Background
Monoglyceride lipase is part of the α/β hydrolase family, having a Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad (Celemnte et al. 2012). MGL terminates the signaling of a primary endocannabinoid, 2-AG (Savinainen et al 2010). MGL is able to hydrolyze 2-arachidonoylglycerol into arachidonic acid and glycerol (Bertrand et al. 2010). One of the key features of MGL is the hydrophobic tunnel, which has been suggested to provide a model for drug research.
Metabolic Role
Component of Endocannabinoid System
MGL degrades 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG). 2-AG is commonly classified as an endocannabinoid. In the brain endocannabinoids are released from postsynaptic neurons, causing the retrograde suppression of synaptic transmission (Taschler et al. 2011).
In Peripheral tissues, EC is active in autonomic nervous system. EC affects processes such as learning, motor control, cognition, and pain (Taschler et al. 2011). EC is also able to regulate lipid metabolism and food intake (Taschler et al. 2011).
Taschler et al. looked at the role of MGL in energy metabolism, finding that MGL deficiency in animals led to the buildup of 2-AG (Taschler et al. 2011).
Structure
Representation of the
Catalytic triad
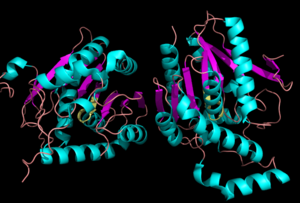
MGL has a classic that contains Ser-His-Asp (figure 1). The triad was found using site-directed mutagenesis and this experiment confirmed that these amino acid residues are catalytically essential. The catalytic triad is located in the binding pocket buried at the bottom of it in the oxyanion hole connected by a water molecule. This triad has a natural attraction to Endocannabinoids, specifically 2-arachidonylglycerol (2-AG). 2-AG contributes to brain signals (neurons) to suppress the pain pathways when a patient is feeling depressed or suffering from any type of pain.
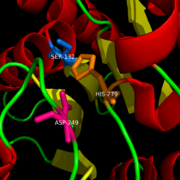
Figure 1: Catalytic Triad of MGL structure
Binding
2-AG binds to the catalytic triad and is hydrolyzed. The structure of 2-AG contains a long and flexible aliphatic chain and a polar head that is cleaved. 2-AG is broken down into arachidonic acid and glycerol which makes 2-AG inactive. See Overall Reaction.
Inhibition
Research on MGL is being geared towards inhibiting 2-AG from binding to the catalytic triad and being hydrolyzed. The binding of 2-AG to the catalytic triad can not be inhibited, but it can be extracted before being hydrolyzed. MPD (2-methyl-pentane-2,4-diol)is located at the end of the tunnel where the catalytic triad is at and the tunnel is filled with MPD molecules. MPD being in the same vicinity will extract 2-AG from the triad and the MPD molecule will sit in there in place of 2-AG. This natural inhibition phenomenon is known as interfacial activation.
Ligand Binding Site
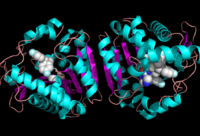
Ligand within the Overall Structure of MGL
The ligand binding pocket of MGL has a large hydrophobic region with a polar bottom (Bertrand et al. 2010). Bertrand found that in MGL the binding pocket is not adjusted to the ligands shape. 2-archidonylglycerol are ligands for cannabinoid receptors (Clemente et al. 2012). Inhibition of MGL leads to increase in 2-AG levels since AG is broken down by MGL (Clemente et al. 2012). Through covalent interactions with a Cys residue, NAM, one of the many possible inhibitors, is able to inhibit MGL (Bertrand et al. 2010).
Overall Reaction
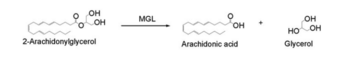
Overall reaction representing the hydrolysis of 2-AG by MGL
In this reaction 2-AG binds to the catalytic triad in the oxyanion hole in the active site. In the oxyanion holes the oxygen of the substrate is stabilized by two nitrogen atoms during the transition step of the catalytic reaction. The triad activates the nucleophilic serine and cleaves the ester bond of 2-AG that is being stabilized by its carbonyl group that is attached to the oxyanion hole. The glycerol molecule is released and it might diffuse to the narrow "exit hole", while the arachidonic acid would diffuse back to the top of the tunnel and leave the protein.
Additional Resources
Serine hydrolases
Lipases
Binding Pockets
References
External links