Single stranded binding protein
From Proteopedia
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
It is believed that Gly15 may play an important role in binding the RecA protein. Mutations in Gly15 have | It is believed that Gly15 may play an important role in binding the RecA protein. Mutations in Gly15 have | ||
extreme effects on recombinational repair. SSB has also been thought to bind with exonuclease I, DNA polymerase II, | extreme effects on recombinational repair. SSB has also been thought to bind with exonuclease I, DNA polymerase II, | ||
| - | and a protein n, which is used to help synthesize RNA primers for the lagging strand. | + | and a protein n, which is used to help synthesize RNA primers for the lagging strand. SSB can also help regulate transcription by competing with other proteins for binding spaces on DNA. SSB has a higher affinity for DNA than most other proteins, and those proteins are not able to remove SSB from DNA and bind themselves. This type of mechanism can not only regulate transcription, but it can provide protection for the DNA. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 04:34, 2 November 2013
Contents |
Sandbox Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein (SSB)
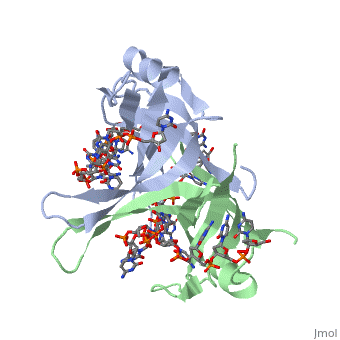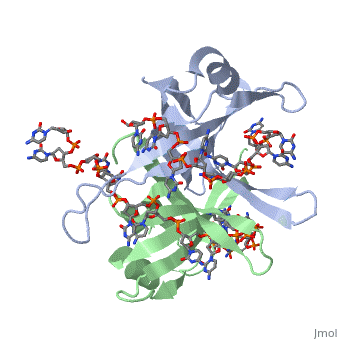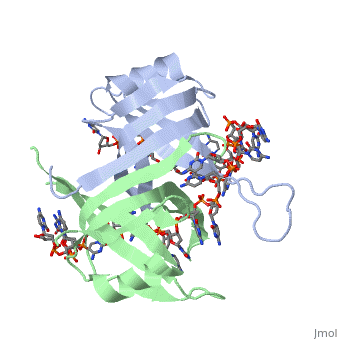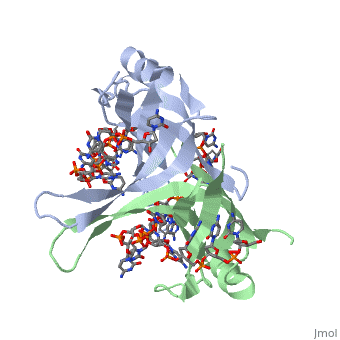
Single-stranded DNA-binding protein, or SSB, binds to single-stranded regions of DNA in order to prevent premature annealing, to protect the single-stranded DNA from being digested by nucleases, and to remove secondary structure from the DNA to allow other enzymes to function effectively upon it. Single-stranded DNA is produced during all aspects of DNA metabolism: replication, recombination and repair. As well as stabilizing this single-stranded DNA, SSB proteins bind to and modulate the function of numerous proteins involved in all of these processes.
Overview
| |||||||||||
Structure
| |||||||||||
Binding Interactions between DNA and SSB of E. coli
| |||||||||||
See Also
References
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Refayat Ahsen, Rachel Craig, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky