Single stranded binding protein
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | Sandbox Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein (SSB) | |
| - | '''Single-stranded DNA-binding protein''', or '''SSB''' | + | ==Overview== |
| + | '''Single-stranded DNA-binding protein''', or '''SSB''' binds to single-stranded regions of DNA. This binding serves a variety of functions - it prevents the strands from hardening too early during replication, it protects the single-stranded DNA from being broken down by nucleases, and it removes the secondary structure of the strands so that other enzymes are able to access them and act effectively upon the strands<ref>PMID: 2087220)</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) is utilized primarily during the course of major aspects of DNA metabolism such as replication, recombination and repair (PMID: 2087220). In addition to stabilizing ssDNA, SSB proteins also bind to and control the function of many other proteins that are involved in all of three of these major DNA metabolic processes. During DNA replication, SSB molecules bind to the newly separated individual DNA strands, keeping the strands separated by holding them in place so that each strand can serve as a template for new DNA synthesis<ref>Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L. ''Biochemistry''. 6th edition. New York: W H Freeman; 2006.</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
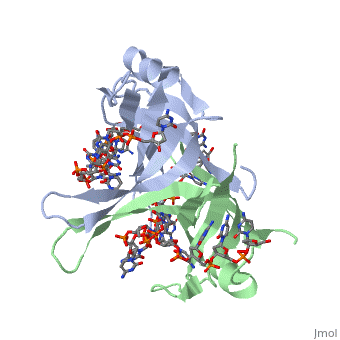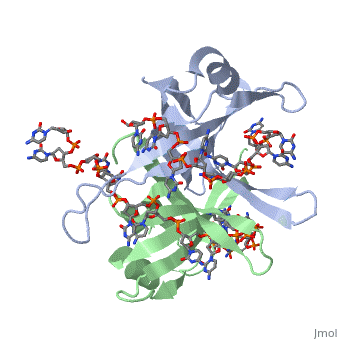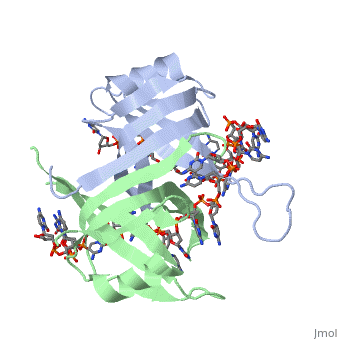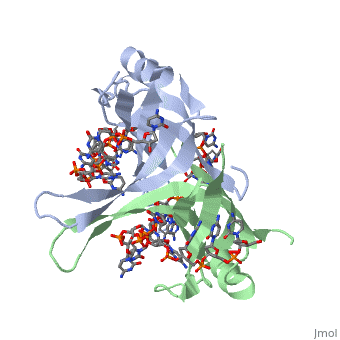
<StructureSection load='1eyg' size='400' side='right' frame='true' caption='Structure of Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein bound to ssDNA (PDB entry [[1eyg]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1eyg' size='400' side='right' frame='true' caption='Structure of Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein bound to ssDNA (PDB entry [[1eyg]])' scene=''> | ||
Revision as of 23:25, 2 November 2013
Sandbox Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein (SSB)
Contents |
Overview
Single-stranded DNA-binding protein, or SSB binds to single-stranded regions of DNA. This binding serves a variety of functions - it prevents the strands from hardening too early during replication, it protects the single-stranded DNA from being broken down by nucleases, and it removes the secondary structure of the strands so that other enzymes are able to access them and act effectively upon the strands[1].
Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) is utilized primarily during the course of major aspects of DNA metabolism such as replication, recombination and repair (PMID: 2087220). In addition to stabilizing ssDNA, SSB proteins also bind to and control the function of many other proteins that are involved in all of three of these major DNA metabolic processes. During DNA replication, SSB molecules bind to the newly separated individual DNA strands, keeping the strands separated by holding them in place so that each strand can serve as a template for new DNA synthesis[2].
Overview
| |||||||||||
Structure
| |||||||||||
Binding Interactions between DNA and SSB of E. coli
| |||||||||||
See Also
References
- ↑ PMID: 2087220)
- ↑ Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L. Biochemistry. 6th edition. New York: W H Freeman; 2006.
- ↑ Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L. Biochemistry. 6th edition. New York: W H Freeman; 2006.
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Meyer RR, Laine PS. The single-stranded DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):342-80. PMID:2087220
- ↑ Agamova KA, Gladunova ZD, Savinkin IuN. [Cytologic method in the diagnosis of precancerous conditions and early cancer of the stomach]. Lab Delo. 1988;(3):43-5. PMID:2453719
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Refayat Ahsen, Rachel Craig, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky