We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Ku protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
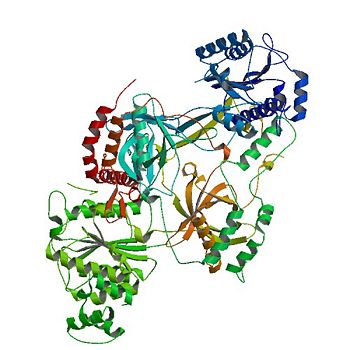
The <scene name='56/567269/Ku_heterodimer/3'>Ku heterodimer</scene> serves to assist in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-homologous_end_joining non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)], and also in telomere synthesis and protection. These functions are separate interactions based on key residues that are being identified through current research. Recent research also links the Ku protein with heterochromatin formation through interaction with [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rif_(GTPase) Rif proteins] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sir2 Sir proteins]. <ref name="source3"/><ref name="source4"/> | The <scene name='56/567269/Ku_heterodimer/3'>Ku heterodimer</scene> serves to assist in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-homologous_end_joining non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)], and also in telomere synthesis and protection. These functions are separate interactions based on key residues that are being identified through current research. Recent research also links the Ku protein with heterochromatin formation through interaction with [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rif_(GTPase) Rif proteins] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sir2 Sir proteins]. <ref name="source3"/><ref name="source4"/> | ||
| - | + | <ref>Berg, Jeremy M., John L. Tymoczko, and Lubert Stryer. Biochemistry. 7th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman and, 2012. [http://www.whfreeman.com/Catalog/product/biochemistry-seventhedition-berg ISBN-10: 1-4292-2936-5]</ref> | |
| - | + | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 23:48, 6 November 2013
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 Walker JR, Corpina RA, Goldberg J. Structure of the Ku heterodimer bound to DNA and its implications for double-strand break repair. Nature. 2001 Aug 9;412(6847):607-14. PMID:11493912 doi:10.1038/35088000
- ↑ Bennett SM, Neher TM, Shatilla A, Turchi JJ. Molecular analysis of Ku redox regulation. BMC Mol Biol. 2009 Aug 28;10:86. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-86. PMID:19715578 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-10-86
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Polotnianka RM, Li J, Lustig AJ. The yeast Ku heterodimer is essential for protection of the telomere against nucleolytic and recombinational activities. Curr Biol. 1998 Jul 2;8(14):831-4. PMID:9663392
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bertuch AA, Lundblad V. The Ku heterodimer performs separable activities at double-strand breaks and chromosome termini. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Nov;23(22):8202-15. PMID:14585978
- ↑ Berg, Jeremy M., John L. Tymoczko, and Lubert Stryer. Biochemistry. 7th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman and, 2012. ISBN-10: 1-4292-2936-5