We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
1qki
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
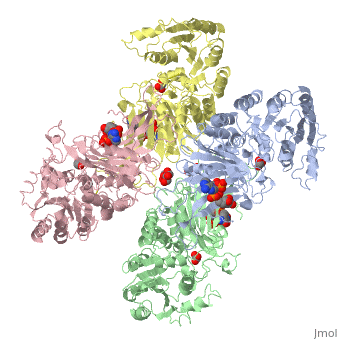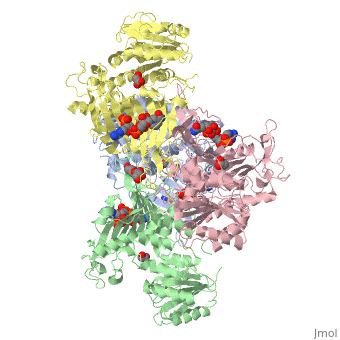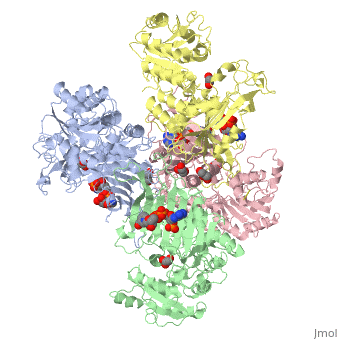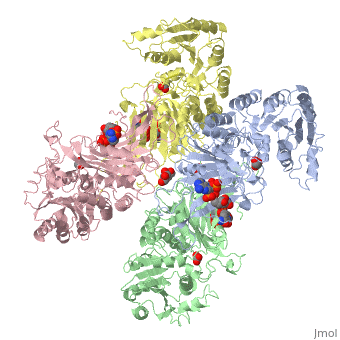
| - | + | ==X-RAY STRUCTURE OF HUMAN GLUCOSE 6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE (VARIANT CANTON R459L) COMPLEXED WITH STRUCTURAL NADP+== | |
| - | + | <StructureSection load='1qki' size='340' side='right' caption='[[1qki]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.00Å' scene=''> | |
| - | + | == Structural highlights == | |
| - | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1qki]] is a 8 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1QKI OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1QKI FirstGlance]. <br> | |
| - | ==Disease== | + | </td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=GOA:GLYCOLIC+ACID'>GOA</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=GOL:GLYCEROL'>GOL</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=NAP:NADP+NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE+PHOSPHATE'>NAP</scene><br> |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/G6PD_HUMAN G6PD_HUMAN]] Defects in G6PD are the cause of chronic non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia (CNSHA) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/305900 305900]]. Deficiency of G6PD is associated with hemolytic anemia in two different situations. First, in areas in which malaria has been endemic, G6PD-deficiency alleles have reached high frequencies (1% to 50%) and deficient individuals, though essentially asymptomatic in the steady state, have a high risk of acute hemolytic attacks. Secondly, sporadic cases of G6PD deficiency occur at a very low frequencies, and they usually present a more severe phenotype. Several types of CNSHA are recognized. Class-I variants are associated with severe NSHA; class-II have an activity <10% of normal; class-III have an activity of 10% to 60% of normal; class-IV have near normal activity.<ref>PMID:1611091</ref> | + | <tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1dpg|1dpg]], [[2dpg|2dpg]]</td></tr> |
| - | + | <tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">G6PD ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 Homo sapiens])</td></tr> | |
| - | ==Function== | + | <tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucose-6-phosphate_dehydrogenase Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=1.1.1.49 1.1.1.49] </span></td></tr> |
| + | <tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1qki FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1qki OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1qki RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1qki PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | ||
| + | <table> | ||
| + | == Disease == | ||
| + | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/G6PD_HUMAN G6PD_HUMAN]] Defects in G6PD are the cause of chronic non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia (CNSHA) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/305900 305900]]. Deficiency of G6PD is associated with hemolytic anemia in two different situations. First, in areas in which malaria has been endemic, G6PD-deficiency alleles have reached high frequencies (1% to 50%) and deficient individuals, though essentially asymptomatic in the steady state, have a high risk of acute hemolytic attacks. Secondly, sporadic cases of G6PD deficiency occur at a very low frequencies, and they usually present a more severe phenotype. Several types of CNSHA are recognized. Class-I variants are associated with severe NSHA; class-II have an activity <10% of normal; class-III have an activity of 10% to 60% of normal; class-IV have near normal activity.<ref>PMID:1611091</ref> | ||
| + | == Function == | ||
[[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/G6PD_HUMAN G6PD_HUMAN]] Produces pentose sugars for nucleic acid synthesis and main producer of NADPH reducing power. | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/G6PD_HUMAN G6PD_HUMAN]] Produces pentose sugars for nucleic acid synthesis and main producer of NADPH reducing power. | ||
| + | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
| + | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| + | Check<jmol> | ||
| + | <jmolCheckbox> | ||
| + | <scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/qk/1qki_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | ||
| + | <scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | ||
| + | <text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | ||
| + | </jmolCheckbox> | ||
| + | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/chain_selection.php?pdb_ID=2ata ConSurf]. | ||
| + | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
| + | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| + | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| + | BACKGROUND: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) catalyses the first committed step in the pentose phosphate pathway; the generation of NADPH by this enzyme is essential for protection against oxidative stress. The human enzyme is in a dimer<-->tetramer equilibrium and its stability is dependent on NADP(+) concentration. G6PD deficiency results from many different point mutations in the X-linked gene encoding G6PD and is the most common human enzymopathy. Severe deficiency causes chronic non-spherocytic haemolytic anaemia; the usual symptoms are neonatal jaundice, favism and haemolytic anaemia. RESULTS: We have determined the first crystal structure of a human G6PD (the mutant Canton, Arg459-->Leu) at 3 A resolution. The tetramer is a dimer of dimers. Despite very similar dimer topology, there are two major differences from G6PD of Leuconostoc mesenteroides: a structural NADP(+) molecule, close to the dimer interface but integral to the subunit, is visible in all subunits of the human enzyme; and an intrasubunit disulphide bond tethers the otherwise disordered N-terminal segment. The few dimer-dimer contacts making the tetramer are charge-charge interactions. CONCLUSIONS: The importance of NADP(+) for stability is explained by the structural NADP(+) site, which is not conserved in prokaryotes. The structure shows that point mutations causing severe deficiency predominate close to the structural NADP(+) and the dimer interface, primarily affecting the stability of the molecule. They also indicate that a stable dimer is essential to retain activity in vivo. As there is an absolute requirement for some G6PD activity, residues essential for coenzyme or substrate binding are rarely modified. | ||
| - | + | Human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: the crystal structure reveals a structural NADP(+) molecule and provides insights into enzyme deficiency.,Au SW, Gover S, Lam VM, Adams MJ Structure. 2000 Mar 15;8(3):293-303. PMID:10745013<ref>PMID:10745013</ref> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | == | + | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> |
| - | + | </div> | |
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase]] | [[Category: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase]] | ||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | ||
Revision as of 14:30, 29 September 2014
X-RAY STRUCTURE OF HUMAN GLUCOSE 6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE (VARIANT CANTON R459L) COMPLEXED WITH STRUCTURAL NADP+
| |||||||||||