We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 911
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
<scene name='57/573125/2vya/5'>membrane</scene> | <scene name='57/573125/2vya/5'>membrane</scene> | ||
| - | + | ||
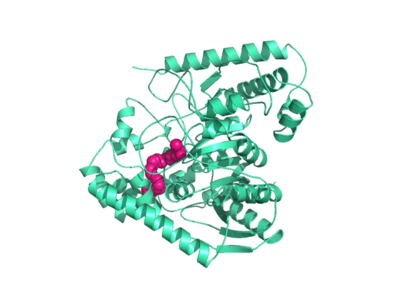
===Catalytic Triad=== | ===Catalytic Triad=== | ||
Mutagenesis and inhibitor studies have shown that FAAH has a <scene name='57/573125/2vya/6'>Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triad</scene>, consisting of S241, S217, and K142. Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triads are not often seen in hydrolases, making FAAH an enzyme of interest for additional research. S241 acts as the catalytic nucleophile for the cleavage of amide bonds. (IMT5) | Mutagenesis and inhibitor studies have shown that FAAH has a <scene name='57/573125/2vya/6'>Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triad</scene>, consisting of S241, S217, and K142. Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triads are not often seen in hydrolases, making FAAH an enzyme of interest for additional research. S241 acts as the catalytic nucleophile for the cleavage of amide bonds. (IMT5) | ||
Revision as of 13:01, 25 March 2014
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 06, 2014, through Aug 22, 2014 for use by the Biochemistry II class at the Butler University at Indianapolis, IN USA taught by R. Jeremy Johnson. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 911 through Sandbox Reserved 922. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
Applications
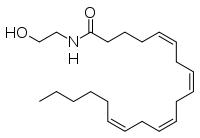
The human nervous system has several types of chemical messengers, including amino acids, lipids, peptide hormones, and monoamines. (IMT5) FAAH primarily degrades anandamide (AEA), a naturally-occurring signaling lipid that functions in the brain. AEA brings pain relief to the body. Inhibiting FAAH would likely sustain AEA signaling, leading to prolonged pain relief and decreased inflammation. (2YVA)