Potassium channel Xavier
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Important: This is a modified version of the original article on [[Potassium Channel]]. The purpose of this modification is simplifying the text and reversing the direction of potassium pumping. | Important: This is a modified version of the original article on [[Potassium Channel]]. The purpose of this modification is simplifying the text and reversing the direction of potassium pumping. | ||
| - | == | + | ==Structure and mechanism of the potassium channel== |
| + | ====Overview of structure==== | ||
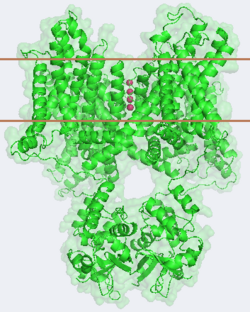
<StructureSection load='' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure of the Potassium Channel complex with K+ ions, ([[2r9r]])' scene='Potassium_Channel/Opening/1'> | <StructureSection load='' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure of the Potassium Channel complex with K+ ions, ([[2r9r]])' scene='Potassium_Channel/Opening/1'> | ||
[[Image:2r9r Picture Proteopedia2.png|250px|left]] [[Potassium Channel]]'''s''' control cell membrane electric potentials by selectively allowing diffusion of K<sup>+</sup> across the membrane.<ref name="Zhou">PMID: 11689936</ref> K<sup>+</sup> | [[Image:2r9r Picture Proteopedia2.png|250px|left]] [[Potassium Channel]]'''s''' control cell membrane electric potentials by selectively allowing diffusion of K<sup>+</sup> across the membrane.<ref name="Zhou">PMID: 11689936</ref> K<sup>+</sup> | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
the <scene name='Potassium_Channel/Pore_opening/5'>channel pore</scene>, composed of interwoven helices in a teepee conformation, the all-important <scene name='Potassium_Channel/Selectivity_filter_opening/2'>“selectivity filter”</scene>, providing the channel with its remarkable 10,00 fold selectivity for K<sup>+</sup> ions over Na<sup>+</sup> ions and the <scene name='Potassium_Channel/Voltage_sensors_opening/4'>“voltage sensor”</scene> which is uses well placed arginine and acidic residues to determine the membrane polarity and open/close the channel in response.<ref name="Long"/> | the <scene name='Potassium_Channel/Pore_opening/5'>channel pore</scene>, composed of interwoven helices in a teepee conformation, the all-important <scene name='Potassium_Channel/Selectivity_filter_opening/2'>“selectivity filter”</scene>, providing the channel with its remarkable 10,00 fold selectivity for K<sup>+</sup> ions over Na<sup>+</sup> ions and the <scene name='Potassium_Channel/Voltage_sensors_opening/4'>“voltage sensor”</scene> which is uses well placed arginine and acidic residues to determine the membrane polarity and open/close the channel in response.<ref name="Long"/> | ||
| + | ====Overall mechanism==== | ||
The main steps that potassium ions go trough when leaving the cell are: | The main steps that potassium ions go trough when leaving the cell are: | ||
| + | * Voltage sensor | ||
* Entering the hydrophobic pocket | * Entering the hydrophobic pocket | ||
* Desolvation | * Desolvation | ||
Revision as of 16:20, 13 September 2014
Important: This is a modified version of the original article on Potassium Channel. The purpose of this modification is simplifying the text and reversing the direction of potassium pumping.
Structure and mechanism of the potassium channel
Overview of structure
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Zhou Y, Morais-Cabral JH, Kaufman A, MacKinnon R. Chemistry of ion coordination and hydration revealed by a K+ channel-Fab complex at 2.0 A resolution. Nature. 2001 Nov 1;414(6859):43-8. PMID:11689936 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35102009
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedLong - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedDoyle