Sandbox reserved 916
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
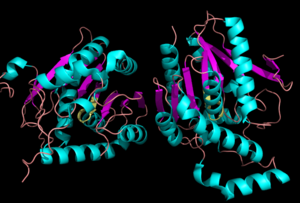
[[Image:Complete_crystal_structure.png|left|300px|thumb|Crystal Structure of MGL]] | [[Image:Complete_crystal_structure.png|left|300px|thumb|Crystal Structure of MGL]] | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
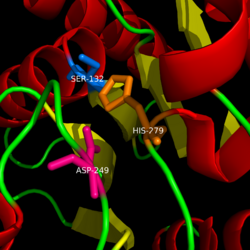
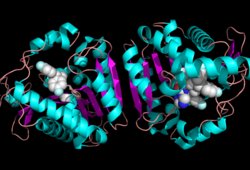
| - | Monoglyceride lipase is part of the α/β hydrolase family, having a Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad (Celemnte et al. 2012). MGL terminates the signaling of a primary endocannabinoid, 2-AG (Savinainen et al 2010). MGL is able to hydrolyze 2-arachidonoylglycerol into arachidonic acid and glycerol (Bertrand et al. 2010). One of the key features of MGL is the hydrophobic tunnel, which has been suggested to provide a model for drug research. | + | Monoglyceride lipase is part of the α/β hydrolase family, having a Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad (Celemnte et al. 2012). This enzyme is present in most cells, providing the rate limiting step for MG (Taschler et al 2011). MGL terminates the signaling of a primary endocannabinoid, 2-AG (Savinainen et al 2010). MGL is able to hydrolyze 2-arachidonoylglycerol into arachidonic acid and glycerol (Bertrand et al. 2010). One of the key features of MGL is the hydrophobic tunnel, which has been suggested to provide a model for drug research. |
===Metabolic Role=== | ===Metabolic Role=== | ||
| - | Monoglyceride lipase is able to hydrolyze monoacylglycerols into fatty acids and glycerol (Taschler et al. 2011). MGL degrades sn-1 and 2-MG at identical specific rates as a part of its metabolic role (Taschler et al. 2011). | + | Monoglyceride lipase is able to hydrolyze monoacylglycerols into fatty acids and glycerol, which are able to then be used for energy production (Taschler et al. 2011). MGL degrades sn-1 and 2-MG at identical specific rates as a part of its metabolic role (Taschler et al. 2011). |
===Component of Endocannabinoid System=== | ===Component of Endocannabinoid System=== | ||
Revision as of 13:43, 25 March 2014
Monoglyceride Lipase (MGL)
| |||||||||||