Background
Monoglyceride lipase is part of the α/β hydrolase family, having a Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad (Celemnte et al. 2012). This enzyme is present in most cells, providing the rate limiting step for MG (Taschler et al 2011). MGL terminates the signaling of a primary endocannabinoid, 2-AG (Savinainen et al 2010). MGL is the main enzyme respondsible for hydrolyzing 2-arachidonoylglycerol into arachidonic acid and glycerol in vivo (Bertrand et al. 2010). One of the key features of MGL is the hydrophobic tunnel, which has been suggested to provide a model for drug research.
Metabolic Role
Monoglyceride lipase is able to hydrolyze monoacylglycerols into fatty acids and glycerol, which are able to then be used for energy production (Taschler et al. 2011). MGL degrades sn-1 and 2-MG at identical specific rates as a part of its metabolic role (Taschler et al. 2011).
Component of Endocannabinoid System
MGL degrades 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG). 2-AG is commonly classified as an endocannabinoid. In the brain endocannabinoids are released from postsynaptic neurons, causing the retrograde suppression of synaptic transmission (Taschler et al. 2011).
In Peripheral tissues, EC is active in autonomic nervous system. EC affects processes such as learning, motor control, cognition, and pain (Taschler et al. 2011). EC is also able to regulate lipid metabolism and food intake (Taschler et al. 2011).
Taschler et al. looked at the role of MGL in energy metabolism, finding that MGL deficiency in animals led to the buildup of 2-AG (Taschler et al. 2011).
Structure
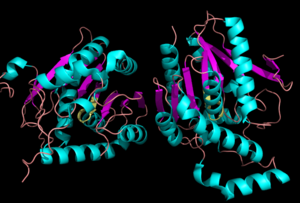
Representation of the . MGL has eight-stranded β-sheet protein fold with seven parallel and one (Bertrand et al. 2010).
Catalytic triad
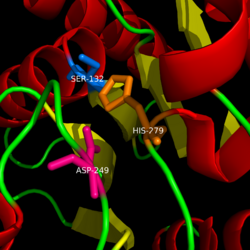
Catalytic Triad of MGL structure
Binding
Ligand Binding Site
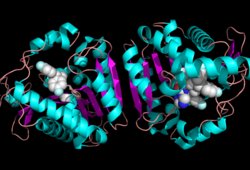
Ligand within the Overall Structure of MGL
The of MGL has a large hydrophobic region with a polar bottom (Bertrand et al. 2010). Bertrand found that in MGL the binding pocket is not adjusted to the ligands shape. 2-archidonylglycerol are ligands for cannabinoid receptors (Clemente et al. 2012). Inhibition of MGL leads to increase in 2-AG levels since AG is broken down by MGL (Clemente et al. 2012). Through covalent interactions with a Cys residue, NAM, one of the many possible inhibitors, is able to inhibit MGL (Bertrand et al. 2010).
Overall Reaction
Literature
Additional Resources
References
-Clemente, J. C., E. Nulton, M. Nelen, M. J. Todd, D. Maguire, C. Schalk-Hihi, L. C. Kuo, S.-P. Zhang, C. M. Flores, and J. K. Kranz. "Screening and Characterization of Human Monoglyceride Lipase Active Site Inhibitors Using Orthogonal Binding and Functional Assays." Journal of Biomolecular Screening 17.5 (2012): 629-40.
-Savinainen, Juha R., Megumi Yoshino, Anna Minkkilä, Tapio Nevalainen, and Jarmo T. Laitinen. "Characterization of Binding Properties of Monoglyceride Lipase Inhibitors by a Versatile Fluorescence-based Technique." Analytical Biochemistry 399.1 (2010): 132-34
-Taschler, U., F. P. W. Radner, C. Heier, R. Schreiber, M. Schweiger, G. Schoiswohl, K. Preiss-Landl, D. Jaeger, B. Reiter, H. C. Koefeler, J. Wojciechowski, C. Theussl, J. M. Penninger, A. Lass, G. Haemmerle, R. Zechner, and R. Zimmermann. "Monoglyceride Lipase Deficiency in Mice Impairs Lipolysis and Attenuates Diet-induced Insulin Resistance." Journal of Biological Chemistry 286.20 (2011): 17467-7477
External links