Introduction
Transpeptidase (TP), also known as penicillin-binding proteins (PBP), catalyze the cross-linking of peptidoglycan polymers during bacterial cell wall synthesis. The natural transpeptidase substrate is the D-Ala D-Ala peptidoglycan side chain terminus. Beta-Lactam (β-Lactam) antibiotics, which include penicillins, cephalosporins and carbapenems, bind and irreversibly inhibit transpeptidases by mimicking the D-Ala-D-Ala moiety, resulting in the inhibition of cell wall synthesis and ultimately bacterial cell growth. Overuse and misuse of beta-lactams has led to the generation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates that have acquired an alternative transpeptidase, PBP2a, which is compromised in its ability to react with beta-lactams. MRSA isolates are resistant to all beta-lactams, can be hospital- or community-acquired, and are often the cause of significant morbidity and mortality. Futhermore, they are often only susceptible to so-called "last resort antibiotics", such as vancomycin. Recently, two broad range cephalosporins, ceftobiprole and ceftaroline, that bind and inhibit PBP2a have been developed.
Background Information
The bacterial cell wall is composed of sheets of peptidoglycan cross-linked together to form a highly polymeric "mesh" that helps maintain the structural strength of the cell (Figure 1). A peptidoglycan sheet consists of alternating residues of
N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) and
N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) linked together by β-(1,4)- glycosidic bonds. In
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), the NAM residues are coupled to a (D-Ala) residues. The sheets of peptidoglycan are cross-linked together with pentaglycine chains. The cross-linking of adjacent peptidoglycan sheets is catalyzed by transpeptidases (TP). Beta-Lactam antibiotics, such as penicillin and the anti-MRSA cephlosporins, ceftobiprole and ceftaroline, stop the production of the cell wall, and so kill bacteria, by irreversibly inhibiting TPs. Therefore, TPs are also called penicillin-binding proteins.
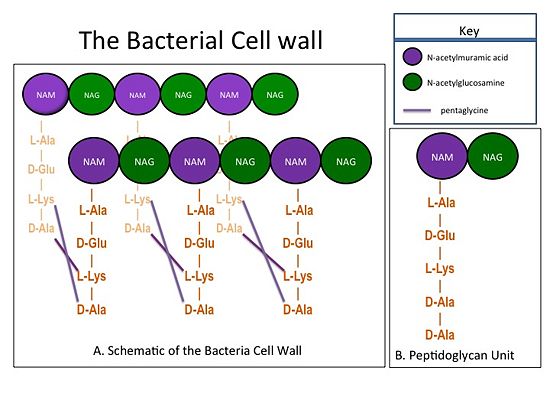
Figure 1.(A) This moiety is polymerized to form sheets of peptidoglycan. Adjacent sheets of peptidoglycan are cross-linked together by pentaglycine "bridges" to form a polymeric "mesh" that is essential for the structural integrity of the bacterial cell. (B) The cell wall is composed of repeating units of a NAM/NAG disaccharide and peptide moiety;
i.e., peptidoglycan.
PBP2a is composed of two domains: a non-penicillin binding domain (residues 27-326) and a transpeptidase domain (residues 327-668). The NBP domain of PBP2a is anchored in the cell membrane, while the TP domain "sits" in the periplasm with its active site facing the inner surface of the cell wall. The active site contains a serine residue position 403 which catalyzes the cross-linking of the peptidoglycan rows with pentaglycine cross-links.
Catalytic Mechanism of Action of Transpeptidases
(A) The peptidoglycan D-Ala D-Ala moiety enters the TP active site, which is in the TP domain (blue) (B) The active site serine residue (star) reacts with and breaks the peptide bond between the D-Ala residues. The terminal D-Ala residue exits the active site. The remaining D-Ala residue is covalently bound to the active site serine residue, and therefore, to TP. The incoming pentaglycine chain reacts with the bound D-Ala residue and is cross-linked to the D-Ala residue.
(D) This results in cross-linking between adjacent peptidoglycan "sheets" and regeneration of the active site serine residue so it can catalyze another cross-linking reaction.
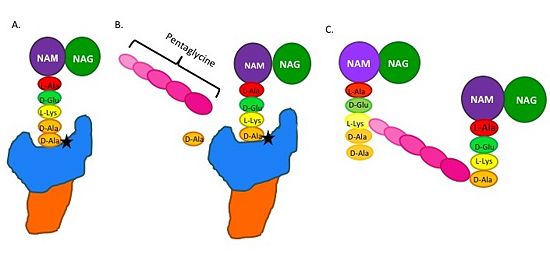
Figure 2.Schematic showing Catalytic Mechanism of PBP2a
Mechanism of Action of Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
The beta-lactam antibiotics irreversibly bind to and inhibit TPs. This results in the disruption of peptidoglycan synthesis and ultimately cell growth. Specifically, beta-lactams, such as penicillin and the anti-MRSA cephalosporins, ceftobiprole and ceftaroline, are molecular mimics of the peptidoglycan D-Ala-D-Ala moiety; the normal TP substrate (Figure 3; Tipper and Strominger, 1965). Therefore, they “trick” the TP active site serine residue to react with them, resulting in the irreversible inhibition of TP activity and of cell wall synthesis.
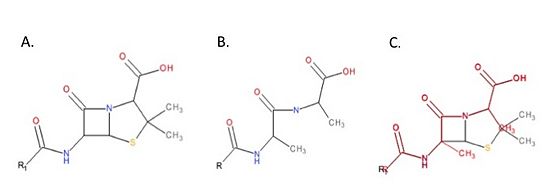
Figure 3. Mechanism of action of beta-lactams. A. Chemical structure of penicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic. B. Chemical structure of the peptidoglycan D-Ala-D-Ala moiety, the normal TP substrate. C. Superimposition of the D-Ala-D-Ala moiety (red) with penicillin (black). The beta-lactams mimic the structure of the D-Ala-D-Ala moiety of peptidoglycan. This ensures TPs react with beta-lactams.
MRSA, PBP2a, and anti-MRSA Cephalosporins
MRSA becomes resistant to beta-lactams by acquiring an alternative TP, PBP2a, that is encoded by the mecA gene (Matsuhashi et al., 1986). PBP2a is compromised in its ability to react with beta-lactam; therefore, MRSA strains are resistant to beta-lactams and are able to make their cell wall in the presence of high concentrations of beta-lactams.
Recently, two broad range cephalosporins: ceftaroline and ceftaroline (Figure), that have anti-MRSA activity because they bind and inhibit PBP2a have been developed.
PBP2a and Ceftobiprole
MRSA becomes resistant to β-lactams by acquiring an alternative PBP, PBP2a, that is neither bound nor inhibited by β-lactams. Ceftobiprole (PDB:) is able to inhibit PBP2a because additional chemical groups at the position of the cephalosporin backbone are able to interact with additional amino acid residues in PBP2a; specifically
. As a result of tighter binding to PBP2a, ceftobiprole is able to more efficiently react with the serine active site residue and therefore inhibit the activity of PBP2a.
PBP2a and Ceftaroline
Structure of PBP2a reveal that the active site is in a closed conformation (Lim et al.,2002). This makes it very difficult for beta-lactams to react with the active site serine residue (serine 403) and results in beta-lactam resistance. However, at some point the PBP2a active site must exist in an open conformation as it must cross-link adjacent peptidoglycan "sheets" to generate the cell wall and ensure bacterial survival.
The structure of the PBP2a/ceftaroline (PDB:) complex showed that binds two different sites on PBP2a: the TP active site (with ceftaroline to serine 403), as expected, and a site distant from the active site, the so-called "allosteric site" (with bound non-covalently), which was unexpected. Biochemical analysis revealed that select to the induced a conformational change in PBP2 that causes the normally closed PBP2a active site. In support of this, strains of S. aureus that are less inhibited by ceftaroline have mutations in the allosteric site.



