Myosin
From Proteopedia
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | + | * Myosin I | |
| - | [[1lkx]] – DdMI HC - ''Dictyostelium discoideum''<br /> | + | **[[1lkx]] – DdMI HC - ''Dictyostelium discoideum''<br /> |
| - | [[4a7f]] - DdMI HC + rActin + rTropomyosin – rabbit – Cryo EM<br /> | + | **[[4a7f]] - DdMI HC + rActin + rTropomyosin – rabbit – Cryo EM<br /> |
| - | [[4a7h]], [[4a7l]] - DdMI HC (mutant) + rActin + rTropomyosin – Cryo EM<br /> | + | **[[4a7h]], [[4a7l]] - DdMI HC (mutant) + rActin + rTropomyosin – Cryo EM<br /> |
| - | [[2drk]], [[2drm]] – MI HC + 10-mer peptide – ''Acanthamoeba castellanii''<br /> | + | **[[2drk]], [[2drm]] – MI HC + 10-mer peptide – ''Acanthamoeba castellanii''<br /> |
| - | [[2xmf]] – mMI SH3 domain - mouse<br /> | + | **[[2xmf]] – mMI SH3 domain - mouse<br /> |
| - | [[4byf]] – hMIC + calmodulin – human<br /> | + | **[[4byf]] – hMIC + calmodulin – human<br /> |
| - | + | * Myosin II | |
| - | [[1o1g]], [[1o1a]] , [[1o1b]], [[1o1c]], [[1o1d]], [[1o1e]], [[1o1f]], [[1o18]], [[1o19]], [[1mvw]], [[1m8q]] – cMII RLC+ELC+HC+actin – tomography - chicken<br /> | + | **[[1o1g]], [[1o1a]] , [[1o1b]], [[1o1c]], [[1o1d]], [[1o1e]], [[1o1f]], [[1o18]], [[1o19]], [[1mvw]], [[1m8q]] – cMII RLC+ELC+HC+actin – tomography - chicken<br /> |
| - | [[3lla]] – cMII HC α-kinase domain+AMPPCP<br /> | + | **[[3lla]] – cMII HC α-kinase domain+AMPPCP<br /> |
| - | [[3lmh]] – cMII HC α-kinase domain+ADP<br /> | + | **[[3lmh]] – cMII HC α-kinase domain+ADP<br /> |
| - | [[3lmi]] – cMII HC α-kinase domain (mutant) +ATP<br /> | + | **[[3lmi]] – cMII HC α-kinase domain (mutant) +ATP<br /> |
| - | [[2fxm]], [[2fxo]] – hMII HC S2 fragment <br /> | + | **[[2fxm]], [[2fxo]] – hMII HC S2 fragment <br /> |
| - | [[2lnk]] – hMII HC + protein S100-A4 – NMR<br /> | + | **[[2lnk]] – hMII HC + protein S100-A4 – NMR<br /> |
| - | [[3zwh]] - hMII HC + protein S100-A4 (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[3zwh]] - hMII HC + protein S100-A4 (mutant)<br /> |
| - | [[3i5f]] – LpMII RLC+HC+ADP+Mg – ''Loligo pealei''<br /> | + | **[[3i5f]] – LpMII RLC+HC+ADP+Mg – ''Loligo pealei''<br /> |
| - | [[3i5g]], [[3i5h]] – LpMII RLC+HC+ELC<br /> | + | **[[3i5g]], [[3i5h]] – LpMII RLC+HC+ELC<br /> |
| - | [[3i5i]] – LpMII RLC+HC+ELC+SO4<br /> | + | **[[3i5i]] – LpMII RLC+HC+ELC+SO4<br /> |
| - | [[2jhr]] – DdMII HC+ADP-VO4+pentabromopseudilin<br /> | + | **[[2jhr]] – DdMII HC+ADP-VO4+pentabromopseudilin<br /> |
| - | [[2xo8]] - DdMII HC MD +pseudilin derivative<br /> | + | **[[2xo8]] - DdMII HC MD +pseudilin derivative<br /> |
| - | [[2y0r]], [[2y8i]], [[2y9e]], [[3myk]] - DdMII HC MD (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[2y0r]], [[2y8i]], [[2y9e]], [[3myk]] - DdMII HC MD (mutant)<br /> |
| - | [[3bz7]], [[3bz9]], [[1yv3]], [[3bz8]] - DdMII HC+blebbistatin<br /> | + | **[[3bz7]], [[3bz9]], [[1yv3]], [[3bz8]] - DdMII HC+blebbistatin<br /> |
| - | [[3mjx]] - DdMII HC+blebbistatin + ADP-VO4<br /> | + | **[[3mjx]] - DdMII HC+blebbistatin + ADP-VO4<br /> |
| - | [[3mnq]] - DdMII HC MD + ADP-VO4 + reservatrol<br /> | + | **[[3mnq]] - DdMII HC MD + ADP-VO4 + reservatrol<br /> |
| - | [[3bas]], [[3bat]], [[1fmv]] - DdMII HC<br /> | + | **[[3bas]], [[3bat]], [[1fmv]] - DdMII HC<br /> |
| - | [[1fmw]] – DdMII HC+ATP<br /> | + | **[[1fmw]] – DdMII HC+ATP<br /> |
| - | [[1jwy]], [[1jx2]] – DdMII HC+dynamin-1<br /> | + | **[[1jwy]], [[1jx2]] – DdMII HC+dynamin-1<br /> |
| - | [[1d0x]], [[1d0y]], [[1d0z]], [[1d1a]], [[1d1b]], [[1d1c]] – DdMII HC (mutant)+BeF3 derivative<br /> | + | **[[1d0x]], [[1d0y]], [[1d0z]], [[1d1a]], [[1d1b]], [[1d1c]] – DdMII HC (mutant)+BeF3 derivative<br /> |
| - | [[1g8x]] – DdMII+actinin 3<br /> | + | **[[1g8x]] – DdMII+actinin 3<br /> |
| - | [[2jj9]], [[2x9h]] - DdMII HC+ADP-VO4<br /> | + | **[[2jj9]], [[2x9h]] - DdMII HC+ADP-VO4<br /> |
| - | [[3mkd]] - DdMII HC MD (mutant) + ADP-VO4 <br /> | + | **[[3mkd]] - DdMII HC MD (mutant) + ADP-VO4 <br /> |
| - | [[1lvk]], [[1mma]], [[1mmg]], [[1mmn]] – DdMII HC (mutant)+Mg+nucleotide<br /> | + | **[[1lvk]], [[1mma]], [[1mmg]], [[1mmn]] – DdMII HC (mutant)+Mg+nucleotide<br /> |
| - | [[1myh]], [[1myk]], [[1myl]], [[3myh]], [[3myl]] - DdMII HC (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[1myh]], [[1myk]], [[1myl]], [[3myh]], [[3myl]] - DdMII HC (mutant)<br /> |
| - | [[1mne]] - DdMII HC (mutant)+Mg+pyrophosphate<br /> | + | **[[1mne]] - DdMII HC (mutant)+Mg+pyrophosphate<br /> |
| - | [[1vom]] - DdMII HC (truncated)+Mg+ADP-VO4<br /> | + | **[[1vom]] - DdMII HC (truncated)+Mg+ADP-VO4<br /> |
| - | [[1mmd]], [[1w9i]], [[1w9k]] - DdMII HC (mutant)+Mg+ADP+BeF3<br /> | + | **[[1mmd]], [[1w9i]], [[1w9k]] - DdMII HC (mutant)+Mg+ADP+BeF3<br /> |
| - | [[1mnd]], [[1w9j]], [[1w9l]] - DdMII HC (mutant)+Mg+ADP+AlF4<br /> | + | **[[1mnd]], [[1w9j]], [[1w9l]] - DdMII HC (mutant)+Mg+ADP+AlF4<br /> |
| - | [[2aka]] - DdMII HC+dynamin-1<br /> | + | **[[2aka]] - DdMII HC+dynamin-1<br /> |
| - | [[2xel]], [[4ae3]] – DdMII HC + inhibitor<br /> | + | **[[2xel]], [[4ae3]] – DdMII HC + inhibitor<br /> |
| - | [[1n2d]] – ScMII LC+IQ2 IQ3 motifs from Myo2p<br /> | + | **[[1n2d]] – ScMII LC+IQ2 IQ3 motifs from Myo2p<br /> |
| - | [[1m45]] - ScMII LC+IQ2 motif from Myo2p<br /> | + | **[[1m45]] - ScMII LC+IQ2 motif from Myo2p<br /> |
| - | [[1m46]] - ScMII LC+IQ4 motif from Myo2p<br /> | + | **[[1m46]] - ScMII LC+IQ4 motif from Myo2p<br /> |
| - | [[2bl0]] – MII RLC +RHC – ''Physarum polycephalum'' | + | **[[2bl0]] – MII RLC +RHC – ''Physarum polycephalum'' |
| - | + | * Myosin III | |
| - | [[2btt]] – ScMIII SH3 domain – NMR<br /> | + | **[[2btt]] – ScMIII SH3 domain – NMR<br /> |
| - | [[1ruw]], [[1va7]] – yMIII SH3 domain | + | **[[1ruw]], [[1va7]] – yMIII SH3 domain |
| - | + | *Myosin IV | |
| - | [[3mmi]] – yMIV globular tail <br /> | + | **[[3mmi]] – yMIV globular tail <br /> |
| - | [[4ll6]] - yMIV globular tail (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[4ll6]] - yMIV globular tail (mutant)<br /> |
| - | [[4ll8]] - yMIV globular tail (mutant) + SHE3P<br /> | + | **[[4ll8]] - yMIV globular tail (mutant) + SHE3P<br /> |
| - | + | * Myosin V (Unconventional myosin) | |
| - | [[1w7i]] – cMV HC+LC+Mg+ADP<br /> | + | **[[1w7i]] – cMV HC+LC+Mg+ADP<br /> |
| - | [[1w7j]] - cMV HC+LC+BEFX+ADP<br /> | + | **[[1w7j]] - cMV HC+LC+BEFX+ADP<br /> |
| - | [[1w8j]] – cMV HC<br /> | + | **[[1w8j]] – cMV HC<br /> |
| - | [[1oe9]] – cMV HC+LC<br /> | + | **[[1oe9]] – cMV HC+LC<br /> |
| - | [[1br2]] – cMV HC+Mg+ADP+AlF4<br /> | + | **[[1br2]] – cMV HC+Mg+ADP+AlF4<br /> |
| - | [[2fcd]] – ScMV LC N-terminal – ''Saccharomices cerevisiae'' – NMR<br /> | + | **[[2fcd]] – ScMV LC N-terminal – ''Saccharomices cerevisiae'' – NMR<br /> |
| - | [[2fce]] – ScMV LC C-terminal – NMR<br /> | + | **[[2fce]] – ScMV LC C-terminal – NMR<br /> |
| - | [[2f6h]] – ScMV CBD<br /> | + | **[[2f6h]] – ScMV CBD<br /> |
| - | [[1yp5]], [[1zyu]] – yMV SH3 domain<br /> | + | **[[1yp5]], [[1zyu]] – yMV SH3 domain<br /> |
| - | [[2ix7]] – mMV+apo-calmodulin <br /> | + | **[[2ix7]] – mMV+apo-calmodulin <br /> |
| - | [[3wb8]] – mMVA tail domain<br /> | + | **[[3wb8]] – mMVA tail domain<br /> |
| - | [[4j5l]], [[4j5m]] – hMVA tail domain<br /> | + | **[[4j5l]], [[4j5m]] – hMVA tail domain<br /> |
| - | [[4kp3]] – mMVA tail domain + RILP-like protein + melanophilin<br /> | + | **[[4kp3]] – mMVA tail domain + RILP-like protein + melanophilin<br /> |
| - | [[4lli]] – hMVA cargo binding domain<br /> | + | **[[4lli]] – hMVA cargo binding domain<br /> |
| - | [[4lx1]] – hMVA globular tail domain<br /> | + | **[[4lx1]] – hMVA globular tail domain<br /> |
| - | [[4lx2]] – hMVA globular tail domain + melanphilin<br /> | + | **[[4lx2]] – hMVA globular tail domain + melanphilin<br /> |
| - | [[4lnz]] – hMVB globular domain<br /> | + | **[[4lnz]] – hMVB globular domain<br /> |
| - | [[4lwz]], [[4lx0]] – hMVB globular tail + RAS-related protein<br /> | + | **[[4lwz]], [[4lx0]] – hMVB globular tail + RAS-related protein<br /> |
| - | [[4l8t]] – hMVC cargo binding domain<br /> | + | **[[4l8t]] – hMVC cargo binding domain<br /> |
| - | [[4l79]] – raMIB + calmodulin - rat<br /> | + | **[[4l79]] – raMIB + calmodulin - rat<br /> |
| - | + | * Myosin VI | |
| - | [[2kia]] – mMVI CBD – mouse – NMR<br /> | + | **[[2kia]] – mMVI CBD – mouse – NMR<br /> |
| - | [[2ld3]] – mMVI lever arm extension - NMR<br /> | + | **[[2ld3]] – mMVI lever arm extension - NMR<br /> |
| - | [[3h8d]] - mMVI CBD+Dab2 peptide<br /> | + | **[[3h8d]] - mMVI CBD+Dab2 peptide<br /> |
| - | [[4e7z]] - pMVI<br /> | + | **[[4e7z]] - pMVI<br /> |
| - | [[4e7s]] - pMVI (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[4e7s]] - pMVI (mutant)<br /> |
| - | [[3gn4]], [[2vb6]] - pMVI neck+calmodulin – pig<br /> | + | **[[3gn4]], [[2vb6]] - pMVI neck+calmodulin – pig<br /> |
| - | [[2vas]], [[3l9i]] - pMVI neck (mutant)+calmodulin<br /> | + | **[[2vas]], [[3l9i]] - pMVI neck (mutant)+calmodulin<br /> |
| - | [[2v26]] - pMVI neck+Mg+ADP-VO4<br /> | + | **[[2v26]] - pMVI neck+Mg+ADP-VO4<br /> |
| - | [[2bkh]], [[2bki]] – pMVI HC+calmodulin<br /> | + | **[[2bkh]], [[2bki]] – pMVI HC+calmodulin<br /> |
| - | [[4dbp]], [[4dbq]]– pMVI HC (mutant) + calmodulin<br /> | + | **[[4dbp]], [[4dbq]] – pMVI HC (mutant) + calmodulin<br /> |
| - | [[4dbr]]– pMVI HC (mutant) <br /> | + | **[[4dbr]] – pMVI HC (mutant) <br /> |
| - | [[4anj]] - pMVI HC/GFP + calmodulin<br /> | + | **[[4anj]] - pMVI HC/GFP + calmodulin<br /> |
| - | [[2x51]] - pMVI d insert1 + calmodulin | + | **[[2x51]] - pMVI d insert1 + calmodulin |
| - | + | *Myosin VII | |
| - | [[2i0n]] - DdMVII SH3 domain - NMR<br /> | + | **[[2i0n]] - DdMVII SH3 domain - NMR<br /> |
| - | [[3pvl]] - mMVII SH3 domain+hUsher syndrome type 1G protein<br /> | + | **[[3pvl]] - mMVII SH3 domain+hUsher syndrome type 1G protein<br /> |
| - | [[4db1]] – hMVII HC | + | **[[4db1]] – hMVII HC |
| - | + | *Myosin X | |
| - | [[2lw9]] - hMX<br /> | + | **[[2lw9]] - hMX<br /> |
| - | [[3au5]] - hMX myth4-ferm tandem<br /> | + | **[[3au5]] - hMX myth4-ferm tandem<br /> |
| - | [[3pzd]], [[3au4]] - hMX myth4-ferm tandem + netrin receptor DCC<br /> | + | **[[3pzd]], [[3au4]] - hMX myth4-ferm tandem + netrin receptor DCC<br /> |
| - | [[3tfm]] – raMX phin-ph2-phic tandem (mutant) | + | **[[3tfm]] – raMX phin-ph2-phic tandem (mutant) |
| - | + | *Myosin XI | |
| - | [[3j04]] – cMXI HC + RLC – Cryo EM | + | **[[3j04]] – cMXI HC + RLC – Cryo EM |
| - | + | *Flight muscle myosin | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | **[[1i84]], [[2w4a]], [[2w4g]], [[2w4h]] - cRLC+cELC+cHC – cryoEM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2mys]] - cRLC+cELC+cHC - papain digested<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1lkm]] – cHC alpha-kinase domain+AMP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2dfs]] – cHC+calmodulin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1br4]] – cELC+cHC+Mg+ADP+BeF3<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1br1]] – cELC+Mg+ADP+AlF4<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2xrf]] – hLC <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3jtd]], [[2w4t]], [[2w4v]], [[2w4w]], [[1scm]] – AiRLC+AiELC+AiHC - ''Argopecten irradians''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1b7t]] - AiRLC+AiELC+AiHC papain digested<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3jvt]] - sRLC+sELC+sHC+Ca – Scallop<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2ec6]], [[2os8]], [[2otg]], [[1s5g]], [[1sr6]], [[1qvi]], [[1kk7]], [[1dfk]], [[3pn7]], [[3ts5]], [[3tuy]] - sRLC+sELC+sHC<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1kqm]] - sRLC+sELC+sHC+AMPPNP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1kwo]] - sRLC+sELC+sHC+ATPgS-PDM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1l2o]] - sRLC+sELC+sHC+ADP-PDM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1kk8]] - sRLC+sELC+sHC+ADP-BEFX<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1dfl]] - sRLC+sELC+sHC+ADP-VO4+Mg<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1wdc]] - sRLC+sELC+sHC - digested<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3dtp]] - RLC+HC+ELC – tarantula – Cryo EM | ||
| + | }} | ||
==Literature Cited== | ==Literature Cited== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Revision as of 10:21, 1 December 2014
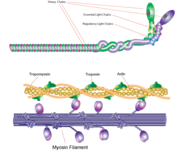
Myosin is one of three major classes of molecular motor proteins: myosin, dynein, and kinesin. As the most abundant of these proteins myosin plays a structural and enzymatic role in muscle contraction and intracellular motility. Myosin was first discovered in muscle in the 19th century. [1] Myosin is a superfamily of proteins which bind actin, hydrolyze ATP and transduce force. Thus most are located in muscle cells. Composed of head, neck and tail domains. Head domain binds the actin and moves along it. The neck is a linker and binds the light chains which have a regulatory function. The tail interacts with cargo molecules (CBD)m. There are 18 classes of myosin. Myosin II (MII) is best studied and contains 2 heavy chains (HC) which constitute the head or motor domain (MD) and the tail domain and 4 light chains (LC) which are referred to as the essential LC (ELC) and the regulatory LC (RLC).
Contents |
Crystallization and X-ray diffraction
Myosin is found in abundance, therefore it can be prepared in gram quantities. [2] For nearly 30 years the myosin head was resistant to crystallization, yet by 1993 researchers discovered a mechanism to obtain x-ray quality crystals. The process modified the protein by reductive methylation. X-ray data was used to determine the tertiary structure of the protein. [2]
Structure
Myosin has a molecular size of approximately 520 kilodaltons with a total of six subunits. It has two 220 kD heavy chains which make the majority of the overall structure and two pairs of light chains which vary in size.[2] The molecule is asymmetric, having a long tail and two globular heads. Each heavy chains composes the bulk of one of the globular heads. Subfragment-1(S1) also termed the myosin head consists of ATP, actin, and two light chain binding sites. Each globular head has a heavy chain and two light chains for a combined molecular size of about 130 kD. [2]
The myosin head is assymetrical with a length of 165 Angstroms and 65 Angstroms in width, with a total thickness of about 40 Angstroms. [2] About 48% of the amino acid residues in the myosin head are dominated by α helices. At the carboxyl terminus one long α helix of about 85 Angstroms extends in a left-handed coil. This particular helix forms the light chain binding region of the globular domain [2] The amino terminus of each heavy chain has a large globular domain containing the site of ATP hydrolysis.
Function
Molecules of myosin aggregate in muscle cells to form thick filaments. [3] The rodlike structure of these thick filaments act as the core in the muscle contractile unit. The aggregation of several hundred myosin forms a bipolar structure which stacks in regular arrays. Muscles consist of another protein called actin. Actin forms the thin filament in muscle fibers. Myosin and actin interact through weak bonds. Without ATP bound, the myosin head binds tightly to actin. With ATP bound, myosin releases the actin subunit and interacts with another subunit further down the thin filament. This process continues in cycle, producing movement. Interaction of myosin and actin is regulated by two other proteins, tropomyosin and troponin. [3]
The cycle of myosin-actin interaction is outlined as follows: [3]
1. ATP binds to myosin and a binding site opens on myosin head to disrupt the actin-myosin interaction, actin is released. ATP is hydrolyzed
2. a conformational change moving the protein to a "high-energy" state causes the myosin head to change orientation moving it to bind with the actin subunit closer the a region called the Z disk than the previous actin subunit
3. the binding site is closed, strengthening the myosin-actin binding
4. a quickly follows and the myosin head undergoes an additional conformational change bringing it back to the resting state in which it began
Click the link to access DNAtube video "A Moving Myosin Motor Protein" http://www.dnatube.com/video/389/A-Moving-Myosin-Motor-Protein-myosin-actin-interaction
3D Structures of Myosin
Updated on 01-December-2014
Literature Cited
- ↑ Spudich JA, Finer J, Simmons B, Ruppel K, Patterson B, Uyeda T. Myosin structure and function. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1995;60:783-91. PMID:8824453
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Rayment I, Rypniewski WR, Schmidt-Base K, Smith R, Tomchick DR, Benning MM, Winkelmann DA, Wesenberg G, Holden HM. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50-8. PMID:8316857
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Nelson, D. and Cox, M.(2005). Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. 4th ed. p.1119.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, David Canner, Laurel Koopmans, Jaime Prilusky