We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 914
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
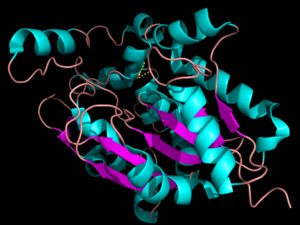
| - | The secondary structure of PPT1 contains several α-helices and few β-sheets (Figure 1). PPT1 includes residues 28-306, after the 27-residue signal peptide has been removed <ref name="RSCB"> | + | The secondary structure of PPT1 contains several α-helices and few β-sheets (Figure 1). PPT1 includes residues 28-306, after the 27-residue signal peptide has been removed <ref name="RSCB">PMID:10781062</ref>. An insertion is found between β6 and β7, residues 140-223, and that forms a <scene name='57/573128/9/1'>second domain</scene>, shown in blue, that is compromised almost entirely of the fatty acid binding site. This second domain region contains six helices, α2-α7<ref name="RSCB"/>. |
The α/β hydrolase fold is common to many other hydrolases <ref name="RSCB"/>. The α/β hydrolase fold has a central 6 stranded parallel β-sheet consisting of <scene name='57/573128/4/1'>β3-β8</scene> and α-helices <scene name='57/573128/5/1'>αA, αB, αC, and αF</scene><ref name="RSCB"/>. A catalytic triad and an oxyanion hole are also common features to the PPT1 protein family. None of the enzymes within the α/β hydrolase fold family require a cofactor for catalytic activity. | The α/β hydrolase fold is common to many other hydrolases <ref name="RSCB"/>. The α/β hydrolase fold has a central 6 stranded parallel β-sheet consisting of <scene name='57/573128/4/1'>β3-β8</scene> and α-helices <scene name='57/573128/5/1'>αA, αB, αC, and αF</scene><ref name="RSCB"/>. A catalytic triad and an oxyanion hole are also common features to the PPT1 protein family. None of the enzymes within the α/β hydrolase fold family require a cofactor for catalytic activity. | ||
Revision as of 23:32, 9 April 2014
ββ
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 06, 2014, through Aug 22, 2014 for use by the Biochemistry II class at the Butler University at Indianapolis, IN USA taught by R. Jeremy Johnson. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 911 through Sandbox Reserved 922. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1 Precursor - Homo Sapiens. N.p., 1 Oct. 1996.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 PPT1. Genetics Home Reference. U.S. National Library of Medicine, Aug. 2015.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Bellizzi JJ 3rd, Widom J, Kemp C, Lu JY, Das AK, Hofmann SL, Clardy J. The crystal structure of palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1 and the molecular basis of infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Apr 25;97(9):4573-8. PMID:10781062 doi:10.1073/pnas.080508097
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Branneby, Cecilia. Exploiting Enzyme Promiscuity for Rational Design. KTH Biotechnology. N.p., May 2005
External Resources
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palmitoyl_protein_thioesterase
https://www.counsyl.com/diseases/ppt1-related-neuronal-ceroid-lipofuscinosis/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha/beta_hydrolase_fold
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalytic_triad
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2121/8/22
http://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=PPT1