User:Alisha, Deepa, Pamiz/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(→Introduction) |
(→Introduction) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
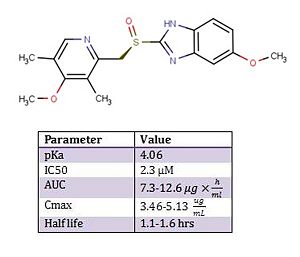
[[Image:eso.jpg|300px|left|thumb|'''2D Structure & Biochemical Parameters of Esomeprazole''' Esomeprazole has two important pyridine and benzimidazole moieties linked through a methylenesulfinyl group. pKa, IC50, AUC, Cmax, and half life values of Esomeprazole. | [[Image:eso.jpg|300px|left|thumb|'''2D Structure & Biochemical Parameters of Esomeprazole''' Esomeprazole has two important pyridine and benzimidazole moieties linked through a methylenesulfinyl group. pKa, IC50, AUC, Cmax, and half life values of Esomeprazole. | ||
]]'''Esomeprazole''' is the (S) enantiomer of Omeprazole. Esomperazole is a '''Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI)''' that binds to '''H+/K+-ATPase''' and inhibits the secretion of gastric acid from parietal cells into the lumen of the stomach. Esomeprazole’s commercial brand name, Nexium, is used to treat Gastro-esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), peptic and gastric ulcers, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.<ref name="one">[Mayo Clinic. Esomeprazole (Oral Route). http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/drug-information/DR603283 (accessed November 11, 2013).]</ref> | ]]'''Esomeprazole''' is the (S) enantiomer of Omeprazole. Esomperazole is a '''Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI)''' that binds to '''H+/K+-ATPase''' and inhibits the secretion of gastric acid from parietal cells into the lumen of the stomach. Esomeprazole’s commercial brand name, Nexium, is used to treat Gastro-esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), peptic and gastric ulcers, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.<ref name="one">[Mayo Clinic. Esomeprazole (Oral Route). http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/drug-information/DR603283 (accessed November 11, 2013).]</ref> | ||
| - | Ulcers caused by the bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' can be treated using Esomeprazole in conjunction with proper antibiotics.<ref name="one"/> Gastric acid is released through the H+/K+-ATPase pump, which is the final step in acid release. | + | Ulcers caused by the bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' can be treated using Esomeprazole in conjunction with proper antibiotics.<ref name="one"/> Gastric acid is released through the H+/K+-ATPase pump, which is the final step in acid release. <ref name="two">[National Institutes of Health: DailyMed. NEXIUM (Esomeprazole magnesium) capsule, delayed release [A-S Medication Solutions LLC]. http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=9af7a792-d38a-4b2a-b5d6-855d2183b029 (accessed November 11, 2013).]</ref> Esomeprazole is a specific, irreversible inhibitor of the pump. <ref name="two"> |
[[Image:PPI gif.gif]] | [[Image:PPI gif.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 20:06, 6 December 2013
Introduction
Esomeprazole is the (S) enantiomer of Omeprazole. Esomperazole is a Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) that binds to H+/K+-ATPase and inhibits the secretion of gastric acid from parietal cells into the lumen of the stomach. Esomeprazole’s commercial brand name, Nexium, is used to treat Gastro-esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), peptic and gastric ulcers, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.[1]
Ulcers caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori can be treated using Esomeprazole in conjunction with proper antibiotics.[1] Gastric acid is released through the H+/K+-ATPase pump, which is the final step in acid release. [2] Esomeprazole is a specific, irreversible inhibitor of the pump. [2]