Hexokinase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
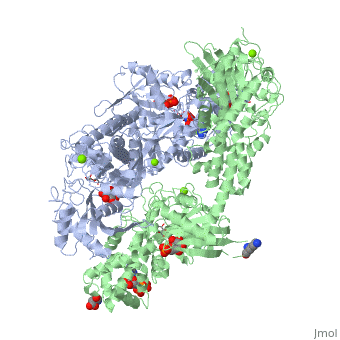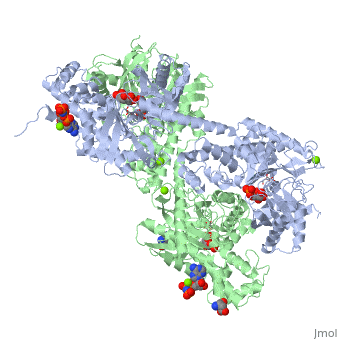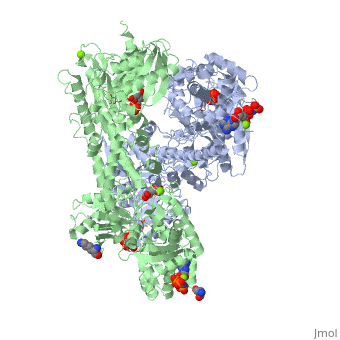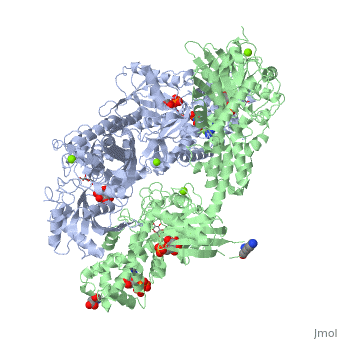
<StructureSection load='1qha' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption='Hexokinase I complex with ATP analog, glucose, glucose-phosphate and Mg+2 ion (PDB code [[1qha]])'> | <StructureSection load='1qha' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption='Hexokinase I complex with ATP analog, glucose, glucose-phosphate and Mg+2 ion (PDB code [[1qha]])'> | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
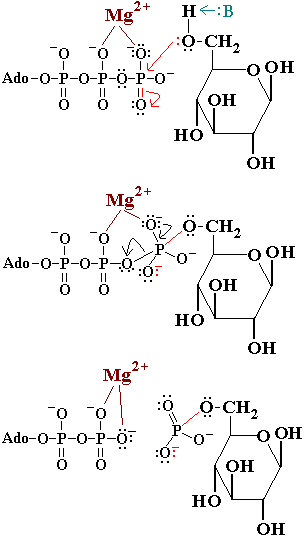
'''Hexokinase''' is an enzyme that phosphorylates a six-carbon sugar, a hexose, to a hexose phosphate. In most tissues and organisms, glucose is the most important substrate of hexokinases, and glucose 6-phosphate the most important product. Hexokinases have been found in every organism checked, ranging from bacteria, yeast, and plants, to humans and other vertebrates. They are categorized as actin fold proteins, sharing a common ATP binding site core surrounded by more variable sequences that determine substrate affinities and other properties. Several hexokinase isoforms or isozymes providing different functions can occur in a single species. | '''Hexokinase''' is an enzyme that phosphorylates a six-carbon sugar, a hexose, to a hexose phosphate. In most tissues and organisms, glucose is the most important substrate of hexokinases, and glucose 6-phosphate the most important product. Hexokinases have been found in every organism checked, ranging from bacteria, yeast, and plants, to humans and other vertebrates. They are categorized as actin fold proteins, sharing a common ATP binding site core surrounded by more variable sequences that determine substrate affinities and other properties. Several hexokinase isoforms or isozymes providing different functions can occur in a single species. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 32: | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | + | *Hexokinase | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | **[[3o08]], [[3o1b]], [[3o1w]], [[3o4w]], [[3o6w]], [[3o80]], [[4jax]] – KlHK – ''Kluyveromyces lactis''<br /> | |
| + | **[[2e2n]] – StHK – ''Sulfolobus tokodaii''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2e2o]] - StHK + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2e2p]] – StHK + ADP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2e2q]] - StHK + ADP + xylose + Mg<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3o5b]], [[3o8m]] – KlHK + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1bdg]] – HK + glucose – ''Schistosoma mansoni'' | ||
| - | + | *Hexokinase I | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | **[[3b8a]] – yHK I + glucose – yeast<br /> | |
| + | **[[1hkg]] – yHK I<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1dgk]] – hHK I (mutant) + ADP + glucose – human<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1cza]] - hHK I (mutant) + ADP + glucose-6-phosphate + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1bg3]] - HK I + glucose-6-phosphate + glucose - rat<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1qha]] – hHK I + AMP-PNP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1hkc]] - hHK I + phosphate + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1hkb]], [[4f9o]] - hHK I + glucose-6-phosphate + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4fpa]] - hHK I (mutant) + glucose-6-phosphate + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4foe]] - hHK I + mannose-6-phosphate + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4foi]] - hHK I (mutant) + glucose 1,6-bisphosphate + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4fpb]] - hHK I + 1,5-anhydroglucitol-6-phosphate + glucose<br /> | ||
| - | + | *Hexokinase II | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | **[[1ig8]], [[2yhx]] – yHK II<br /> | |
| + | **[[2nzt]] – hHK II | ||
| - | + | *Hexokinase III | |
| - | + | **[[3hm8]] – hHK III C terminal | |
| - | + | *Hexokinase IV (Glucokinase GK) | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | '' | + | **[[3qic]] – hHK IV residues 12-465 (mutant) <br /> |
| + | **[[1v4t]] – hGK <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3mcp]] – GK – ''Parabacterioides distasonis''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2qm1]] – GK – ''Enterococcus faecalis''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3vgk]] – SgGK – ''Streptomyces griseus''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1q18]] – EcGK – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4eun]] – GK – ''Janibacter''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3vov]] – GK – ''Thermus thermophilus'' | ||
| - | + | *''Hexokinase IV binary complex'' | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | **[[1sz2]] - EcGK + glucose<br /> | |
| + | **[[3vgm]] - SgGK + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3idh]] - hHK IV residues 12-465 + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3h1v]], [[3imx]], [[3a0i]], [[3goi]],[[1v4s]], [[3s41]], [[3vev]], [[3vf6]], [[4dch]], [[4dhy]] - hHK IV residues 12-465 + synthetic activator<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3fr0]], [[4l3q]], [[4ise]], [[4isf]], [[4isg]], [[4iwv]], [[4ixc]], [[4mlh]], [[4mle]] - hHK IV residues 12-465 + activator<br /> | ||
| - | + | *''Hexokinase IV ternary complex'' | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | **[[3id8]], [[3fgu]] - hHK IV residues 12-465 + AMP-PNP + glucose<br /> | |
| + | **[[3f9m]], [[4l3q]] - hHK IV residues 12-465 + activator + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2q2r]] - GK + glucose + ADP – ''Trypanosoma cruzi''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3vgl]] - SgGK + glucose + AMP-PNP<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3vey]] - hGK + glucose + ATPgS<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4lc9]], [[3w0l]] – rGK + fructose-6-phosphate + GK regulator<br /> | ||
| - | + | *ADP-dependent GK | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | **[[4b8r]] – TlAGK – ''Thermococcus litoralis''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1gc5]] – TlAGK + ADP <br /> | ||
| + | **[[4b8s]] – TlAGK + AMP <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1l2l]] – AGK – ''Pyrococcus horikoshii''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1ua4]] - AGK – ''Pyrococcus furiosus'' | ||
| + | }} | ||
==Additional Resources== | ==Additional Resources== | ||
For additional information, see: [[Carbohydrate Metabolism]] | For additional information, see: [[Carbohydrate Metabolism]] | ||
Revision as of 09:35, 27 November 2014
| |||||||||||
3D structures of hexokinase
Updated on 27-November-2014
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
References
1.↑ Pollard-Knight D, Cornish-Bowden A. Mechanism of liver glucokinase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Apr 30;44(2):71-80. PMID:7048063
2.↑ 2.0 2.1 Kamata K, Mitsuya M, Nishimura T, Eiki J, Nagata Y. Structural basis for allosteric regulation of the monomeric allosteric enzyme human glucokinase. Structure. 2004 Mar;12(3):429-38. PMID:15016359 doi:10.1016/j.str.2004.02.005
3.↑ Postic C, Shiota M, Magnuson MA. Cell-specific roles of glucokinase in glucose homeostasis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001;56:195-217. PMID:11237213
4.↑ Zeng C, Aleshin A, Hardie J, Harrison R, Fromm H. ATP-Binding site of Human Brain Hexokinase as Studied by Molecular Modeling and Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Biochem. 1996 Aug 6;35:13157-13164.
5.↑ hammes G, and Kochavi D. Studies of the Enzyme Hexokinase: Kinetic Inhibition by Products. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 1961 Oct 5.
6.↑ Ralph E, Thomson J, Almaden J, Sun S. Glucose Modulation fo Glucokinase Activation by Small Molecules. Biochem. 2008 Feb 15;47:5028-5036.
7.↑ Pal P, and Miller B. Activating Mutations in the Human Glucokinase Gene Revealed by Genetic Selection. Biochem. 2008 Dec 3;48:814-816.
8.↑ Aleshin A, Malfois M, Liu X, Kim C, Fromm H, Honzatko R, Koch M, Svergun D. Nonaggregating Mutant of Recombinant Human Hexokinase I Exhibits Wild-Type Kinetics and Rod-like Conformations in Solution. Biochem. 1999 Apr 29;38:8359-8366.
Seth Bawel and Kyle_Schroering created this page in Che 361 at Wabash College.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Karsten Theis, Ann Taylor, Alexander Berchansky