Sandbox reserved 919
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction to hormone-sensitive lipase== | ==Introduction to hormone-sensitive lipase== | ||
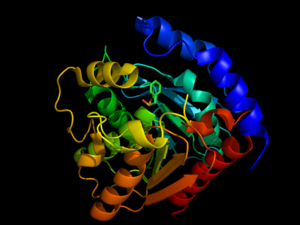
| - | [[Image:HPL_Movie0006.png|300 px|left|thumb|Hormone-Sensitive Lipase from [[3dnm]]]] | + | [[Image:HPL_Movie0006.png|300 px|left|thumb|Hormone-Sensitive Lipase from [[3dnm]]. Alpha helices and beta sheets are shown in red and yellow, respectively.]] |
Hormone-sensitive [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Lipase lipases] (HSL) represent a class of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Esterase esterases] within the [http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Hydrolase hydrolase] family that catalyzes the cleavage of ester bonds in fatty acid molecules when stimulated by a hormone. The activation and mobilization of these hormone-sensitive lipases can be triggered by various [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catecholamine catecholamines] and inhibited by [http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Insulin insulin]. HSL is clinically relevant because the mobilization of fats in cells is directly related to fat accumulation seen in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atherosclerosis artherosclerosis], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diabetes_mellitus_type_2 type 2 diabetes], and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obesity obesity]. Investigation of HSL's structure and function could provide a better clinical understanding of these diseases. <ref name= "Yeaman">PMID:14725507</ref> | Hormone-sensitive [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Lipase lipases] (HSL) represent a class of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Esterase esterases] within the [http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Hydrolase hydrolase] family that catalyzes the cleavage of ester bonds in fatty acid molecules when stimulated by a hormone. The activation and mobilization of these hormone-sensitive lipases can be triggered by various [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catecholamine catecholamines] and inhibited by [http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Insulin insulin]. HSL is clinically relevant because the mobilization of fats in cells is directly related to fat accumulation seen in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atherosclerosis artherosclerosis], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diabetes_mellitus_type_2 type 2 diabetes], and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obesity obesity]. Investigation of HSL's structure and function could provide a better clinical understanding of these diseases. <ref name= "Yeaman">PMID:14725507</ref> | ||
Revision as of 13:31, 15 April 2014
Contents |
Introduction to hormone-sensitive lipase
Hormone-sensitive lipases (HSL) represent a class of esterases within the hydrolase family that catalyzes the cleavage of ester bonds in fatty acid molecules when stimulated by a hormone. The activation and mobilization of these hormone-sensitive lipases can be triggered by various catecholamines and inhibited by insulin. HSL is clinically relevant because the mobilization of fats in cells is directly related to fat accumulation seen in artherosclerosis, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. Investigation of HSL's structure and function could provide a better clinical understanding of these diseases. [1]
Briefly, binding of catecholamines to β-adrenergic receptors coupled with adenylate cyclase (AC) stimulates G-proteins to increase the levels of cystolic cAMP. Elevated levels of cAMP leads to an activation protein kinase A (PKA) leading to phosphorylation of serine residues on HSL activating and translocating HSL to lipid droplets for lipolysis. Conversely, insulin signaling decreases cystolic cAMP levels, resulting in a decreased HSL mobilization. [2]
Structure of hormone-sensitive lipase
| |||||||||||
Additional pages about hormone-sensitive lipase
References
- ↑ Yeaman SJ. Hormone-sensitive lipase--new roles for an old enzyme. Biochem J. 2004 Apr 1;379(Pt 1):11-22. PMID:14725507 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BJ20031811
- ↑ Holm C. Molecular mechanisms regulating hormone-sensitive lipase and lipolysis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Dec;31(Pt 6):1120-4. PMID:14641008 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/
- ↑ Nam KH, Kim MY, Kim SJ, Priyadarshi A, Kwon ST, Koo BS, Yoon SH, Hwang KY. Structural and functional analysis of a novel hormone-sensitive lipase from a metagenome library. Proteins. 2009 Mar;74(4):1036-40. PMID:19089974 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/prot.22313
- ↑ Kanwar SS, Kaushal RK, Jawed A, Gupta R, Chimni SS. Methods for inhibition of residual lipase activity in colorimetric assay: a comparative study. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2005 Aug;42(4):233-7. PMID:23923547
- ↑ Kraemer FB, Shen WJ. Hormone-sensitive lipase: control of intracellular tri-(di-)acylglycerol and cholesteryl ester hydrolysis. J Lipid Res. 2002 Oct;43(10):1585-94. PMID:12364542