This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
2iov
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[ | + | ==Bright-state structure of the reversibly switchable fluorescent protein Dronpa== |
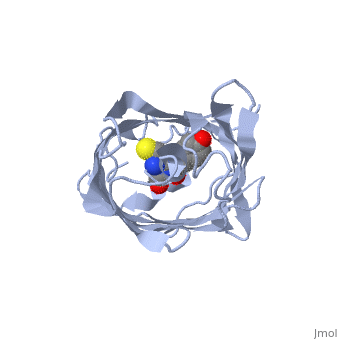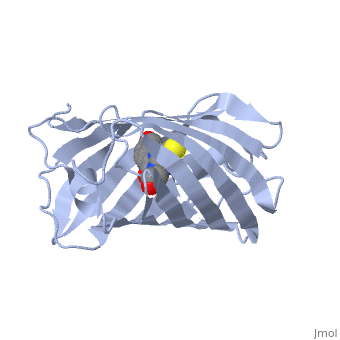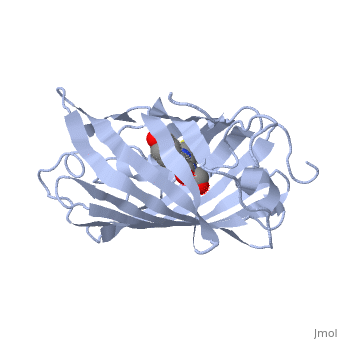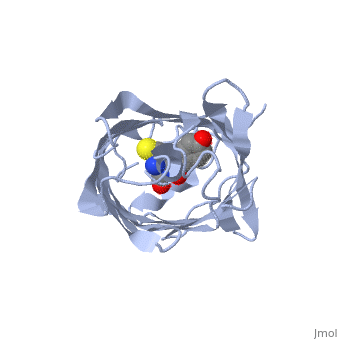
| + | <StructureSection load='2iov' size='340' side='right' caption='[[2iov]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.80Å' scene=''> | ||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2iov]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Echinophyllia_sp._sc22 Echinophyllia sp. sc22]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2IOV OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2IOV FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
| + | </td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Non-Standard_Residue|NonStd Res:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=GYC:[(4Z)-2-[(1R)-1-AMINO-2-MERCAPTOETHYL]-4-(4-HYDROXYBENZYLIDENE)-5-OXO-4,5-DIHYDRO-1H-IMIDAZOL-1-YL]ACETIC+ACID'>GYC</scene></td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">Dronpa ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=301887 Echinophyllia sp. SC22])</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2iov FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2iov OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2iov RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2iov PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | ||
| + | <table> | ||
| + | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
| + | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| + | Check<jmol> | ||
| + | <jmolCheckbox> | ||
| + | <scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/io/2iov_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | ||
| + | <scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | ||
| + | <text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | ||
| + | </jmolCheckbox> | ||
| + | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/chain_selection.php?pdb_ID=2ata ConSurf]. | ||
| + | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
| + | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| + | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| + | RSFPs (reversibly switchable fluorescent proteins) may be repeatedly converted between a fluorescent and a non-fluorescent state by irradiation and have attracted widespread interest for many new applications. The RSFP Dronpa may be switched with blue light from a fluorescent state into a non-fluorescent state, and back again with UV light. To obtain insight into the underlying molecular mechanism of this switching, we have determined the crystal structure of the fluorescent equilibrium state of Dronpa. Its bicyclic chromophore is formed spontaneously from the Cys62-Tyr63-Gly64 tripeptide. In the fluorescent state, it adopts a slightly non-coplanar cis conformation within the interior of a typical GFP (green fluorescent protein) b-can fold. Dronpa shares some structural features with asFP595, another RSFP whose chromophore has previously been demonstrated to undergo a cis-trans isomerization upon photoswitching. Based on the structural comparison with asFP595, we have generated new Dronpa variants with an up to more than 1000-fold accelerated switching behaviour. The mutations which were introduced at position Val157 or Met159 apparently reduce the steric hindrance for a cis-trans isomerization of the chromophore, thus lowering the energy barrier for the blue light-driven on-to-off transition. The findings reported in the present study support the view that a cis-trans isomerization is one of the key events common to the switching mechanism in RSFPs. | ||
| - | + | 1.8 A bright-state structure of the reversibly switchable fluorescent protein Dronpa guides the generation of fast switching variants.,Stiel AC, Trowitzsch S, Weber G, Andresen M, Eggeling C, Hell SW, Jakobs S, Wahl MC Biochem J. 2007 Feb 15;402(1):35-42. PMID:17117927<ref>PMID:17117927</ref> | |
| - | + | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |
| - | + | </div> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| - | *[[Alyssa Marsico/Sandbox 1|Alyssa Marsico/Sandbox 1]] | ||
| - | *[[Devon McCarthy/Sandbox 1|Devon McCarthy/Sandbox 1]] | ||
*[[Dronpa|Dronpa]] | *[[Dronpa|Dronpa]] | ||
*[[Green Fluorescent Protein|Green Fluorescent Protein]] | *[[Green Fluorescent Protein|Green Fluorescent Protein]] | ||
| - | + | == References == | |
| - | + | <references/> | |
| - | + | __TOC__ | |
| - | == | + | </StructureSection> |
| - | < | + | |
[[Category: Echinophyllia sp. sc22]] | [[Category: Echinophyllia sp. sc22]] | ||
[[Category: Andresen, M.]] | [[Category: Andresen, M.]] | ||
Revision as of 05:33, 3 October 2014
Bright-state structure of the reversibly switchable fluorescent protein Dronpa
| |||||||||||