We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 820
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
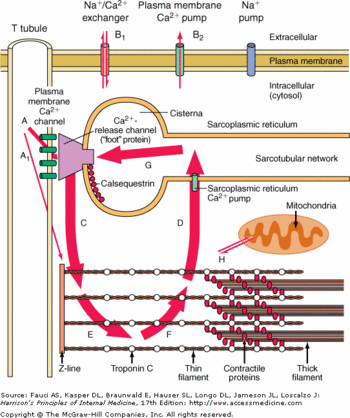
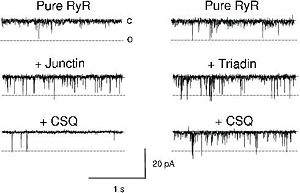
=== Consequences of CASQ2 binding === | === Consequences of CASQ2 binding === | ||
| + | [[Image:CASQ2 Triadin Junctin.jpg|300px|left|thumb|CASQ2 and the regulation of Ca<sup>2+</sup> release in the cytoplasm.]] | ||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
When CASQ2 binds to triadin and junctin, it induces the inhibition of RyR and then the inhibition of calcium release in the cytoplasm. On the contrary, when CASQ2 unbinds triadin and junctin, it induces the activation of Ryr and an efflux of Ca<sup>2+</sup> from the SR to the cytoplasm.<ref name="Calsequestrin and the calcium release channel of skeletal and cardiac muscle (Beard et Al., 2004)">http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15050380</ref> CASQ2 is free when the concentration of Ca<sup>2+</sup> is higher than 1 mM in the SR lumen.<ref name="Regulation of Ryanodine Receptors by Calsequestrin: Effect of High Luminal Ca2+ and Phosphorylation (Beard et Al., 2005)">http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15731387</ref> | When CASQ2 binds to triadin and junctin, it induces the inhibition of RyR and then the inhibition of calcium release in the cytoplasm. On the contrary, when CASQ2 unbinds triadin and junctin, it induces the activation of Ryr and an efflux of Ca<sup>2+</sup> from the SR to the cytoplasm.<ref name="Calsequestrin and the calcium release channel of skeletal and cardiac muscle (Beard et Al., 2004)">http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15050380</ref> CASQ2 is free when the concentration of Ca<sup>2+</sup> is higher than 1 mM in the SR lumen.<ref name="Regulation of Ryanodine Receptors by Calsequestrin: Effect of High Luminal Ca2+ and Phosphorylation (Beard et Al., 2005)">http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15731387</ref> | ||
Revision as of 10:31, 4 January 2014
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Cerrone M, Napolitano C, Priori SG. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: A paradigm to understand mechanisms of arrhythmias associated to impaired Ca(2+) regulation. Heart Rhythm. 2009 Nov;6(11):1652-9. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2009.06.033. Epub 2009 , Jun 30. PMID:19879546 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2009.06.033
- ↑ NCBI Gene Ressource: CASQ2 calsequestrin 2 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/845
- ↑ Martin JL. Thioredoxin--a fold for all reasons. Structure. 1995 Mar 15;3(3):245-50. PMID:7788290
- ↑ NCBI Structure Ressource: CASQ2 calsequestrin 2 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi?ascbin=8&maxaln=10&seltype=2&uid=239372&querygi=429544235&aln=1,227,0,109
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Crystal Structure of calsequestrin from rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum (Wang et al., 1998) http://www.nature.com/nsmb/journal/v5/n6/abs/nsb0698-476.html
- ↑ NCBI Structure Ressource: CASQ2 calsequestrin 2 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi
- ↑ 2+</sup> and interacts with triadin (Shin et al., 2000)">The Asp-rich region at the carboxyl-terminus of calsequestrin binds to Ca2+ and interacts with triadin (Shin et al., 2000) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014579300022468
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 8.7 Beard NA, Laver DR, Dulhunty AF. Calsequestrin and the calcium release channel of skeletal and cardiac muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2004 May;85(1):33-69. PMID:15050380 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2003.07.001
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Beard NA, Casarotto MG, Wei L, Varsanyi M, Laver DR, Dulhunty AF. Regulation of ryanodine receptors by calsequestrin: effect of high luminal Ca2+ and phosphorylation. Biophys J. 2005 May;88(5):3444-54. Epub 2005 Feb 24. PMID:15731387 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.104.051441
Proteopedia page contributors and editors
Marc-Antoine JACQUES and Thomas VUILLEMIN