We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 186
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Secondary Structure and the Thioredoxin Like Fold == | == Secondary Structure and the Thioredoxin Like Fold == | ||
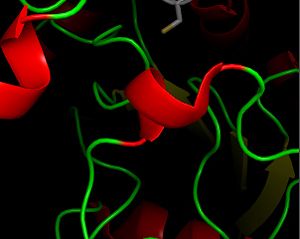
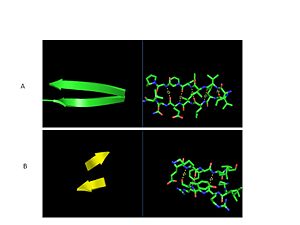
| - | The secondary structure of GPx-1 consists of nine β-strands and nine α-helices with | + | The secondary structure of GPx-1 consists of nine β-strands and nine α-helices with five of the helices being of the 310 form (Figure 2)[[Image:Helix310.jpg|300px|left|thumb|]]. Interestingly two of the β-strands form a parallel β-sheet (Figure 3)[[Image:Beta_sheets3.jpg|300px|right|thumb|]]. GPx-1 exhibits a thioredoxin like fold. The classic thioredoxin fold consists of a four stranded β-sheet that is surrounded by three α-helices (5). However the thioredoxin fold is commonly subject to the insertion of additional secondary structural elements between the second β-strand and the second α-helices (6). This is seen in GPx-1 as there is an addition of an α-helix and a β-strand between the second β-strand and the second α-helices (6). A similar insertion is found in peroxiredoxins, a different family of proteins which also catalyze the reduction of hydroperoxides(6). |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
Revision as of 05:34, 30 April 2014
| |||||||||||