We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
1nfk
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m (Protected "1nfk" [edit=sysop:move=sysop]) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
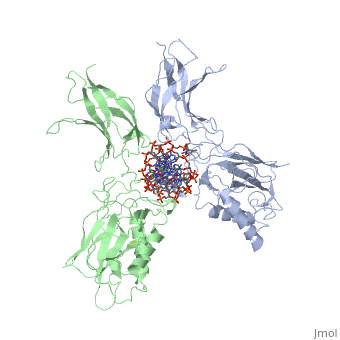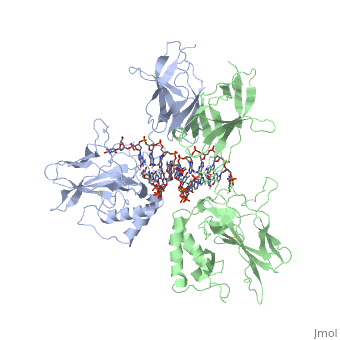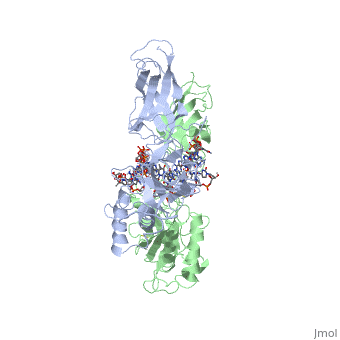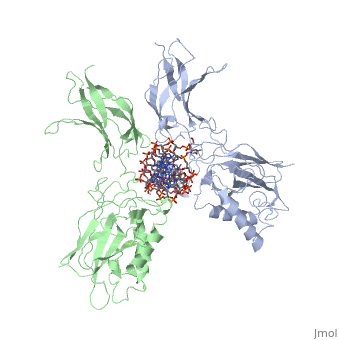
| - | [[ | + | ==STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEAR FACTOR KAPPA-B (NF-KB) P50 HOMODIMER== |
| + | <StructureSection load='1nfk' size='340' side='right' caption='[[1nfk]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> | ||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1nfk]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mus_musculus Mus musculus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1NFK OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1NFK FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
| + | </td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1nfk FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1nfk OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1nfk RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1nfk PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | ||
| + | <table> | ||
| + | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
| + | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| + | Check<jmol> | ||
| + | <jmolCheckbox> | ||
| + | <scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/nf/1nfk_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | ||
| + | <scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | ||
| + | <text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | ||
| + | </jmolCheckbox> | ||
| + | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/chain_selection.php?pdb_ID=2ata ConSurf]. | ||
| + | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
| + | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| + | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| + | The 2.3-A crystal structure of the transcription factor NK-kappa B p50 homodimer bound to a palindromic kappa B site reveals that the Rel homology region folds into two distinct domains, similar to those in the immunoglobulin superfamily. The p50 dimer envelopes an undistorted B-DNA helix, making specific contacts along the 10-base-pair kappa B recognition site mainly through loops connecting secondary structure elements in both domains. The carboxy-terminal domains form a dimerization interface between beta-sheets using residues that are strongly conserved in the Rel family. | ||
| - | + | Structure of NF-kappa B p50 homodimer bound to a kappa B site.,Ghosh G, van Duyne G, Ghosh S, Sigler PB Nature. 1995 Jan 26;373(6512):303-10. PMID:7530332<ref>PMID:7530332</ref> | |
| - | + | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |
| + | </div> | ||
| - | + | ==See Also== | |
| - | + | *[[NF-kB|NF-kB]] | |
| - | == | + | == References == |
| - | [[ | + | <references/> |
| - | + | __TOC__ | |
| - | == | + | </StructureSection> |
| - | < | + | |
[[Category: Mus musculus]] | [[Category: Mus musculus]] | ||
[[Category: Duyne, G Van.]] | [[Category: Duyne, G Van.]] | ||
Revision as of 16:46, 28 September 2014
STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEAR FACTOR KAPPA-B (NF-KB) P50 HOMODIMER
| |||||||||||