Maureen E. Hill/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
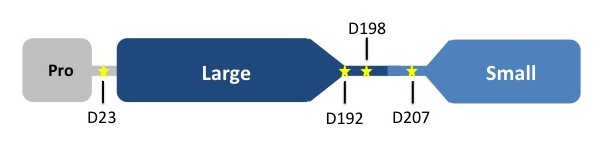
Caspases are crystallized as homodimers. Each monomer contains a large (~20 kDa) and a small (~10 kDa) subunit. [[Image:CASP7cleavagesites.jpg]] | Caspases are crystallized as homodimers. Each monomer contains a large (~20 kDa) and a small (~10 kDa) subunit. [[Image:CASP7cleavagesites.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
The <scene name='56/566502/Active_site_conformation/1'>active site</scene> is made up of four flexible loops which include L2, L3 and L4 from one half of the dimer that interact with L2' from the opposite half of the dimer. In the <scene name='56/566502/Procaspase_zymogen/1'>procaspase-7 zymogen</scene>, the loops are disordered, which prevents substrate binding. Upon cleavage at the intersubunit linker, the active-site loop bundle becomes partially ordered, whereas L2' stays in the inactive, down conformation. At this point, caspase-7 may bind either substrate or allosteric inhibitors. <scene name='56/566502/Active_site_substrate/2'>Caspase-7 bound to suicide inhibitor/substrate mimic DEVD-CHO</scene> traps the protein an active/substrate bound conformation. Substrate binding forces L2' to move upward, creating a foundation beneath the L2 bundle. However, it has been shown that if caspase-7 were to bind an allosteric inhibitor, such as 5-Fluoro-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid (2-mercapto-ethyl)-amide ('''FICA''') or 2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)-N-(2-mercapto-ethyl)-acetamide ('''DICA'''), at the dimer-interface cavity, the L2' loop would be locked in the down conformation, thereby inactivating the enzyme. | The <scene name='56/566502/Active_site_conformation/1'>active site</scene> is made up of four flexible loops which include L2, L3 and L4 from one half of the dimer that interact with L2' from the opposite half of the dimer. In the <scene name='56/566502/Procaspase_zymogen/1'>procaspase-7 zymogen</scene>, the loops are disordered, which prevents substrate binding. Upon cleavage at the intersubunit linker, the active-site loop bundle becomes partially ordered, whereas L2' stays in the inactive, down conformation. At this point, caspase-7 may bind either substrate or allosteric inhibitors. <scene name='56/566502/Active_site_substrate/2'>Caspase-7 bound to suicide inhibitor/substrate mimic DEVD-CHO</scene> traps the protein an active/substrate bound conformation. Substrate binding forces L2' to move upward, creating a foundation beneath the L2 bundle. However, it has been shown that if caspase-7 were to bind an allosteric inhibitor, such as 5-Fluoro-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid (2-mercapto-ethyl)-amide ('''FICA''') or 2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)-N-(2-mercapto-ethyl)-acetamide ('''DICA'''), at the dimer-interface cavity, the L2' loop would be locked in the down conformation, thereby inactivating the enzyme. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
| - | + | <scene name='Molecular_Playground/Caspase_Dynamics/1f1j/2'>Caspase-7 bound to suicide inhibitor/substrate mimic DEVD-CHO</scene>, trapping protein in active/substrate bound conformation. | |
| + | |||
<scene name='56/566502/Dica_bound_caspase_7/2'>Caspase-7 bound to allosteric inhibitor DICA</scene> at the dimer interface. The allosteric inhibitor binds to C290 within the dimer interface displacing Y223. The displacement of tyrosine from the active site conformation of the enzyme forces R187 into a position that both physically blocks substrate binding, as well as, move the active site cystine 186. Ultimately, these conformational changes inactivate the enzyme. | <scene name='56/566502/Dica_bound_caspase_7/2'>Caspase-7 bound to allosteric inhibitor DICA</scene> at the dimer interface. The allosteric inhibitor binds to C290 within the dimer interface displacing Y223. The displacement of tyrosine from the active site conformation of the enzyme forces R187 into a position that both physically blocks substrate binding, as well as, move the active site cystine 186. Ultimately, these conformational changes inactivate the enzyme. | ||
| - | + | <scene name='Molecular_Playground/Caspase_Dynamics/1shj-234234/1'>Caspase-7 bound to allosteric inhibitor DICA through CYS290</scene> trapping protein in a form incompatible with substrate binding. | |
| - | + | ||
| + | <scene name='Molecular_Playground/Caspase_Dynamics/Morph2/2'>Conformational change between substrate bound and substrate incompatible forms</scene> of Caspase-7. | ||
Revision as of 23:15, 2 December 2013
Caspase-7 Dynamics
| |||||||||||