We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Renin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
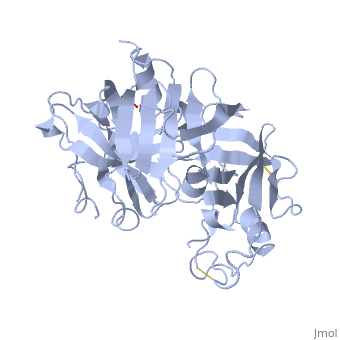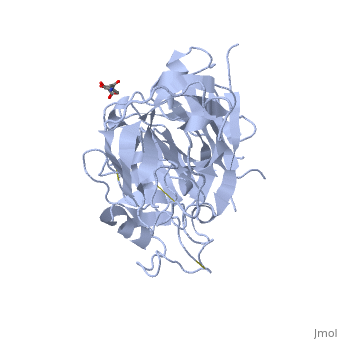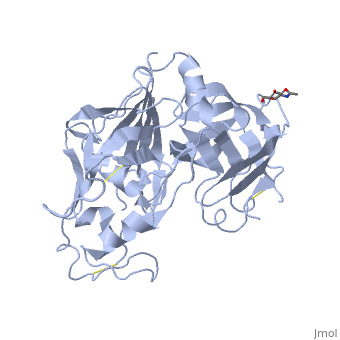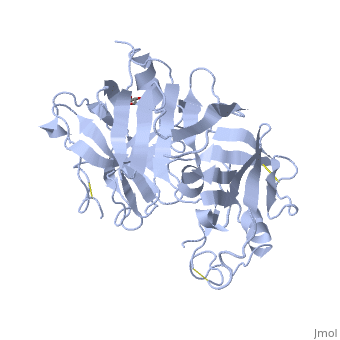
| - | <StructureSection load='2ren' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption=' | + | <StructureSection load='2ren' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption='Glycosylated human renin (PDB code [[2ren]])'> |
| - | + | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
'''Renin''', also known as angiotensinogenase, is an aspartyl protease and belongs to the protein family peptidase A1. Aspartyl proteases are endopeptidases that typically use two aspartate residues in the active site to specifically cleave peptide substrates using an acid-base hydrolysis mechanism. Mature renin circulates in the blood stream and contains 340 amino acid residues and has a mass of approximately 37 kDa. The function of renin is to cleave angiotensinogen to produce angiotensin I. | '''Renin''', also known as angiotensinogenase, is an aspartyl protease and belongs to the protein family peptidase A1. Aspartyl proteases are endopeptidases that typically use two aspartate residues in the active site to specifically cleave peptide substrates using an acid-base hydrolysis mechanism. Mature renin circulates in the blood stream and contains 340 amino acid residues and has a mass of approximately 37 kDa. The function of renin is to cleave angiotensinogen to produce angiotensin I. | ||
Revision as of 07:59, 20 August 2014
| |||||||||||
3D structures of renin
Updated on 20-August-2014
1bbs, 2ren – hRen – human
1rne – hRen + transition state analog inhibitor
1hrn, 1bil, 1bim, 2bks, 2bkt, 2fs4, 2g1n, 2g1o, 2g1r, 2g1s, 2g1y, 2g21, 2g22, 2g24, 2g26, 2g27, 2g20, 2i4q, 2iko, 2iku, 2il2, 2v0z, 2v10, 2v11, 3d91, 2v13, 2v16, 3gw5, 3g6z, 3g70, 3g72, 3km4, 3k1w, 3oqf, 3oot, 3oqk, 3oad, 3oag, 3own, 3o9l, 3q3t, 3sfc, 3q4b, 3q5h, 3vsw, 3vsx, 2v12, 3vuc, 3vyd, 3vye, 3vyf, 4gj5, 4gj6, 4gj7, 4gj8, 4gj9, 4gja, 4gjb, 4gjc, 4gjd - hRen + inhibitor
2x0b – hRen + angiotensinogen
1smr - Ren + peptide inhibitor – mouse
References
- ↑ Margrane M. and the UnitProt consortium, Uniprot Knowledgebase: a hub of integrated protein data, Database, 2012: bar009 (2011). Public Accession Number P00797
- ↑ Sielecki AR, Hayakawa K, Fujinaga M, Murphy ME, Fraser M, Muir AK, Carilli CT, Lewicki JA, Baxter JD, James MN. Structure of recombinant human renin, a target for cardiovascular-active drugs, at 2.5 A resolution. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1346-51. PMID:2493678
- ↑ Suguna K, Padlan EA, Smith CW, Carlson WD, Davies DR. Binding of a reduced peptide inhibitor to the aspartic proteinase from Rhizopus chinensis: implications for a mechanism of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7009-13. PMID:3313384
- ↑ Nguyen G, Delarue F, Burckle C, Bouzhir L, Giller T, Sraer JD. Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J Clin Invest. 2002 Jun;109(11):1417-27. PMID:12045255 doi:10.1172/JCI14276
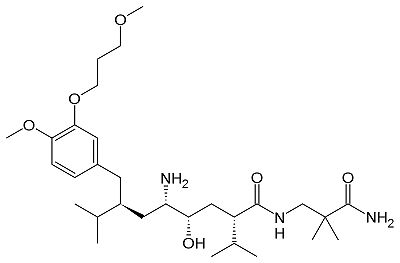
- ↑ Gradman AH, Schmieder RE, Lins RL, Nussberger J, Chiang Y, Bedigian MP. Aliskiren, a novel orally effective renin inhibitor, provides dose-dependent antihypertensive efficacy and placebo-like tolerability in hypertensive patients. Circulation. 2005 Mar 1;111(8):1012-8. Epub 2005 Feb 21. PMID:15723979 doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000156466.02908.ED
- ↑ Webb RL, Schiering N, Sedrani R, Maibaum J. Direct renin inhibitors as a new therapy for hypertension. J Med Chem. 2010 Nov 11;53(21):7490-520. PMID:20731374 doi:10.1021/jm901885s
- ↑ Politi A, Durdagi S, Moutevelis-Minakakis P, Kokotos G, Mavromoustakos T. Development of accurate binding affinity predictions of novel renin inhibitors through molecular docking studies. J Mol Graph Model. 2010 Nov;29(3):425-35. Epub 2010 Aug 27. PMID:20855222 doi:10.1016/j.jmgm.2010.08.003
- ↑ Wu Y, Shi C, Sun X, Wu X, Sun H. Synthesis, biological evaluation and docking studies of octane-carboxamide based renin inhibitors with extended segments toward S3' site of renin. Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Jul 15;19(14):4238-49. Epub 2011 Jun 1. PMID:21708467 doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2011.05.059
- ↑ Lowes, Robert. "Aliskiren in Certain Rx Combos Nixed for Diabetic Patients." Webscape Medical News. Web MD, 2012. 20 April 2012. <http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/762425>
- ↑ Rahuel J, Rasetti V, Maibaum J, Rueger H, Goschke R, Cohen NC, Stutz S, Cumin F, Fuhrer W, Wood JM, Grutter MG. Structure-based drug design: the discovery of novel nonpeptide orally active inhibitors of human renin. Chem Biol. 2000 Jul;7(7):493-504. PMID:10903938
- ↑ Keevil SF, Dolke G, Armstrong P, Smith MA. Calibration of a 0.08 Tesla magnetic resonance imager for in vivo T1 and T2 measurement. Br J Radiol. 1992 May;65(773):438-42. PMID:1611425
- ↑ Zivna M, Hulkova H, Matignon M, Hodanova K, Vylet'al P, Kalbacova M, Baresova V, Sikora J, Blazkova H, Zivny J, Ivanek R, Stranecky V, Sovova J, Claes K, Lerut E, Fryns JP, Hart PS, Hart TC, Adams JN, Pawtowski A, Clemessy M, Gasc JM, Gubler MC, Antignac C, Elleder M, Kapp K, Grimbert P, Bleyer AJ, Kmoch S. Dominant renin gene mutations associated with early-onset hyperuricemia, anemia, and chronic kidney failure. Am J Hum Genet. 2009 Aug;85(2):204-13. Epub 2009 Aug 6. PMID:19664745 doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.07.010