RuBisCO
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
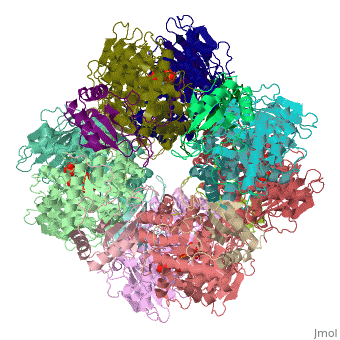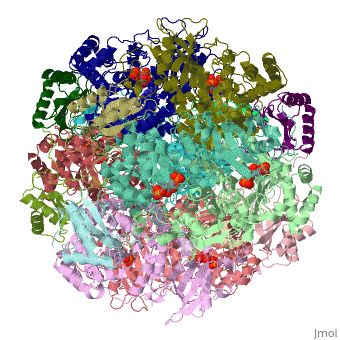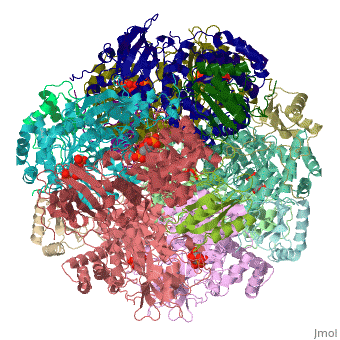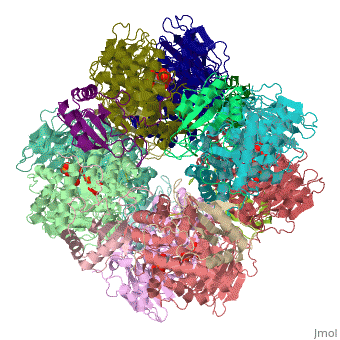
{{STRUCTURE_1rcx| PDB=1rcx | SIZE=400| SCENE= |right|CAPTION=Spinach RuBisCO 8 large and 8 small chains complex with substrate ribulose-1,5- bisphosphate, [[1rcx]] }} | {{STRUCTURE_1rcx| PDB=1rcx | SIZE=400| SCENE= |right|CAPTION=Spinach RuBisCO 8 large and 8 small chains complex with substrate ribulose-1,5- bisphosphate, [[1rcx]] }} | ||
| - | '''Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase – RuBisCO''' (RBCO) catalyzes the first step in carbon fixation. RBCO | + | '''Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase – RuBisCO''' (RBCO) catalyzes the first step in carbon fixation, and it is the most abundant protein on earth. RBCO can either carboxylate or oxygenate ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RUBP) with CO<sub>2</sub> or O<sub>2</sub>, respectively. RBCO from flowering plants usually consists of eight large subunits and eight small subunits. 2-carboxylarabinitol-1,5-bisphosphate (2-CABP) is an inhibitor of RCBO. Some additional details can be found in [[Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase]]. |
{{TOC limit|limit=2}} | {{TOC limit|limit=2}} | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
(under construction) | (under construction) | ||
| - | Here is an isolated <scene name='46/463261/Rubisco_lsu_pair/7'>pair of large subunits</scene>. Each subunit has a large C-terminal lobe and a small N-terminal lobe, and the subunits are arranged head-to-toe (antiparallel) in the pair. <scene name='46/463261/Rubisco_lsu_pair/5'>Two active sites</scene> are located in the interface of the large subunit pair. The subunits are shown in cartoon with one shown in the secondary structure color scheme. Each active | + | Here is an isolated <scene name='46/463261/Rubisco_lsu_pair/7'>pair of large subunits</scene>. Each subunit has a large C-terminal lobe and a small N-terminal lobe, and the subunits are arranged head-to-toe (antiparallel) in the pair. <scene name='46/463261/Rubisco_lsu_pair/5'>Two active sites</scene> are located in the interface of the large subunit pair. The subunits are shown in cartoon with one shown in the secondary structure color scheme. Each active site is occupied by RUBP, which is shown in CPK spacefill. Here is a <scene name='46/463261/Rubisco_lsu_monomer/1'>single large subunit</scene> showing that both lobes contain alpha helices (pink) and beta strands (yellow). The large lobe is dominated by an <scene name='46/463261/Rubisco_lsu_monomer/2'>α-β barrel</scene>, which contributes most of the residues in the active site. |
== Active Site Structure == | == Active Site Structure == | ||
(under construction) | (under construction) | ||
| - | The active site is formed by an α-β barrel, which comprises the C-terminal lobe of the large subunit | + | The active site is formed by an α-β barrel, which comprises the C-terminal lobe of the large subunit. Some additional residues are contributed by the N-terminal lobe of the adjacent subunit. Here is an <scene name='46/463261/Rubisco_lsu_pair/5'>isolated pair of subunits</scene>, , and here is the α-β barrel of that subunit. |
Revision as of 20:05, 3 December 2013
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase – RuBisCO (RBCO) catalyzes the first step in carbon fixation, and it is the most abundant protein on earth. RBCO can either carboxylate or oxygenate ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RUBP) with CO2 or O2, respectively. RBCO from flowering plants usually consists of eight large subunits and eight small subunits. 2-carboxylarabinitol-1,5-bisphosphate (2-CABP) is an inhibitor of RCBO. Some additional details can be found in Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase.
Contents |
Quaternery Structure
The Rubisco is shown in spacefill with its 8 large subunits in shades of blue and and its 8 small subunits in shades of yellow. The large subunits are arranged in head-to-toe pairs like staves in a barrel and the small subunits are arranged at the ends of the barrel. The large subunits contain the active sites and the function of the small subunits is not understood.
Large Subunit Structure
(under construction)
Here is an isolated . Each subunit has a large C-terminal lobe and a small N-terminal lobe, and the subunits are arranged head-to-toe (antiparallel) in the pair. are located in the interface of the large subunit pair. The subunits are shown in cartoon with one shown in the secondary structure color scheme. Each active site is occupied by RUBP, which is shown in CPK spacefill. Here is a showing that both lobes contain alpha helices (pink) and beta strands (yellow). The large lobe is dominated by an , which contributes most of the residues in the active site.
Active Site Structure
(under construction)
The active site is formed by an α-β barrel, which comprises the C-terminal lobe of the large subunit. Some additional residues are contributed by the N-terminal lobe of the adjacent subunit. Here is an , , and here is the α-β barrel of that subunit.
3D Structures of RuBisCO
Updated February 2013
RuBisCO
3rg6, 1rbl – SeRBCO – Synechococcus elongatus
2ybv - RBCO – Thermosynechococcus elongatus
3qfw - RBCO large subunit – Rhodopseudomonas palustris
1uzh, 1gk8 – CrRBCO – Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
1uw9, 1uwa – CrRBCO (mutant)
1svd – RBCD – Halothiobacillus neapolitanus
1bxn – RBCO – Cupriavidus necator
1aus - spRBCO – spinach
1rba - RrRBCO (mutant) – Rhododpirillum rubrum
5rub - RrRBCO
2wvw – RBCO – Anabena – Cryo EM
2vdh, 2vdi, 2v67, 2v68, 2v63, 2v69, 2v6a - CrRBCO (mutant)
1mlv - pRBCO LSMT – pea
2cxe, 2cwx – PhRBCO - Pyrococcus horikoshii
1uzd – CrRBCO/spRBCO
1geh – TkRBCO – Thermococcus kodakaraensis
1iwa - GpRBCO – Galdieria partita
1tel – RBCO large subunit – Chlorobium tepidum
1rld, 3rub, 3t15, 3zw6, 4rub – tRBCO – tobacco
3thg – RBCO – creosote bush
4hhh – RBCO - pea
RuBisCO complex with inhibitor 2-CABP
3kdn, 3a12 – TkRBCO III + 2-CABP
3kdo, 3a13 - TkRBCO III (mutant) + 2-CABP
1ir2 - CrRBCO + 2-CABP
1upm, 1upp, 1rbo, 3ruc, 8ruc - spRBCO + 2-CABP + cation
1ir1 - spRBCO + 2-CABP + CO2 + Mg
1wdd – rRBCO + 2-CABP – rice
1bwv - GpRBCO + 2-CABP
1rlc - tRBCO + 2-CABP
RuBisCO complex with product
1aa1 – spRBCO + phosphoglycerate
1rus - RrRBCO + phosphoglycerate
RuBisCO complex with substrate
1rcx, 1rxo – spRBCO + ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate
9rub - RrRBCO + ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate
1rsc - SeRBCO + xylulose-1,5-bisphosphate
1rco - spRBCO + xylulose-diol-1,5-bisphosphate
3zxw - SeRBCO + carboxyarabinitol-1,5-bisphosphate
RuBisCO complexes
2h21 – pRBCO LSMT + AdoMet
2h23 - pRBCO LSMT + AdoHcy
2h2e, 1ozv, 1p0y - pRBCO LSMT + AdoMet + lysine
2h2j - pRBCO LSMT + sinefungin
2d69 – PhRBCO + sulfate
2rus - RrRBCO + CO2 + Mg
4f0h – GsRBCO + O2 – Galdieria sulphuraria
4f0k - GsRBCO + CO2 + Mg
4f0m - GsRBCO + Mg
1ej7 – tRBCO + phosphate
3axk – rRBCO + NADP
3axm – rRBCO + 6PG
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alice Harmon, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky