Introduction
Lysozyme - also known as muramidase, or glycoside hydrolase - is a powerful enzyme of biological significance found in abundance in tears, saliva, and human milk. In humans, it is encoded in the LYZ gene. Although it is responsible for the initial digestion of starches in the mouth, it is most widely identified as a non-specific defense in gram positive bacteria and in many species of fungi. Due to its antibacterial effects, it is a strong component of the innate immune system, and is an important part of an infant's diet to ward off diarrheal diseases. Since it is a small, easily available, and highly stable protein containing only 129 amino acid residues, it has been subject to extensive research regarding its function and structure. Hen Egg White (HEW) Lysozyme is shown below.
Lysozyme is an enzyme known for its unique ability to degrade the polysaccharide architecture of many kinds of cell walls, normally for the purpose of protection against bacterial infection[1]. Its effects were first noticed by Laschtschenko in 1909. It was officially characterized and termed “lysozyme” by Alexander Fleming, the same person credited for the accidental discovery of penicillin.
The characterization of lysozyme in 1922 by Alexander Fleming was providential in that the undertaken experiment related to the discovery of lysozyme was not geared toward any knowledge of such a protein as lysozyme [2]. During the unrelated experiment, nasal drippings were inadvertently introduced to a petri dish containing a bacterial culture, which culture consequently exhibited the results of an as yet unknown enzymatic reaction. The observation of this unknown reaction led to further research on the components of this reaction as well as to the corresponding identification of the newfound "lysozyme." Fleming's discovery was complemented by David C. Phillips' 1965 description of the three-dimensional structure of lysozyme via a 200 pm resolution model obtained from X-ray crystallography [3]. Phillips' work was especially groundbreaking since Phillips had managed to successfully elucidate the structure of an enzyme via X-ray crystallography - a feat that had never before been accomplished[4]. Phillips' research also led to the first sufficiently described enzymatic mechanism of catalytic action [5]. Thus, Phillips' elucidation of the function of lysozyme led Phillips to reach a more general conclusion on the diversity of enzymatic chemical action in relation to enzymatic structure. Clearly, the findings of Phillips as well as the more general historical development of the understanding of the structure and function of lysozyme have been paramount to the more general realm of enzyme chemistry. See also Molecular Playground/Lysozyme and User:Judy Voet/Lysozyme.
Function
Lysozyme is known for damaging bacterial cell walls by catalyzing the hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (NAG) residues in peptidoglycan, and between N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitodextrins. In this way, lysozyme is efficient in lysing the cell walls of both bacteria and fungi. The location of cleavage for lysozyme on this architectural theme is the β(1-4) glycosidic linkage connecting the C1 carbon of NAM to the C4 carbon of NAG.
The particular substrate of preference for this cleavage type is a (NAG-NAM)₃ hexasaccharide, within which substrate occurs the
cleaving target glycosidic bond, NAM₄-β-O-NAG₅. The individual hexasaccharide binding units are designated A-F, with NAM₄-β-O-NAG₅ glycosidic bond cleavage preference corresponding to a D-E unit glycosidic bond cleavage preference.
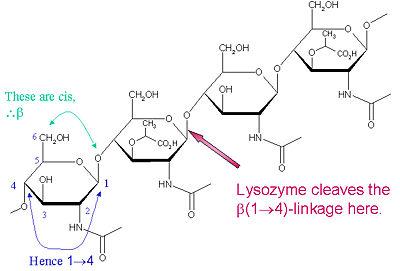
Lysozyme Cleavage Site
[6] Composition and Structure of Lysozyme
All proteins consist of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur, as do most organic molecules. Enzymes are composed in such a way as to maximize their reactivity with their desired substrate, increasing the efficiency of biological reactions. The can be seen on the left, with the carbon atoms outlined in gray, oxygen atoms in red, nitrogen atoms in blue, sulfur atoms in yellow, and the three-letter abbreviation for the in purple. Lysozyme, like all proteins, also contains , and these can be seen by following the colors of the rainbow across the molecule. Starting at the red end, the C terminal end, one can work the entire way through to the N terminal end, showing the folding pattern and chain of the protein.
Lysozyme contains five regions and five regions containing as displayed in this . Linking these secondary structures, a number of beta turns and a large number of random coils make up the remainder of the polypeptide backbone. The polypeptide backbone of lysozyme involved in the 3 antiparallel beta sheets display the beta hairpin motif of supersecondary structure. This depiction of lysozyme contains an antiparallel beta-pleated sheet, which contributes greatly to the stability of the molecule by providing the correct alignment of hydrogen bonds. Lysozyme also contains a great deal of random coil, which is seen in the white regions of the molecule.
Intermolecular Interactions
Polarity
The nature of the amino acid sidechains in the lysozyme polypeptide sequence leads to regions of varying hydrophobicities and polarities of the enzyme structure. The presence of certain regions of hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity is a driving force in determining protein structure when folding. The varying polarities of the side chains influence the locations of residues in the enzyme structure. Nonpolar residues appear blue, and polar residues appear red in the following display of lysozyme. Nonpolar residues will display hydrophobic tendencies occurring mostly on the interior of the enzyme while polar residues will increase in abundance on the surface of the protein in order to increase contact with the aqueous solvent so as to satisfy their hydrophilic nature. By observing a space-filled structural depiction of with polar molecules colored red and nonpolar molecules colored blue the influence of polarity on protein folding is evident, with the blue (nonpolar) regions inside the red (polar) regions. The presence of interacting with the various hydrophilic residues is depicted to further display how polarity affects structure. Water is depicted as yellow, and the polar and nonpolar regions remain their respective color.
Hydrogen Bonding
In all proteins are essential for stability. In this ribbon diagram, the hydrogen bonds can be seen between the secondary structures of lysozyme highlighted in orange. Since the double bonds of the alpha carbons in the main chain of lysozyme cause torsional strain, lysozyme is limited to very specific hydrogen bonding between the amino acid residues. This representation clearly shows how crucial hydrogen bonding is to help maintain the stability of the protein.
Disulfide Bonding in Lysozyme
Lysozyme contains four involving eight cysteine residues, which are highlighted in yellow on the left. Disulfide bonds are intramolecular forces that stabilize the tertiary structure of many proteins. Disulfide bonds are present in four locations in lysozyme: between Cys 6 and Cys 127, between Cys 30 and Cys 115, between Cys 64 and Cys 80 and between Cys 76 and Cys 94.
Mechanism
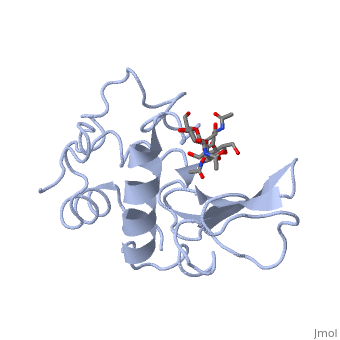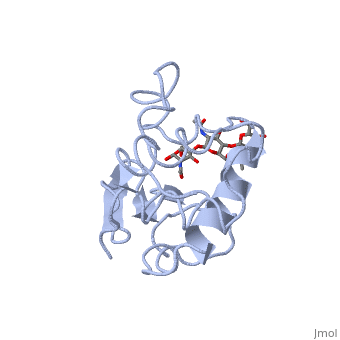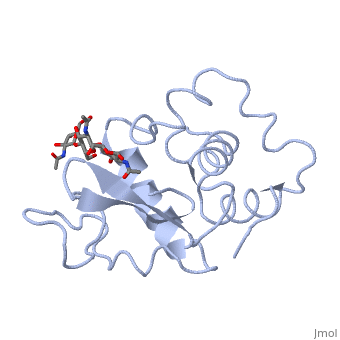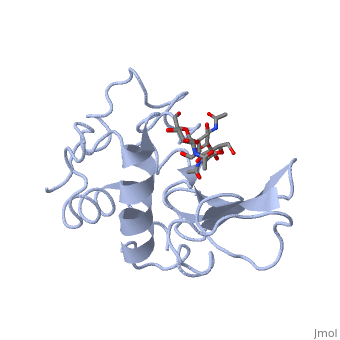
A ligand is able to bind to the active site of an enzyme to form a biologically relevant complex. The ligand can be seen in this
, with the ligand protruding as a ball and stick model from the active site. Here, it is clear that the ligand is a polysaccharide.
The lysozyme reaction is characterized by hydrolysis of the beta (1-4) glycosidic bond between NAM and NAG. Lysozyme has a very specific active site, which can bind only six sugar rings from a polysaccharide chain. Once lysozyme binds to this chain, it hydrolyzes them. These six sugar rings represent the ligand of lysozyme. The lysozyme then distorts the fourth sugar in the six-membered complex, producing stress on the molecule and breaking the glycosidic bond.
Lysozyme is best inhibited by small saccharides which act competitively with the natural substrate. The smaller saccharides will bind to the first three binding sites of the cleft (sites A-C), but will not reach sites D and E, where the enzyme cuts the glycosidic bond. So, the competitive inhibitor will stick in the cleft, not allowing the substrate to bind to the enzyme complex.[7] Several known inhibitors of lysozyme are: SDS, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, and various alcohols and oxidizing agents.[8]
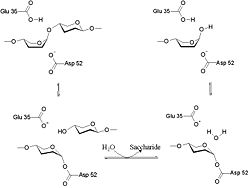
The lysozyme mechanism of action results in the hydrolysis of a glycoside (hence the familial distinction of lysozyme as a glycosylase[10]), which corresponds to the conversion of an acetal to a hemiacetal, which reaction (general degradation of glycosidic bond to units "capped" by newly formed hydroxyl groups) necessitates acid catalysis, since the conversion of acetal to hemiacetal involves the protonation of the reactant oxygen prior to actual bond cleavage. [11]. Furthermore, the transition state obtained from this protonation is a covalent, oxonium ion, intermediate that must obtain resonance stabilization. The need for some means of acid catalysis and covalent resonance stabilization is adequately provided by the Glu 35 and Asp 52 residues of lysozyme, respectively. The reaction mechanism of lysozyme is demonstrated on the left. The reaction begins at the upper left-hand side, and proceeds according to reaction arrows. Lysozyme works by hydrolyzing the glycosidic bond, distorting the bond between the NAM and NAG. This produces a glycosyl enzyme intermediate, which reacts with a water molecule to produce the product and the unchanged enzyme. The of lysozyme is formulated as a prominent cleft outlined by the two aforementioned catalytic amino acids, Glu 35 and Asp 52. The active site is geometrically bent to augment ligand binding, and the two amino acids interact with the ligand in the binding site. Asp52 is depicted in red, and Glu35 is depicted in green.
Applications of Lysozyme
Since lysozyme has been widely recognized for its antibacterial and antifungal properties, it has a wide variety of uses both in biochemical and pharmaceutical applications. In molecular biology, lysozyme is often used in the alkaline-lysis procedure for extracting and isolating plasmid DNA. It is used extensively in the pharmaceutical field for destroying gram-positive bacteria, and can be used to support already-existing immune defenses to fight bacterial infections. This enzyme is particularly important for preventing bacterial diseases in infants. Because of its antibacterial properties, lysozyme can also be used in the food industry to help prevent spoilage of foods.
Structural history of Hen Egg-White Lysozyme
Lysozyme was the first enzyme whose X-ray structure was determined [12][13]. This shows Hen Egg White (HEW) lysozyme containing a trisaccharide of N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) bound to a cleft in the enzyme. David Phillips, who determined the structure in 1965, saw that the cleft was large enough to fit three more saccharide units.
He therefore built a model extending the trisaccharide to a
that fits into the cleft, labeling the sugar subsites A-F[14]. Alternately click on and to turn the modeled portion of the hexasaccharide on and off.
The interesting thing about the model was that the only way that the hexasaccharide would fit into the cleft was if the 4th saccharide (in subsite D) was strained into a . This conformation is what would be necessary for the formation of an oxocarbonium ion (oxionium ion). When the model was studied, was found to be in an ideal location to act as a general acid catalyst, 3.34 Angstroms from the bridging oxygen between the 4th and 5th saccharide units. appeared to be too far away (2.69 angstroms) in the static lysozyme structure to have formed a covalent bond with C1 of the half-chair model in the D site, and no covalent intermediate had ever been detected, so Phillips proposed that it acted as an electrostatic stabilizer of the oxonium ion (referred to as The Phillips Mechanism).
Then, in 2001, Stephen Withers published ,[15] in which Glu 35 had been mutated to Gln to remove the general acid catalyst. The substrate contained NAG-2-fluoro-glucosyl fluoride (NAG2FGlcF). The fluoro group on C-1 does not require acid catalysis to be a good leaving group, and the remaining saccharide, in the absence of the acid necessary to catalyse the second step of the reaction, was demonstrated to form a . In this of the half chair model with 1HEW (greens) and the covalent intermediate in 1H6M (blues), note the relatively small motions of Asp 52 and C1 of the sugar ring in going from the model to the covalent intermediate. to observe the motion from the to the just toggle between the two green links.