1hjm
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:1hjm.jpg|left|200px]] | + | [[Image:1hjm.jpg|left|200px]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | '''HUMAN PRION PROTEIN AT PH 7.0''' | + | {{Structure |
| + | |PDB= 1hjm |SIZE=350|CAPTION= <scene name='initialview01'>1hjm</scene> | ||
| + | |SITE= | ||
| + | |LIGAND= | ||
| + | |ACTIVITY= | ||
| + | |GENE= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''HUMAN PRION PROTEIN AT PH 7.0''' | ||
| + | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| Line 10: | Line 19: | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 1HJM is a [ | + | 1HJM is a [[Single protein]] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1HJM OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| - | Influence of pH on NMR structure and stability of the human prion protein globular domain., Calzolai L, Zahn R, J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 12;278(37):35592-6. Epub 2003 Jun 25. PMID:[http:// | + | Influence of pH on NMR structure and stability of the human prion protein globular domain., Calzolai L, Zahn R, J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 12;278(37):35592-6. Epub 2003 Jun 25. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12826672 12826672] |
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | ||
[[Category: Single protein]] | [[Category: Single protein]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category: signal]] | [[Category: signal]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Mar 20 11:37:55 2008'' |
Revision as of 09:37, 20 March 2008
| |||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
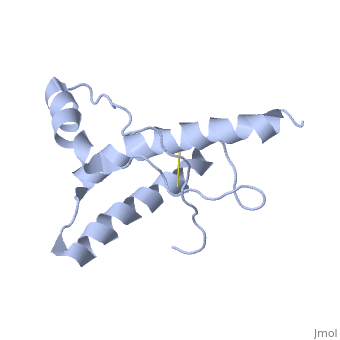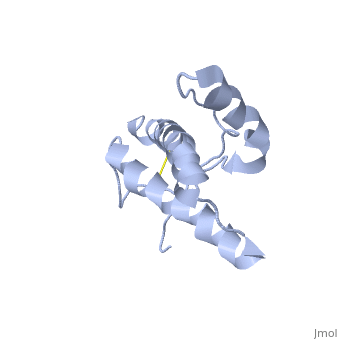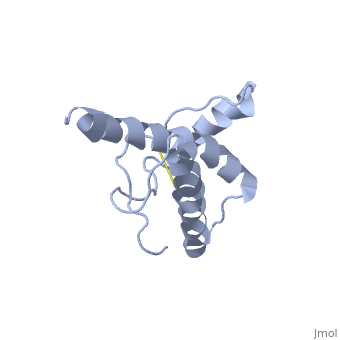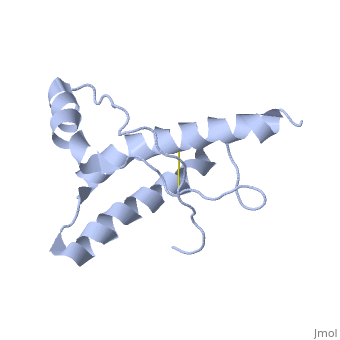
HUMAN PRION PROTEIN AT PH 7.0
Contents |
Overview
The NMR structure of the globular domain of the human prion protein (hPrP) with residues 121-230 at pH 7.0 shows the same global fold as the previously published structure determined at pH 4.5. It contains three alpha-helices, comprising residues 144-156, 174-194, and 200-228, and a short anti-parallel beta-sheet, comprising residues 128-131 and 161-164. There are slight, strictly localized, conformational changes at neutral pH when compared with acidic solution conditions: helix alpha1 is elongated at the C-terminal end with residues 153-156 forming a 310-helix, and the population of helical structure in the C-terminal two turns of helix alpha 2 is increased. The protonation of His155 and His187 presumably contributes to these structural changes. Thermal unfolding monitored by far UV CD indicates that hPrP-(121-230) is significantly more stable at neutral pH. Measurements of amide proton protection factors map local differences in protein stability within residues 154-157 at the C-terminal end of helix alpha 1 and residues 161-164 of beta-strand 2. These two segments appear to form a separate domain that at acidic pH has a larger tendency to unfold than the overall protein structure. This domain could provide a "starting point" for pH-induced unfolding and thus may be implicated in endosomic PrPC to PrPSc conformational transition resulting in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies.
Disease
Known diseases associated with this structure: Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease OMIM:[176640], Gerstmann-Straussler disease OMIM:[176640], Huntington disease-like 1 OMIM:[176640], Insomnia, fatal familial OMIM:[176640], Prion disease with protracted course OMIM:[176640], Retinitis pigmentosa-11 OMIM:[606419]
About this Structure
1HJM is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Influence of pH on NMR structure and stability of the human prion protein globular domain., Calzolai L, Zahn R, J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 12;278(37):35592-6. Epub 2003 Jun 25. PMID:12826672
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Mar 20 11:37:55 2008
Categories: Homo sapiens | Single protein | Calzolai, L. | Zahn, R. | Brain | Glycoprotein | Gpi-anchor | Prion | Repeat | Signal