We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Raghad zoubi
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
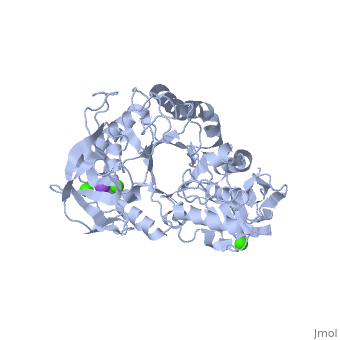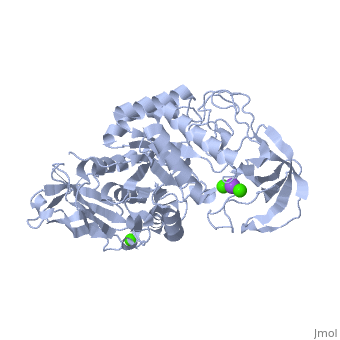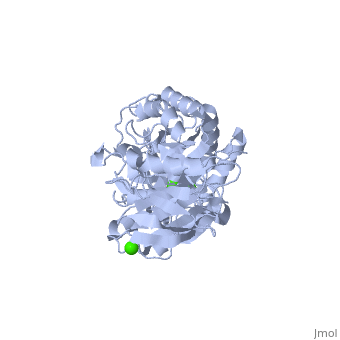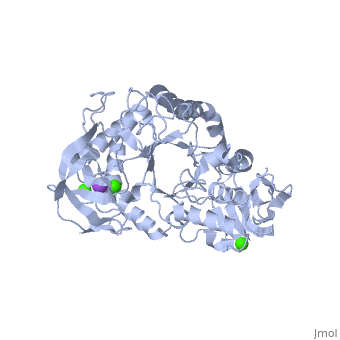
==Example page for α-Ameylase== | ==Example page for α-Ameylase== | ||
<StructureSection load='1hvx' size='340' side='right' caption='α-Ameylase' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1hvx' size='340' side='right' caption='α-Ameylase' scene=''> | ||
| - | |||
α-Amylase is a protein enzyme EC 3.2.1.1 that hydrolyses alpha bonds of large, alpha-linked polysaccharides, such as starch and glycogen, yielding glucose and maltose. It is the major form of amylase found in humans and other mammals.It is also present in seeds containing starch as a food reserve, and is secreted by many fungi. <ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-amylase]</ref> | α-Amylase is a protein enzyme EC 3.2.1.1 that hydrolyses alpha bonds of large, alpha-linked polysaccharides, such as starch and glycogen, yielding glucose and maltose. It is the major form of amylase found in humans and other mammals.It is also present in seeds containing starch as a food reserve, and is secreted by many fungi. <ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-amylase]</ref> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Revision as of 16:12, 22 November 2014
Example page for α-Ameylase
| |||||||||||