We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 828
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
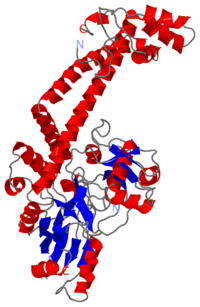
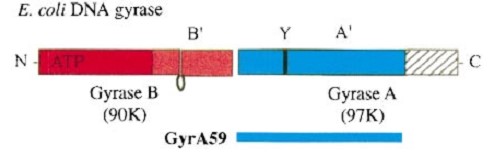
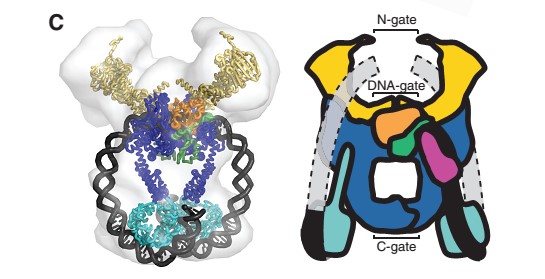
'''The A protein''' breaks and religates DNA as the DNA cleavage core and the CTD lies on it. | '''The A protein''' breaks and religates DNA as the DNA cleavage core and the CTD lies on it. | ||
| - | The gyrA 59kDa N-ter domain is called Breakage and reunion domain | + | The gyrA 59kDa N-ter domain is called Breakage and reunion domain. It is composed of two domains at the head region : a winged-helix-turn-helix domain or winged helix domain (WHD) where lies the catalytic tyrosines and a tower domain with alpha/beta structure that participates in DNA bending during cleavage. |
| - | And a single domain with a helical core at the tail region. Two long helices (a14 anda18) emanate from this core and connect, together with the C-terminal helix (a19), the head and tail fragments. | + | |
| + | |||
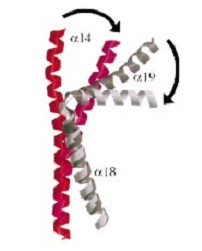
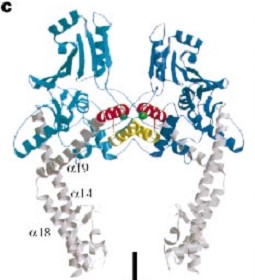
| + | And a single domain, folowing the tower, with a helical core at the tail region. Two long helices (a14 anda18) emanate from this core and connect, together with the C-terminal helix (a19), the head and tail fragments. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
[[Image:helixrot.jpg]] [[Image:gyrA592.jpg]] | [[Image:helixrot.jpg]] [[Image:gyrA592.jpg]] | ||
| - | The tail is structurally conserved although large surface loops emanating from different points give it a different outward appearance | + | The tail is structurally conserved although large surface loops emanating from different points give it a different outward appearance. |
| - | The remaining 30–35 kDa comprising the C-terminal domain (CTD) of GyrA shows a domain forming a b-pinwheel with a positively charged amino-acid perimeter. This carboxy-terminal domain of GyrA (cyan) is required for the introduction of DNA supercoils), DNA | + | GyrA forms a heart-shaped homodimer with two protein interfaces, the DNA- and C-gates. GyrA59 is the minimal fragment of the A-subunit which, when complexed with the B-subunit, has DNA-cleavage activity. |
| + | The remaining 30–35 kDa comprising the C-terminal domain (CTD) of GyrA shows a domain forming a b-pinwheel with a positively charged amino-acid perimeter. This carboxy-terminal domain of GyrA (cyan) is required for the introduction of DNA supercoils), DNA wraps around it. It is linked to the central part of Gyrase A by a flexible 13-15 residues region and stands close to the C-gate and may present an up and down movement in the early stades of the catalytic cycle and may be involved in the helping of G segment and D-gate binding so as the CTD binding of DNA. | ||
| - | '''The B protein''' has the ATPase domain and the Toprim fold on it. Two ATPase domains dimerize to form a closed conformation. The Toprim fold is a Rossmann fold (beta-alpha-beta-alpha-beta) that contains three invariant acidic residues that coordinate magnesium ions involved in DNA cleavage and DNA religation. | + | '''The B protein''' has the GHKL ATPase domain, a transducer domain and the Toprim fold on it. |
| + | Two ATPase domains from two monomers dimerize to form a closed conformation, the N-gate. | ||
| + | The Toprim fold is a Rossmann fold (beta-alpha-beta-alpha-beta) that contains three invariant acidic residues that coordinate magnesium ions involved in DNA cleavage and DNA religation. This torpim fold interacts with the Winged helix domain of gyrA to create the D-gate. | ||
Revision as of 09:33, 25 December 2013
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||