We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Introduction to protein structure
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Levels of Protein Structure == | == Levels of Protein Structure == | ||
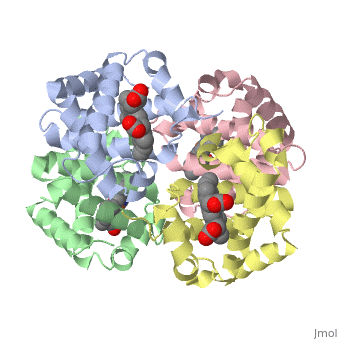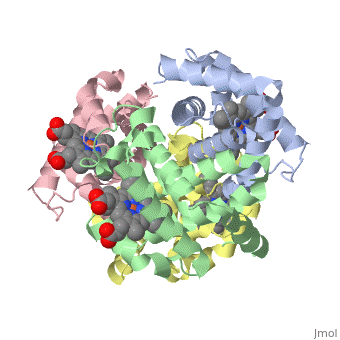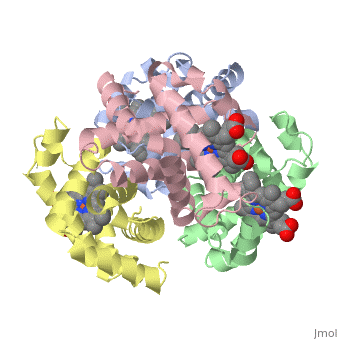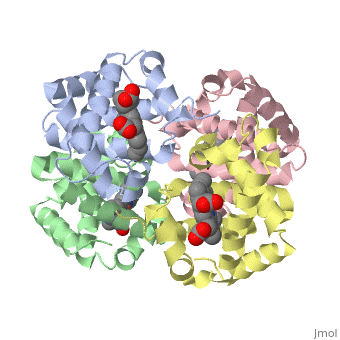
<StructureSection load='1A3N' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of Hemoglobin (PDB entry [[1A3N]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1A3N' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of Hemoglobin (PDB entry [[1A3N]])' scene=''> | ||
| + | This tutorial illustrates some basic properties of protein structure and useful commands in Jmol and Proteopedia. Clicking the green links changes the view in the structure box to illustrate the principle described by the text. | ||
| + | |||
Proteins are condensation polymers of amino acids. The <scene name='57/575866/Primary_sequence/1'>primary structure</scene> is the amino acid sequence. The <scene name='57/575866/Secondary_sequence/1'>secondary structure</scene> is the local structure over short distances. This level of structure is stabilized by <scene name='57/575866/H_bond_a_helix/1'>hydrogen bonds</scene> along the <scene name='57/575866/Backbone/1'>backbone</scene>. These secondary structures <scene name='57/575866/Global_secondary_structures/1'>pack together</scene> to form the overall form of the entire peptide chain, called the <scene name='57/575866/Tertiary/1'>tertiary structure</scene>. Some proteins, such as the displayed hemoglobin molecule, have more than one polypeptide chain that associate to form the functional unit of the protein; this is called <scene name='57/575866/Tertiary/2'>quaternary structure</scene>. | Proteins are condensation polymers of amino acids. The <scene name='57/575866/Primary_sequence/1'>primary structure</scene> is the amino acid sequence. The <scene name='57/575866/Secondary_sequence/1'>secondary structure</scene> is the local structure over short distances. This level of structure is stabilized by <scene name='57/575866/H_bond_a_helix/1'>hydrogen bonds</scene> along the <scene name='57/575866/Backbone/1'>backbone</scene>. These secondary structures <scene name='57/575866/Global_secondary_structures/1'>pack together</scene> to form the overall form of the entire peptide chain, called the <scene name='57/575866/Tertiary/1'>tertiary structure</scene>. Some proteins, such as the displayed hemoglobin molecule, have more than one polypeptide chain that associate to form the functional unit of the protein; this is called <scene name='57/575866/Tertiary/2'>quaternary structure</scene>. | ||
'''Questions based upon these scenes:''' | '''Questions based upon these scenes:''' | ||
| Line 38: | Line 40: | ||
--Hold the shift button while you try the same manipulations. What does each do? | --Hold the shift button while you try the same manipulations. What does each do? | ||
| - | Clicking the right mouse button brings up an extensive menu. This exercise will use commands in the style, color,zoom, measurements, and set picking categories. | + | Clicking the right mouse button in the structure box brings up an extensive menu. This exercise will use commands in the style, color,zoom, measurements, and set picking categories. |
We will begin with the <scene name='57/575866/Cartoon/4'>cartoon</scene> structure of an alpha helix from hemoglobin. From this view, can you determine: | We will begin with the <scene name='57/575866/Cartoon/4'>cartoon</scene> structure of an alpha helix from hemoglobin. From this view, can you determine: | ||
| Line 62: | Line 64: | ||
Notice that hydrogens are not shown on this model. Xray crystallography is not able to resolve hydrogens, so they are omitted from the images. This also simplifies the data set, as there are many fewer atoms to position. | Notice that hydrogens are not shown on this model. Xray crystallography is not able to resolve hydrogens, so they are omitted from the images. This also simplifies the data set, as there are many fewer atoms to position. | ||
| + | |||
| + | From this view, it is possible to determine the number of amino acids in one turn. <scene name='57/575866/No_sidechains/1'>This structure</scene> has the side chains removed (though the alpha carbons show where the side chain would be). | ||
| + | |||
| - | -- | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 17:48, 16 January 2014
Levels of Protein Structure
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Ann Taylor, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky, Eric Martz, Israel Hanukoglu, Jaime Prilusky, Nick Kenworthy