This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox reserved 915
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
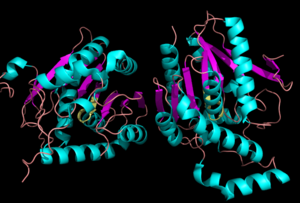
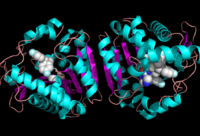
[[Image:Complete_crystal_structure.png|left|300px|thumb|'''Figure 1:'''Crystal Structure of MGL Alpha helixes are in blue and beta sheets in purple. This protein is a dimer that is linked by antiparallel beta sheets]] | [[Image:Complete_crystal_structure.png|left|300px|thumb|'''Figure 1:'''Crystal Structure of MGL Alpha helixes are in blue and beta sheets in purple. This protein is a dimer that is linked by antiparallel beta sheets]] | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
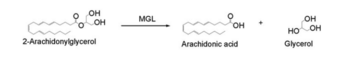
| - | Monoglyceride lipase is part of the α/β hydrolase family, having a Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad <ref name="Clemente">[Clemente, J. C., E. Nulton, M. Nelen, M. J. Todd, D. Maguire, C. Schalk-Hihi, L. C. Kuo, S.-P. Zhang, C. M. Flores, and J. K. Kranz. "Screening and Characterization of Human Monoglyceride Lipase Active Site Inhibitors Using Orthogonal Binding and Functional Assays." Journal of Biomolecular Screening 17.5 (2012): 629-40]</ref>. This enzyme is present in most cells, providing the rate limiting step for | + | Monoglyceride lipase is part of the α/β hydrolase family, having a Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad <ref name="Clemente">[Clemente, J. C., E. Nulton, M. Nelen, M. J. Todd, D. Maguire, C. Schalk-Hihi, L. C. Kuo, S.-P. Zhang, C. M. Flores, and J. K. Kranz. "Screening and Characterization of Human Monoglyceride Lipase Active Site Inhibitors Using Orthogonal Binding and Functional Assays." Journal of Biomolecular Screening 17.5 (2012): 629-40]</ref>. This enzyme is present in most cells, providing the rate limiting step for [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monoacylglycerol_lipase MGL] <ref name="Taschler">[Taschler, U., F. P. W. Radner, C. Heier, R. Schreiber, M. Schweiger, G. Schoiswohl, K. Preiss-Landl, D. Jaeger, B. Reiter, H. C. Koefeler, J. Wojciechowski, C. Theussl, J. M. Penninger, A. Lass, G. Haemmerle, R. Zechner, and R. Zimmermann. "Monoglyceride Lipase Deficiency in Mice Impairs Lipolysis and Attenuates Diet-induced Insulin Resistance." Journal of Biological Chemistry 286.20 (2011): 17467-7477]</ref>. MGL terminates the signaling of a primary endocannabinoid, 2-AG <ref name="Savinainen">[Savinainen, Juha R., Megumi Yoshino, Anna Minkkilä, Tapio Nevalainen, and Jarmo T. Laitinen. "Characterization of Binding Properties of Monoglyceride Lipase Inhibitors by a Versatile Fluorescence-based Technique." Analytical Biochemistry 399.1 (2010): 132-34]</ref>MGL is the main enzyme respondsible for hydrolyzing 2-arachidonoylglycerol into arachidonic acid and glycerol ''in vivo'' <ref name="Bertrand">[ Bertrand, T., F. Augé, J. Houtmann, A. Rak, F. Vallée, V. Mikol, P.f. Berne, N. Michot, D. Cheuret, C. Hoornaert, and M. Mathieu. "Structural Basis for Human Monoglyceride Lipase Inhibition." Journal of Molecular Biology 396.3 (2010): 663-73.]</ref>. One of the key features of MGL is the hydrophobic tunnel, which has been suggested to provide a model for drug research. |
===Metabolic Role=== | ===Metabolic Role=== | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
===Component of Endocannabinoid System=== | ===Component of Endocannabinoid System=== | ||
| - | MGL degrades 2- | + | MGL degrades [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2-Arachidonoylglycerol 2-AG]. 2-AG is commonly classified as an [http://books.google.com/booksid=BxfLB4n3uoMC&pg=PA34&lpg=PA34&dq=hydrolysis+of+2-AG+by+MGL&source=bl&ots=R6Xm0KgGdK&sig=K3AwwtDNxbNUKJoa3zsd_25wVKs&hl=en&sa=X&ei=yOI5U43kCcbUsAT9_4DoBw&ved=0CGEQ6AEwCg#v=onepage&q=hydrolysis%20of%202-AG%20by%20MGL&f=false Endocannabinoid] |
| + | . In the brain endocannabinoids are released from postsynaptic neurons, causing the retrograde suppression of synaptic transmission. | ||
In Peripheral tissues, EC is active in autonomic nervous system. EC affects processes such as learning, motor control, cognition, and pain. EC is also able to regulate lipid metabolism and food intake. | In Peripheral tissues, EC is active in autonomic nervous system. EC affects processes such as learning, motor control, cognition, and pain. EC is also able to regulate lipid metabolism and food intake. | ||
Taschler et al. looked at the role of MGL in energy metabolism, finding that MGL deficiency in animals led to the buildup of 2-AG <ref name="Taschler" />. | Taschler et al. looked at the role of MGL in energy metabolism, finding that MGL deficiency in animals led to the buildup of 2-AG <ref name="Taschler" />. | ||
===Inhibition of MGL=== | ===Inhibition of MGL=== | ||
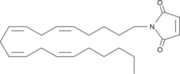
| - | The importance of | + | The importance of [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2013872/ Inhibition] of Monoglyceride lipase is to keep it from breaking down 2-arachidonoyl glycerol. When 2-Ag is broken down it is not able to suppress pain and depression brain functions that human beings experience. N-arachidonyl maleimide (NAM) is one inhibitor of MGL that reacts with the amino acid <scene name='58/580298/Cys252/1'>Cys252</scene>. '''Figure 2:''' |
[[Image:NAM.png|thumb|'''Figure 2:''' The structure of N-arachidonyl maleimide (NAM)that interacts with Cys252.]] | [[Image:NAM.png|thumb|'''Figure 2:''' The structure of N-arachidonyl maleimide (NAM)that interacts with Cys252.]] | ||
This Cysteine is buried in the active site near the catalytic serine and functions by sterically clashing with the natural ligand. A possible conformational change to Cys252 upon the binding of NAM could also lead to an inactive form of MGL. | This Cysteine is buried in the active site near the catalytic serine and functions by sterically clashing with the natural ligand. A possible conformational change to Cys252 upon the binding of NAM could also lead to an inactive form of MGL. | ||
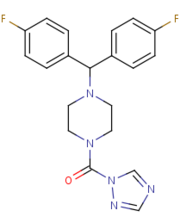
| - | MGL is also inhibited by being in complex with <scene name='58/580298/Sar629/2'>SAR629</scene> that is covalently bound to the catalytic Ser132. SAR629 adopts a Y shape and interacts with the MGL by hydrophobic interactions, with a few polar interactions as well. | + | MGL is also inhibited by being in complex with <scene name='58/580298/Sar629/2'>SAR629</scene> that is covalently bound to the catalytic Ser132. SAR629 adopts a Y shape and interacts with the MGL by hydrophobic interactions, with a few polar interactions as well. '''Figure 3:''' |
| - | [[Image:SAR.png|thumb|'''Figure 3:''' The structure and shape of SAR629.]] | + | [[Image:SAR.png|left|thumb|'''Figure 3:''' The structure and shape of SAR629.]] |
With SAR629 interacting with the catalytic triad it inhibits the triad from breaking down 2-AG and inactivates MGL <ref name="Bertrand" /> | With SAR629 interacting with the catalytic triad it inhibits the triad from breaking down 2-AG and inactivates MGL <ref name="Bertrand" /> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
== Catalytic triad == | == Catalytic triad == | ||
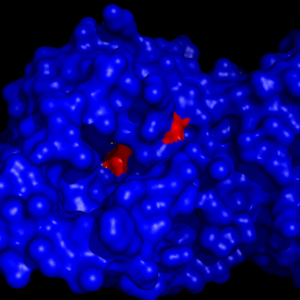
| - | MGL has a classic <scene name='58/580298/Catalytic_triad/1'>catalytic triad</scene> that contains Ser-His-Asp. The triad was found using site-directed mutagenesis of each individual residue and each of these amino acid residues are catalytically essential to MGL <ref name="Bertrand" />. The catalytic triad is located in the binding pocket buried at the bottom of it in the oxyanion hole connected by a water molecule. | + | MGL has a classic <scene name='58/580298/Catalytic_triad/1'>catalytic triad</scene> that contains Ser-His-Asp. The triad was found using site-directed mutagenesis of each individual residue and each of these amino acid residues are catalytically essential to MGL <ref name="Bertrand" />. The catalytic triad is located in the binding pocket buried at the bottom of it in the oxyanion hole connected by a water molecule.'''Figure 4:''' |
[[Image:Catalytic_triad_binding_pocket.png|300px|thumb|'''Figure 4:''' The binding pocket of MGL with the catalytic triad (shown in red) buried in it.]] | [[Image:Catalytic_triad_binding_pocket.png|300px|thumb|'''Figure 4:''' The binding pocket of MGL with the catalytic triad (shown in red) buried in it.]] | ||
Revision as of 03:41, 9 April 2014
Monoglyceride Lipase (MGL)
| |||||||||||