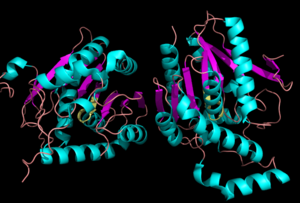
Figure 1:Crystal Structure of MGL (α-helixes are in blue and β-sheets in purple). MGL is a dimer that is linked by antiparallel beta sheets
Introduction
Monoglyceride Lipase (MGL, MAGL, MGLL) is a 33 kDa protein [1] found mostly in the cell membrane (). MGL is a serine hydrolase enzyme that contains an α/β hydrolase fold. MGL plays a key role in the hydrolysis of 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), an endocannabinoid produced by the the central nervous system.[1][2][3][4] The hydrolase fold, along with a characteristic amphipathic occluded tunnel, allows MGL's active site to selectively bind to 2-AG and degrade it into arachidonic acid and glycerol.[2] 2-AG has been found to possess anti-nociceptive, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory and tumor-reductive character when it binds to cannabinoid receptors. [1] [2] Due to the vast medical and therapeutic utility of 2-AG, the inhibition of MGL is a high interest target in pharmaceutical research. Furthermore, MGL has also been cited as having both negative and positive effector roles in cancer pathology. [5] [6]
3D Structure
The first complete crystal structure of MGL was determined in 2009 in its apo form. [2] MGL is a part of the α-β hydrolase family of enzymes.[1][2][3] This category of proteins contains an beta sheet, specifically containing seven parallel and one antiparallel constituent strand, by alpha-helices. [2]
MGL has a characteristic lid domain comprised of two large loops that surround .[2] This region of the enzyme is the membrane-interacting moiety of the protein, which is consistent with its amphipathic nature and outward-facing (graphite being nonpolar and cyan being highly polar). 2-AG and other lipids suspended in the hydrophobic section of the cell membrane have been proposed to associate with this region of MGL before entering the active tunnel.[2] Interestingly, MGL’s lid domain may be more flexible than its analogs in other α-β hydrolases, due to the various conformations it assumed in crystallographic studies. [2] Currently, there is no consensus regarding the quaternary arrangement of MGL. Some studies show that MGL is primarily found as a monomer, [2] [3] whereas other studies have found it to be a physiologically active . [1] One compelling piece of evidence for the dimeric quartenary structure is the presence of a pair of beta strands between the two molecules of MGL in 3JW8.
Active Site
MGL contains an active site
roughly 25Å long and 8Å wide residing beneath its lid region. Like its substrates, 2-AG and other monoacylglycerols, the tunnel is largely amphipathic. Hydrophobic residues dominate the tunnel with the exception of the terminal occluded region, which houses the catalytic triad. In its apo form, the catalytic region is not solvent-exposed, unlike the wide opening of the tunnel. [1][2] A unique structural motif in MGL is a 5Å solvent-exposed hole connecting the exterior to the catalytic site. This structure is proposed to act as an “exit hole” through which the glycerol product leaves MGL. The fatty acid product, namely arachidonic acid, presumably travels back through the active site tunnel. [1][2][3]
Catalytic Triad
MGL’s serine hydrolase chemistry is executed by a (Ser132-His279-Asp249) and seems to utilize the same mechanism as the much-studied chymotrypsin. In this mechanism, an activated serine nucleophile cleaves the ester bond of the substrate.[1][2][3] The subsequent tetrahedral intermediate is stabilized by the , formed by the main-chain nitrogens of Ala61 and Met (or Se-Met) 133.[2] The triad was found using site-directed mutagenesis of each individual residue and each of these amino acid residues are catalytically essential to MGL [7]. The catalytic triad is located in the Binding Pocket buried at the bottom of it in the oxyanion hole connected by a water molecule.
Ligand Binding Site
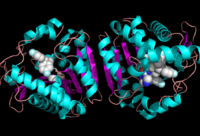
Figure 2: Ligand within the Overall Structure of MGL
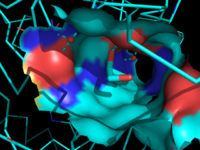
Figure 3: Ligand binding pocket showing the hydrophobic and polar regions
The of MGL has a large hydrophobic region with a polar bottom. The entrance of the binding pocket for MGL contains a lid, which is very flexible [7]. The binding pocket or tunnel within MGL matches with the overall structure of 2-AG, with 2-AG's polar head being cleaved by the catalytic triad Figure 3. The binding pocket is not being adjusted to the ligand's shape. However, the main movements of MGL involve the lid region of the ligand binding pocket upon the ligand binding. When 2-AG and its isomer 1(3)-AG bind to MGL, the hydrophobic chain is first aligned with the left part of the binding pocket. The carbonyl on 2-AG and 1(3)-AG is then hydrogen bonded to . The polar head group of the ligand is then fixed by three hydrogen bonds. The large lipophilic portion of the binding pocket is being used to design more selectivie inhibitors [7].
Biological/Medical Relevance
Monoglyceride Lipase is involved in energy metabolism through two mechanisms. In the first mechanism, MGL hydrolyzes monoacylglycerols into fatty acids and glycerol, which are able to then be used for energy production [8]. The second mechanism involves the degradation of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG), which is a common endogenous ligand of cannabinoid receptors, by MGL.
2-AG Metabolism
2-AG activates the same cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) for both anandamide and the main psychoactive compound found in Cannabis sativa, Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), via retrograde signaling. [2][1] In the brain, endocannabinoids (ECs) are released from postsynaptic neurons, causing the retrograde suppression of synaptic transmission. [8] In peripheral tissues, endocannabinoids (ECs) are active in autonomic nervous system. EC signalling affects processes such as learning, motor control, cognition, and pain [8]. EC signalling is also able to regulate lipid metabolism and food intake.
2-AG is the most abundant endocannabinoid found in the brain, possessing analgesic, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulating, neuroprotective, and hypotensive effects.[1][5] MGL degrades 2-AG, preventing 2-AG from remaining bound to the cannabinoid receptor and therefore terminating the pain signal. Without the degradation of 2-AG by MGL, 2-AG levels would increase which would lead to a prolonged nociceptive effect [9] Approximately 85% of the 2-AG in the rat brain is metabolized by MGL, while other lipases such as fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) process the remainder of the metabolite.[4] Based on these studies, MGL has been assigned as the primary enzyme for the metabolism of 2-AG in humans, making it a highly desirable target enzyme for the modulation of 2-AG concentration in the body. [1][2][3] A deficiency in MGL in animals led to the buildup of 2-AG [8]. The endocannabinoid 2-AG has a nociceptive effect in pain signalling [9]. Although the most-studied role of MGL is the degradation of 2-AG in the brain, MGL may also play a role in adipose tissue, completing the hydrolysis of triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol, as well as working in the liver to mobilize triglycerides for secretion. [1][3]
MGL Inhibitors
Three general MGL
inhibitor classes have been observed: noncompetitive, partially irreversible inhibitors such as
URB602; cysteine-reactive inhibitors such as
N-arachidonoylmaleimide (NAM); and irreversible serine-reactive inhibitors such as
JZL184 and .
[2] SAR629 covalently binds to the catalytic Serine-132; the oxygen of the nucleophilic serene residue attacks the carbonyl carbon of SAR629, forming a
carbamate. This covalent bond is believed to be reversible via hydrolysis, albeit slowly.
[2]SAR629 adopts a Y shape and interacts with the MGL by hydrophobic interactions, with a few polar interactions as well.
Figure 4 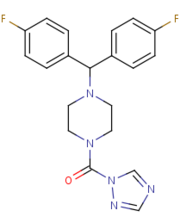
Figure 4: The structure and shape of SAR629.
Due to JZL184's similar structure to SAR629, it may undergo a similar reaction with MGL.
[2] Despite the existence of multiple lead compounds, there is a strong demand for the creation of more highly-specific and more potent inhibitors that could be used as anti-pain drugs for their ability to keep 2-AG active in the neuronal synapses.
[1]
N-arachidonyl maleimide (NAM) is another inhibitor of MGL. NAM reacts with the amino acid . Cys252 is buried in the active site near the catalytic serine and functions by sterically clashing with the natural ligand. A possible conformational change to Cys252 upon the binding of NAM could also lead to an inactive form of MGL.
Cancer Relevance
MGL is also a target for continuing cancer research, with the potential to help distinguish the role of fatty acids in malignancy. Also of interest is the varying efficacy of endocannabinoids as anti-cancer agents in different body tissues and the multifarious influences on the PI-3k/Akt signaling pathway in carcinogenesis. [6]
MGL exerts a twofold influence on cancer growth; endocannabinoids such as 2-AG have been shown to have anti-tumorigenic properties [1] [5] and a high fatty-acid concentration may play a role in the promotion of cancer aggressiveness and malignancy. In aggressive breast, melanoma, ovarian, and prostate cancer cells, MGL activity was found to be higher than in nonaggressive malignant cells.[5] Subsequently, the creation of effective MGL inhibitors may help to treat highly aggressive cancers in addition to their proposed use as analgesics.
Recent evidence, however, has suggested that in lung, breast, ovary, stomach, and colorectal cancer, MGL expression was reduced. In addition to controlling 2-AG degradation and fatty acid synthesis pathways, MGL also interacts with key phospholipids (specifically, the 3-phosphorylated phosphoinositide products of PI-3K) in the PI3K/Akt signaling and tumor growth pathway. MGL serves as a negative effector in the pathway: as the concentration of MGL decreases, Akt phosphorylation increases. [6]
MGL’s role in different body tissues is an ongoing area of research aimed at elucidating its complex role in cancer pathology. MGL’s effect on exogenous cannabinoid medications that are administered to cancer patients as a palliative medication is of particular scientific interes. [5]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 Labar G, Bauvois C, Borel F, Ferrer JL, Wouters J, Lambert DM. Crystal structure of the human monoacylglycerol lipase, a key actor in endocannabinoid signaling. Chembiochem. 2010 Jan 25;11(2):218-27. PMID:19957260 doi:10.1002/cbic.200900621
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 Bertrand T, Auge F, Houtmann J, Rak A, Vallee F, Mikol V, Berne PF, Michot N, Cheuret D, Hoornaert C, Mathieu M. Structural basis for human monoglyceride lipase inhibition. J Mol Biol. 2010 Feb 26;396(3):663-73. Epub 2009 Dec 3. PMID:19962385 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.11.060
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Schalk-Hihi C, Schubert C, Alexander R, Bayoumy S, Clemente JC, Deckman I, Desjarlais RL, Dzordzorme KC, Flores CM, Grasberger B, Kranz JK, Lewandowski F, Liu L, Ma H, Maguire D, Macielag MJ, McDonnell ME, Haarlander TM, Miller R, Milligan C, Reynolds C, Kuo LC. Crystal structure of a soluble form of human monoglyceride lipase in complex with an inhibitor at 1.35 A resolution. Protein Sci. 2011 Feb 3. doi: 10.1002/pro.596. PMID:21308848 doi:10.1002/pro.596
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Blankman JL, Simon GM, Cravatt BF. A comprehensive profile of brain enzymes that hydrolyze the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Chem Biol. 2007 Dec;14(12):1347-56. PMID:18096503 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2007.11.006
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Nomura DK, Lombardi DP, Chang JW, Niessen S, Ward AM, Long JZ, Hoover HH, Cravatt BF. Monoacylglycerol lipase exerts dual control over endocannabinoid and fatty acid pathways to support prostate cancer. Chem Biol. 2011 Jul 29;18(7):846-56. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.05.009. PMID:21802006 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.05.009
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Sun H, Jiang L, Luo X, Jin W, He Q, An J, Lui K, Shi J, Rong R, Su W, Lucchesi C, Liu Y, Sheikh MS, Huang Y. Potential tumor-suppressive role of monoglyceride lipase in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2013 Jan 10;32(2):234-41. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.34. Epub 2012 Feb 20. PMID:22349814 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.34
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref> tag;
no text was provided for refs named Bertrand
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref> tag;
no text was provided for refs named Taschler
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref> tag;
no text was provided for refs named Clemente




