We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 820
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}} | {{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}} | ||
<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | <!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| - | |||
<Structure load='2vaf' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Crystal Structure of Human Cardiac Calsequestrin, (PDB code [[2vaf]]) ' scene='56/568018/General_structure/4'/> | <Structure load='2vaf' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Crystal Structure of Human Cardiac Calsequestrin, (PDB code [[2vaf]]) ' scene='56/568018/General_structure/4'/> | ||
| - | Calsequestrin-2 (or CASQ2) is the soluble CA2+ binding protein in the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen of the cardiac muscle cells. CASQ2 could be either in a monomeric, homodimeric, or homooligomeric chain form depending on its bounds with Ca2+. Mutations of CASQ2 are involved in cardiac diseases such as Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia. | + | '''Calsequestrin-2''' (or '''CASQ2''') is the soluble CA2+ binding protein in the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen of the cardiac muscle cells. CASQ2 could be either in a monomeric, homodimeric, or homooligomeric chain form depending on its bounds with Ca2+. Mutations of CASQ2 are involved in cardiac diseases such as Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia. |
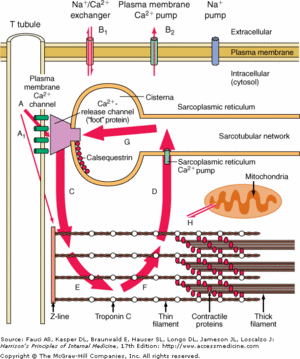
[[Image:LoadBinary 004.gif|300px|left|thumb|Calsequestrin in the calcium cycle of myocyte contraction]] | [[Image:LoadBinary 004.gif|300px|left|thumb|Calsequestrin in the calcium cycle of myocyte contraction]] | ||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
== General Structure == | == General Structure == | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
There are <scene name='56/568018/Alpha_helix/1'>12 alpha helix</scene> and <scene name='56/568018/Beta_sheet/2'>15 beta sheet</scene>. | There are <scene name='56/568018/Alpha_helix/1'>12 alpha helix</scene> and <scene name='56/568018/Beta_sheet/2'>15 beta sheet</scene>. | ||
<scene name='56/568018/Acidic_amino_acids/1'>The acidics amino acids</scene> can bind the Ca2+ especially the <scene name='56/568018/Glu/1'>glutamate</scene> and the <scene name='56/568018/Asp/1'>aspartate</scene>. | <scene name='56/568018/Acidic_amino_acids/1'>The acidics amino acids</scene> can bind the Ca2+ especially the <scene name='56/568018/Glu/1'>glutamate</scene> and the <scene name='56/568018/Asp/1'>aspartate</scene>. | ||
Revision as of 13:20, 29 December 2013
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
|
Calsequestrin-2 (or CASQ2) is the soluble CA2+ binding protein in the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen of the cardiac muscle cells. CASQ2 could be either in a monomeric, homodimeric, or homooligomeric chain form depending on its bounds with Ca2+. Mutations of CASQ2 are involved in cardiac diseases such as Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia.
General Structure
There are and . can bind the Ca2+ especially the and the .