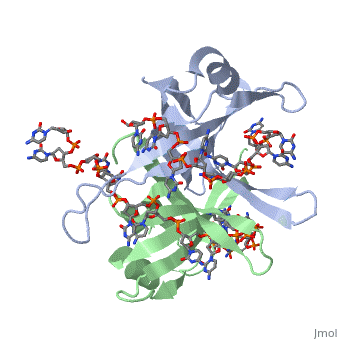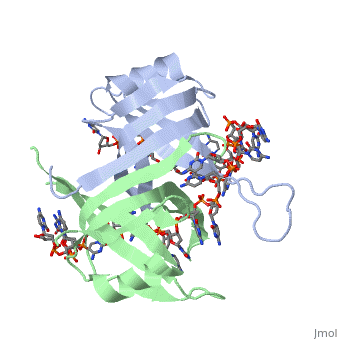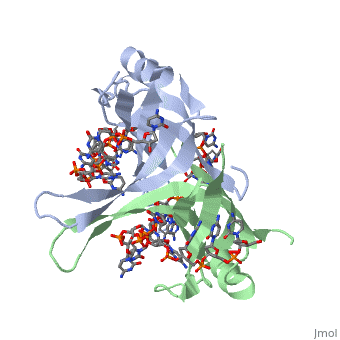
<StructureSection load='1eyg' size='400' side='right' frame='true' caption='Structure of Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein bound to ssDNA (PDB entry [[1eyg]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1eyg' size='400' side='right' frame='true' caption='Structure of Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein bound to ssDNA (PDB entry [[1eyg]])' scene=''> | ||
Revision as of 02:23, 2 November 2013
Contents |
Sandbox Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein (SSB)
Single-stranded DNA-binding protein, or SSB, binds to single-stranded regions of DNA in order to prevent premature annealing, to protect the single-stranded DNA from being digested by nucleases, and to remove secondary structure from the DNA to allow other enzymes to function effectively upon it. Single-stranded DNA is produced during all aspects of DNA metabolism: replication, recombination and repair. As well as stabilizing this single-stranded DNA, SSB proteins bind to and modulate the function of numerous proteins involved in all of these processes.
Introduction
| |||||||||||
Structure
| |||||||||||
Binding Interactions between DNA and SSB of E. coli
| |||||||||||
See Also
References
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Refayat Ahsen, Rachel Craig, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky