This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
RuBisCO
From Proteopedia
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
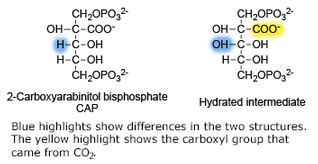
<scene name='46/463261/8ruc_active-site/10'>Residues that are involved in catalysis</scene> are shown shown here in CPK ball & stick. Asp 203 and Glu 204 bind to and position the magnesium ion. The carbamylated lysine residue KCX 201 coordinates Mg<sup>2+</sup> and initiates catalysis by extracting a proton from C3 of RUBP. Note the proximity of the carbamyl group to carbon 3 in this structure. His 294 acts as a catalytic base in the carboxylation step of the mechanism and accepts a proton from the hydroxyl of carbon 3. Mg<sup>2+</sup> is coordinated by six ligands. In addition to oxygen atoms in the three residues already mentioned, the ion binds to two oxygen atoms of RUBP. The 6th ligand is either water or in the carboxylation step it binds the incoming CO<sub>2</sub>. In the structure shown, Mg<sup>2+</sup> is bound to the carboxyl group in CAP that corresponds to the fixed CO<sub>2</sub> in the hydrated intermediate.</StructureSection> | <scene name='46/463261/8ruc_active-site/10'>Residues that are involved in catalysis</scene> are shown shown here in CPK ball & stick. Asp 203 and Glu 204 bind to and position the magnesium ion. The carbamylated lysine residue KCX 201 coordinates Mg<sup>2+</sup> and initiates catalysis by extracting a proton from C3 of RUBP. Note the proximity of the carbamyl group to carbon 3 in this structure. His 294 acts as a catalytic base in the carboxylation step of the mechanism and accepts a proton from the hydroxyl of carbon 3. Mg<sup>2+</sup> is coordinated by six ligands. In addition to oxygen atoms in the three residues already mentioned, the ion binds to two oxygen atoms of RUBP. The 6th ligand is either water or in the carboxylation step it binds the incoming CO<sub>2</sub>. In the structure shown, Mg<sup>2+</sup> is bound to the carboxyl group in CAP that corresponds to the fixed CO<sub>2</sub> in the hydrated intermediate.</StructureSection> | ||
| - | == 3D Structures of RuBisCO == | ||
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | + | ==3D structures of RuBisCO (Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}}) == |
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | + | * RuBisCO | |
| - | [[3rg6]], [[1rbl]] – SeRBCO – ''Synechococcus elongatus''<br /> | + | ** [[3rg6]], [[1rbl]] – SeRBCO – ''Synechococcus elongatus''<br /> |
| - | [[2ybv]] - RBCO – ''Thermosynechococcus elongatus''<br /> | + | ** [[2ybv]] - RBCO – ''Thermosynechococcus elongatus''<br /> |
| - | [[3qfw]] - RBCO large subunit – ''Rhodopseudomonas palustris''<br /> | + | ** [[3qfw]] - RBCO large subunit – ''Rhodopseudomonas palustris''<br /> |
| - | [[1uzh]], [[1gk8]] – CrRBCO – ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii''<br /> | + | ** [[1uzh]], [[1gk8]] – CrRBCO – ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii''<br /> |
| - | [[1uw9]], [[1uwa]] – CrRBCO (mutant) <br /> | + | ** [[1uw9]], [[1uwa]] – CrRBCO (mutant) <br /> |
| - | [[1svd]] – RBCD – ''Halothiobacillus neapolitanus''<br /> | + | ** [[1svd]] – RBCD – ''Halothiobacillus neapolitanus''<br /> |
| - | [[1bxn]] – RBCO – ''Cupriavidus necator''<br /> | + | ** [[1bxn]] – RBCO – ''Cupriavidus necator''<br /> |
| - | [[1aus]] - spRBCO – spinach<br /> | + | ** [[1aus]] - spRBCO – spinach<br /> |
| - | [[1rba]] - RrRBCO (mutant) – ''Rhododpirillum rubrum''<br /> | + | ** [[1rba]] - RrRBCO (mutant) – ''Rhododpirillum rubrum''<br /> |
| - | [[5rub]] - RrRBCO<br /> | + | ** [[5rub]] - RrRBCO<br /> |
| - | [[2wvw]] – RBCO – ''Anabena'' – Cryo EM<br /> | + | ** [[2wvw]] – RBCO – ''Anabena'' – Cryo EM<br /> |
| - | [[2vdh]], [[2vdi]], [[2v67]], [[2v68]], [[2v63]], [[2v69]], [[2v6a]] - CrRBCO (mutant) <br /> | + | ** [[2vdh]], [[2vdi]], [[2v67]], [[2v68]], [[2v63]], [[2v69]], [[2v6a]] - CrRBCO (mutant) <br /> |
| - | [[1mlv]] - pRBCO LSMT – pea<br /> | + | ** [[1mlv]] - pRBCO LSMT – pea<br /> |
| - | [[2cxe]], [[2cwx]] – PhRBCO - ''Pyrococcus horikoshii''<br /> | + | ** [[2cxe]], [[2cwx]] – PhRBCO - ''Pyrococcus horikoshii''<br /> |
| - | [[1uzd]] – CrRBCO/spRBCO <br /> | + | ** [[1uzd]] – CrRBCO/spRBCO <br /> |
| - | [[1geh]] – TkRBCO – ''Thermococcus kodakaraensis''<br /> | + | ** [[1geh]] – TkRBCO – ''Thermococcus kodakaraensis''<br /> |
| - | [[1iwa]] - GpRBCO – ''Galdieria partita''<br /> | + | ** [[1iwa]] - GpRBCO – ''Galdieria partita''<br /> |
| - | [[1tel]] – RBCO large subunit – ''Chlorobium tepidum''<br /> | + | ** [[1tel]] – RBCO large subunit – ''Chlorobium tepidum''<br /> |
| - | [[1rld]], [[3rub]], [[3t15]], [[3zw6]], [[4rub]] – tRBCO – tobacco<br /> | + | ** [[1rld]], [[3rub]], [[3t15]], [[3zw6]], [[4rub]] – tRBCO – tobacco<br /> |
| - | [[3thg]] – RBCO – creosote bush<br /> | + | ** [[3thg]] – RBCO – creosote bush<br /> |
| - | [[4hhh]] – RBCO - pea | + | ** [[4hhh]] – RBCO - pea |
| - | + | * RuBisCO complex with inhibitor 2-CABP | |
| - | [[3kdn]], [[3a12]] – TkRBCO III + 2-CABP <br /> | + | ** [[3kdn]], [[3a12]] – TkRBCO III + 2-CABP <br /> |
| - | [[3kdo]], [[3a13]] - TkRBCO III (mutant) + 2-CABP<br /> | + | ** [[3kdo]], [[3a13]] - TkRBCO III (mutant) + 2-CABP<br /> |
| - | [[1ir2]] - CrRBCO + 2-CABP <br /> | + | ** [[1ir2]] - CrRBCO + 2-CABP <br /> |
| - | [[1upm]], [[1upp]], [[1rbo]], [[3ruc]], [[8ruc]] - spRBCO + 2-CABP + cation<br /> | + | ** [[1upm]], [[1upp]], [[1rbo]], [[3ruc]], [[8ruc]] - spRBCO + 2-CABP + cation<br /> |
| - | [[1ir1]] - spRBCO + 2-CABP + CO2 + Mg<br /> | + | ** [[1ir1]] - spRBCO + 2-CABP + CO2 + Mg<br /> |
| - | [[1wdd]] – rRBCO + 2-CABP – rice<br /> | + | ** [[1wdd]] – rRBCO + 2-CABP – rice<br /> |
| - | [[1bwv]] - GpRBCO + 2-CABP <br /> | + | ** [[1bwv]] - GpRBCO + 2-CABP <br /> |
| - | [[1rlc]] - tRBCO + 2-CABP | + | ** [[1rlc]] - tRBCO + 2-CABP |
| - | + | * RuBisCO complex with product | |
| - | [[1aa1]] – spRBCO + phosphoglycerate<br /> | + | ** [[1aa1]] – spRBCO + phosphoglycerate<br /> |
| - | [[1rus]] - RrRBCO + phosphoglycerate<br /> | + | ** [[1rus]] - RrRBCO + phosphoglycerate<br /> |
| - | + | * RuBisCO complex with substrate | |
[[1rcx]], [[1rxo]] – spRBCO + ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate<br /> | [[1rcx]], [[1rxo]] – spRBCO + ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate<br /> | ||
Revision as of 17:17, 2 November 2014
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase – RuBisCO (RBCO) catalyzes the first step in photosynthetic carbon fixation, and it is the most abundant protein on earth. RBCO can either carboxylate or oxygenate ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RUBP) with CO2 or O2, respectively. RBCO from flowering plants consists of eight large subunits and eight small subunits.
Contents |
Structural Features
| |||||||||||
3D structures of RuBisCO (Updated on 02-November-2014)
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0|
- RuBisCO
- 3rg6, 1rbl – SeRBCO – Synechococcus elongatus
- 2ybv - RBCO – Thermosynechococcus elongatus
- 3qfw - RBCO large subunit – Rhodopseudomonas palustris
- 1uzh, 1gk8 – CrRBCO – Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- 1uw9, 1uwa – CrRBCO (mutant)
- 1svd – RBCD – Halothiobacillus neapolitanus
- 1bxn – RBCO – Cupriavidus necator
- 1aus - spRBCO – spinach
- 1rba - RrRBCO (mutant) – Rhododpirillum rubrum
- 5rub - RrRBCO
- 2wvw – RBCO – Anabena – Cryo EM
- 2vdh, 2vdi, 2v67, 2v68, 2v63, 2v69, 2v6a - CrRBCO (mutant)
- 1mlv - pRBCO LSMT – pea
- 2cxe, 2cwx – PhRBCO - Pyrococcus horikoshii
- 1uzd – CrRBCO/spRBCO
- 1geh – TkRBCO – Thermococcus kodakaraensis
- 1iwa - GpRBCO – Galdieria partita
- 1tel – RBCO large subunit – Chlorobium tepidum
- 1rld, 3rub, 3t15, 3zw6, 4rub – tRBCO – tobacco
- 3thg – RBCO – creosote bush
- 4hhh – RBCO - pea
- 3rg6, 1rbl – SeRBCO – Synechococcus elongatus
- RuBisCO complex with inhibitor 2-CABP
- RuBisCO complex with product
- RuBisCO complex with substrate
1rcx, 1rxo – spRBCO + ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate
9rub - RrRBCO + ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate
4mkv - pRBCO + ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate
1rsc - SeRBCO + xylulose-1,5-bisphosphate
1rco - spRBCO + xylulose-diol-1,5-bisphosphate
3zxw - SeRBCO + carboxyarabinitol-1,5-bisphosphate
RuBisCO other complexes
2h21 – pRBCO LSMT + AdoMet
2h23 - pRBCO LSMT + AdoHcy
2h2e, 1ozv, 1p0y - pRBCO LSMT + AdoMet + lysine
2h2j - pRBCO LSMT + sinefungin
2d69 – PhRBCO + sulfate
2rus - RrRBCO + CO2 + Mg
4f0h – GsRBCO + O2 – Galdieria sulphuraria
4f0k - GsRBCO + CO2 + Mg
4f0m - GsRBCO + Mg
1ej7 – tRBCO + phosphate
3axk – rRBCO + NADP
3axm – rRBCO + 6PG
See Also
Some additional details can be found in Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase.
References
- ↑ Andersson I. Large structures at high resolution: the 1.6 A crystal structure of spinach ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase complexed with 2-carboxyarabinitol bisphosphate. J Mol Biol. 1996 May 31;259(1):160-74. PMID:8648644 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0310
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alice Harmon, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky