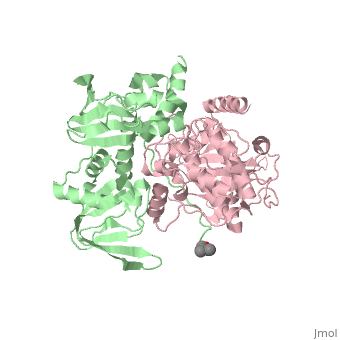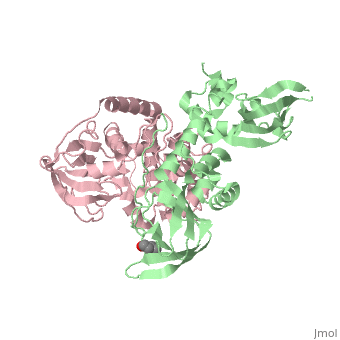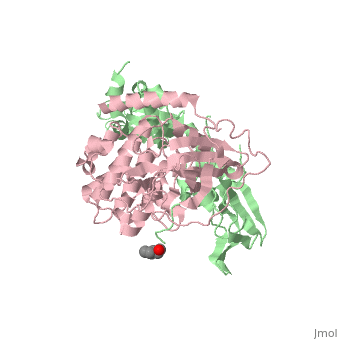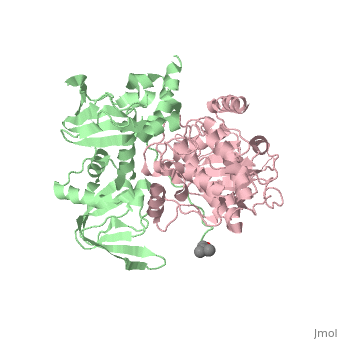Protein Kinase A
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Protein kinase A (PKA)== | ==Protein kinase A (PKA)== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='3tnp' size='340' side='right' caption='Protein kinase A (PKA)' scene=''> |
'''Protein kinase A (PKA)''' is a group of enzymes whose activity is dependent on the concentration of cAMP, and is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase. | '''Protein kinase A (PKA)''' is a group of enzymes whose activity is dependent on the concentration of cAMP, and is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | PKA consists of two types of subunits. It has a 49-kd regulatory <scene name='58/582909/Regulatory_subunits/1'> | + | PKA consists of two types of subunits. It has a 49-kd regulatory <scene name='58/582909/Regulatory_subunits/1'>regulatory subunit</scene>)(R) and a 38-kd <scene name='58/582909/Catalytic_subunits/1'>catalytic subunit</scene> (C).When PKA is enzymatically inactive (absence of cAMP), it is a tetrameric complex of a regulatory dimer bound to two catalytic subunits, forming the R2C2 complex. In its active state, the complex dissociates to form an R2 subunit and two C subunits. The catalytic subunit has two lobes. The larger lobe binds the peptide and contributes the key catalytic residues and the smaller lobe makes many contacts with ATP-Mg2+. |
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
Revision as of 15:37, 29 April 2014
Protein kinase A (PKA)
| |||||||||||
References
[1]Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644 [2]C. Kim, N.-H. Xuong, and S.S. Taylor, "Crystal structure of a complex between catalytic and regulatory (Rlα) subunits of PKA,"Science 307, 690 (2005) [doi:10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2012_8]