We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Ku protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
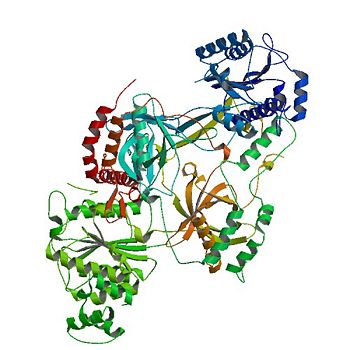
Unlike other DNA binding proteins, the Ku protein is asymmetrical from the differences between the Ku70 and Ku80 subunits. | Unlike other DNA binding proteins, the Ku protein is asymmetrical from the differences between the Ku70 and Ku80 subunits. | ||
This asymmetry leads to different favorable locations for DNA based on major and minor grooves.<ref name="Walker"/> | This asymmetry leads to different favorable locations for DNA based on major and minor grooves.<ref name="Walker"/> | ||
| - | The Ku70 subunit is <scene name='56/567269/Ku70_subunit/ | + | The Ku70 subunit is <scene name='56/567269/Ku70_subunit/5'>angled closer</scene> to DNA at the double strand break, providing protection and interaction with its domains.<ref name="source2"> PMID: 19715578</ref> |
In contrast, the Ku80 subunit <scene name='56/567269/Ku80_subunit/4'>associates with</scene> DNA away from the free end.<ref name="Walker"/> Once a homodimer, the protein has diverged into two domains that are now 15% similar in residues. <ref name="source3"> PMID: 9663392</ref> | In contrast, the Ku80 subunit <scene name='56/567269/Ku80_subunit/4'>associates with</scene> DNA away from the free end.<ref name="Walker"/> Once a homodimer, the protein has diverged into two domains that are now 15% similar in residues. <ref name="source3"> PMID: 9663392</ref> | ||
Revision as of 14:33, 5 November 2013
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 Walker JR, Corpina RA, Goldberg J. Structure of the Ku heterodimer bound to DNA and its implications for double-strand break repair. Nature. 2001 Aug 9;412(6847):607-14. PMID:11493912 doi:10.1038/35088000
- ↑ Bennett SM, Neher TM, Shatilla A, Turchi JJ. Molecular analysis of Ku redox regulation. BMC Mol Biol. 2009 Aug 28;10:86. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-86. PMID:19715578 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-10-86
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Polotnianka RM, Li J, Lustig AJ. The yeast Ku heterodimer is essential for protection of the telomere against nucleolytic and recombinational activities. Curr Biol. 1998 Jul 2;8(14):831-4. PMID:9663392
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bertuch AA, Lundblad V. The Ku heterodimer performs separable activities at double-strand breaks and chromosome termini. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Nov;23(22):8202-15. PMID:14585978