User:Yunlong Zhao/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
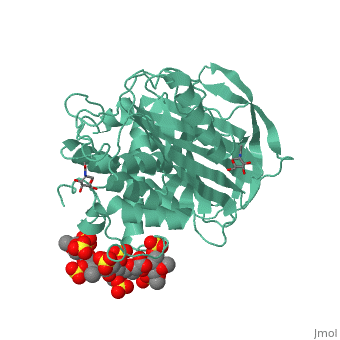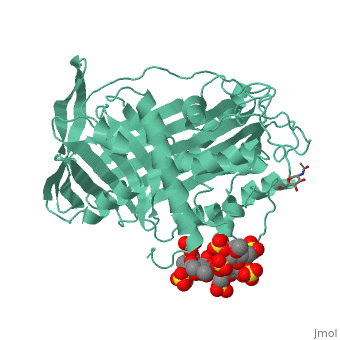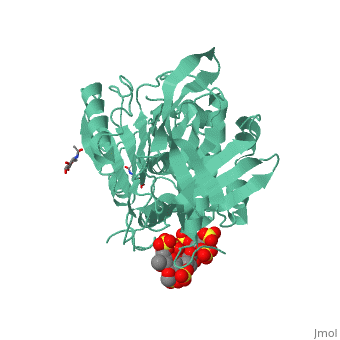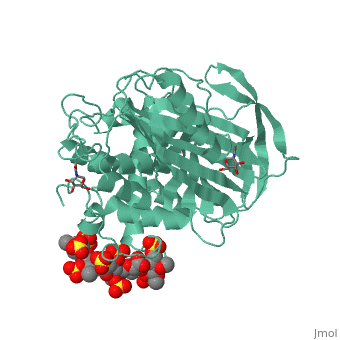
== Anticoagulation effects of heparin and the interaction with antithrombin == | == Anticoagulation effects of heparin and the interaction with antithrombin == | ||
<StructureSection load='1azx' size='340' side='right' caption='Pentasaccharides-bound Antithrombin' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1azx' size='340' side='right' caption='Pentasaccharides-bound Antithrombin' scene=''> | ||
| + | == Introduction == | ||
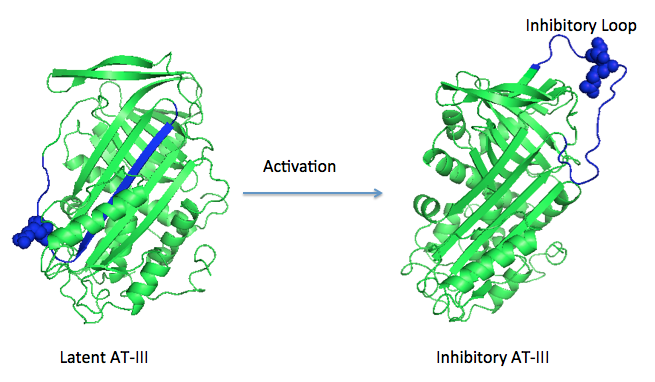
Heparin is a type of glycosaminoglycan chain that is secreted by human mast cell. Heparin exists in many isoforms and is often sulfated at specific sites. Because of the heterogeneity in structure and distribution of negative charge within those sulfate groups, heparin can bind multiple types of proteins and participate in many different biological processes, such as anticoagulation. Therefore polysaccharides, the low molecular weight products that are originated from digested heparin was often used in the therapy of many diseases such as atrial fibrillation and thrombosis. | Heparin is a type of glycosaminoglycan chain that is secreted by human mast cell. Heparin exists in many isoforms and is often sulfated at specific sites. Because of the heterogeneity in structure and distribution of negative charge within those sulfate groups, heparin can bind multiple types of proteins and participate in many different biological processes, such as anticoagulation. Therefore polysaccharides, the low molecular weight products that are originated from digested heparin was often used in the therapy of many diseases such as atrial fibrillation and thrombosis. | ||
Revision as of 04:17, 11 May 2014
Anticoagulation effects of heparin and the interaction with antithrombin
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Lane DA, Denton J, Flynn AM, Thunberg L, Lindahl U. Anticoagulant activities of heparin oligosaccharides and their neutralization by platelet factor 4. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):725-32. PMID:6721831
- ↑ Olson ST, Bjork I, Sheffer R, Craig PA, Shore JD, Choay J. Role of the antithrombin-binding pentasaccharide in heparin acceleration of antithrombin-proteinase reactions. Resolution of the antithrombin conformational change contribution to heparin rate enhancement. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12528-38. PMID:1618758