Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) is a glycolytic enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from to to yield and . Mg2+ is also important in this reaction (). Phosphofructokinase-2 (PFK-2) acts on the same substrates to yield ADP and . . PFK reaction is strongly exergonic (irreversible) under physiological conditions and hence is one of the glycolytic pathway's rate-determining steps. In most organisms/tissues, PFK is the glycolytic pathway's major flux-regulating enzyme; its activity is controlled by the concentrations of an unusually large number of metabolites including ATP, ADP, AMP, PEP and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate.
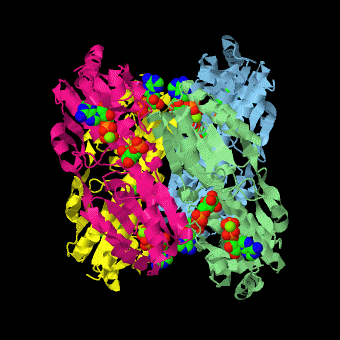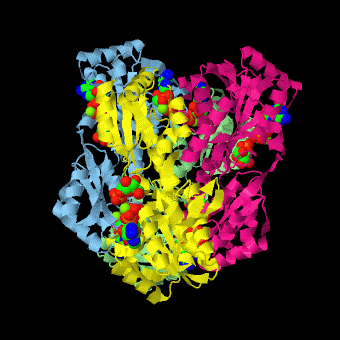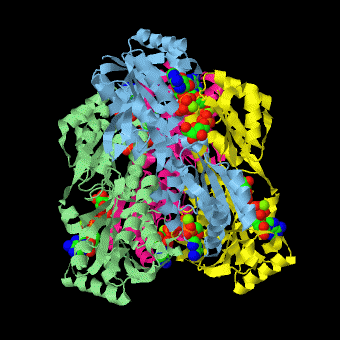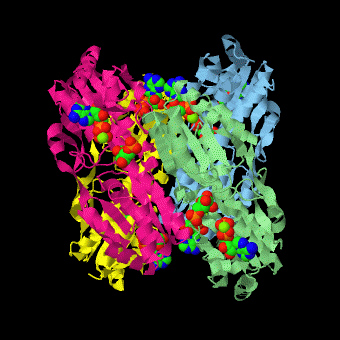
is a tetramer of identical 320-residue subunits. It is an allosteric enzyme that is described using the symmetry model of allosterism whereby there is a concerted transition from its high-activity R state to its low-activity T state. The X-ray structures of both R and T states of the enzyme have been reported.[1] The binding of one molecule of its substrate F6P, which binds to the R state enzyme with high affinity but to the T state enzyme with low affinity, causes PFK to take up the R state, which in turn, increases the binding affinity of the enzyme for additional F6P (a homotropic effect). Activators, such as ADP and AMP bind to so-called allosteric sites, binding sites distinct from the active site, where they likewise facilitate the formation of the R state and hence activate the enzyme (a heterotropic effect; ADP, being a product of the PFK reaction, also binds at the enzyme's active site). Similarly, inhibitors such as PEP bind to allosteric sites (which in the case of PFK overlaps the activating allosteric site) where they promote the formation of the T state, thereby inhibiting the enzyme.
Two of the active sites of the enzyme are located at the interface of with the active site interfaces in magenta with the substrates in cyan. Two more active sites are at the interface of subunits B (green) and C (pink). A closeup of the of subunit D (Yellow) shows that amino acids from both subunits A (light blue) and D (Yellow) contribute to the binding of F6P. Two of the allosteric sites are located at the interface of and two at the interface of subunits C and D. Again the interfaces are magenta with the allosteric ligand in cyan. A closeup of the of subunit A shows contributions from both subunits to the binding of ADP. The conformational changes in going between the R and T states of PFK are illustrated below.
The atomic coordinates for R state PFK were obtained from 4pfk; those for T state PFK were obtained from Philip Evans, MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, U. K. but are now available as 6pfk.
Role in Glycolysis
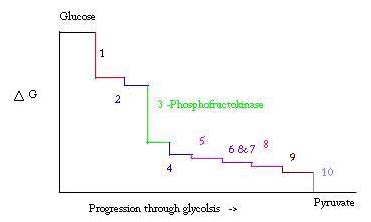
Glycolysis is the process for preparing, and breaking down, glucose to make pyruvic acid, which is used in anaerobic respiration or as one of the starting reactants in the citric acid cycle. Three points in the process of glycolysis occur with a large negative free energy and are therefore, irreversible. These three points are hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase; of these three PFK is considered the major regulatory point for glycolysis in muscle with a ΔG= -25.9 kJ/mol. [2]
Mechanism and Regulation of Phosphofructokinase
Phosphofructokinase binds both Mg2+-ATP and fructose-6-phosphate (F6P) to make fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and Mg2+-ADP. Although the image with both of these products has not been determined, bound to the enzyme has been. There are three ligand binding sites per subunit. Two make up the active site, which binds F6P and ATP, while the third is an allosteric binding site.[3] Some proposed residues involved at the active site include .[4] PFK exist in two conformational states, both and which are in equilibrium. ATP binds both active and allosteric sites in both conformations. While ATP binds the active site equally well, it preferentially binds the allosteric site of the T state [5] This preferential binding causes a shift from equilibrium of the two states, to a greater amount of T state [6], which decreases the affinity for F6P. also binds to allosteric site to increase the ratio of R state phosphofructokinase. Along with ADP,AMP and F2,6P inhibit the regulatory role of ATP.
The PFK's Km for ATP is .020mM and .032mM.[7]
Regulation
Glycolysis is an essential metabolic process for survival. Therefore, in its activation and suppression it must be highly regulated. Three points in the process of glycolysis occur with a large negative free energy and are therefore, irreversible. These three points are hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase. These three reactions are candidates to be the major points of regulation because of their high negative free energies. Of the three, PFK is considered the major regulatory point for glycolysis (#3 in the picture below) in muscle, with a ΔG= -25.9 kJ/mol, because it is a committed step. Once PFK converts F6P to F1,6P, the reaction will not be easily reversed because of the high amount of energy that must be overcome to go backward. [8]. This energy barrier makes sense seeing as pyruvate kinase catalyzes the final reaction (#10) and hexokinase (#1) is not involved in glycolysis at all when the process is begun from glycogen.[9]
PFK is regulated by ATP, AMP, and ADP. While ATP binds at the active site equally well in both R and T states, it preferentially binds the allosteric site of the T state [10] This preferential binding causes a shift from equilibrium of the two states, to a greater amount of T state [11], which decreases the affinity for F6P. Allosteric activator ADP also binds to the allosteric site to increase the ratio of R state phosphofructokinase. As can be seen from the graph below, the plots for the activity of PFK are sigmoidal. This further demonstrates the cooperative nature of the enzyme. The initial binding of substrate to the enzyme is difficult, but once it is bound and forces the change in state from T -> R, the other substrates bind much more easily. The graph also shows that adding ATP moves the plot right (ie decreases affinity for F6P), while adding AMP moves it to the left.
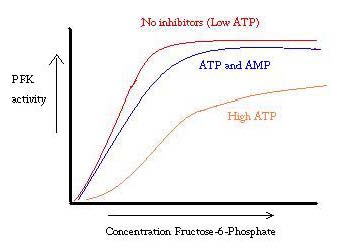
The system of regulation matches well with the function of PFK. When PFK is active, ATP is being produced down stream from it as further products are broken down more completely. Thus, when ATP levels are low and more needs to be made, the activity of PFK will be increased, because ADP will be in high concentration. The opposite holds true as well, because high ATP concentration inhibits protein activity. And yet, this explanation cannot completely account for the regulation of PFK, because the levels of ATP do not vary greatly enough between active and resting muscles. Another means of allosteric regulation must be found.[12]
PFK's Km for ATP is .020mM and .032mM.[13]
This Kinemage exercise consists of two kinemage scenes that illustrate some of the allosterically-induced conformational changes that occur in PFK from Bacillus stearothermophilus.
Conformational Changes in a Dimeric Unit of PFK
This kinemage shows the two subunits of the tetramer whose interface contains two active sites.
(KineMage currently not supported)
The first view, 1: PFK dimer, shows the two subunits in their R state conformation as represented by their Ca backbones with Subunit 1 in pink tint and Subunit 2 in pink. Two side chains in each subunit are shown, those of Glu 161 (red) and Arg 162 (cyan), which are part of the F6P binding site in the T and R states, srespectively(see below). An F6P (hotpink) and an ADP (green; "ADP-active") are bound in the active site of each subunit. An additional ADP (yellow; "ADP-allo") is bound in a separate so-called allosteric site of each subunit. The ADPs each have an associated Mg2+, which is represented here by a ball of the same color as the ADP to which it binds.
Click the "ANIMATE" button to switch the dimer between its R and T states. In its T state, Subunit 1 is bluetint and Subunit 2 is skyblue. The side chains of Glu 161 and Arg 162 in both subunits are red and cyan as before (only the Ca and Cb atoms of the Arg 162 side chain in Subunit 1 are observed in the X-ray structure of the T state; those of Subunit 2 are all observed). The T state enzyme binds the inhibitor 2-phosphoglycolate (gold; "PGC"), a nonphysiological analog of the glycolytic intermediate phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). Note that the binding site of PGC in the T state overlaps the allosteric binding site of ADP in the R state ("ADP-allo") and hence their binding is mutually exclusive. The T state active sites, which do not contain F6P, are marked by "ghost" F6Ps (gray;"F6P site"), which have the same positions as do the F6Ps in the R state enzyme.
The second view, 2: Allo/Act Sites, is a closeup of the upper portion of the first view showing both the active site and the allosteric site in this region. Note that the active site is located at the interface between two subunits and that the allosteric site interacts directly with the active site on the adjacent subunit. Compare the R state and T state conformations by displaying both at once or clicking on "ANIMATE". Can you identify the Mg2+ ion associated with each of the ADPs bound to the enzyme in the R state? Which ADP atoms coordinate these Mg2+ ions?
The phosphate group of PGC binds to the allosteric site in the T state in very nearly the same position that the beta phosphate group of "ADP-allo" binds to the R state allosteric site; both phosphate groups bind to the side chains of the same three residues (2 arg and 1 Lys; not shown).
In the high-activity R state, the positively charged side chain of Arg 162 forms a hydrogen bonded salt bridge with the negatively charged 6-phosphate group of F6P (white dashed lines), an interaction which presumably stabilizes the R state relative to the T state and is therefore in part responsible for F6P's homotropic effect.
The Major Conformational Changes in a Subunit of PFK.
This KINEMAGE shows those segments near the allosteric site (residues 53-60 are not shown here). As in KINEMAGE 1, the polypeptide is represented by its Ca chain with R state Subunits 1 and 2 in redtint and pink, and T state Subunits 1 and 2 in bluetint and skyblue.
(KineMage currently not supported)
KINEMAGE 2 comes up in view 1: The Allosteric Site, in the R state showing the phosphate group of F6P (hotpink) bound in the enzyme's active site in a hydrogen bonded salt bridge (dashed white lines) with the side chain of Arg 162 (cyan). An ADP (yellow; "ADP-allo") occupies the adjacent allosteric site. Click once on "ANIMATE" to switch to the T state. This replaces the ADP in the R state allosteric site with the inhibitor and PEP analog PGC (gold). F6P no longer occupies the active site but its position in the R state is indicated by the "ghost" F6P (gray; viewed by clicking on "F6P site").
What happens to the central polypeptide helical segment (residues 149-164) in the R to T transition? What does this do to the relative positions of the negatively charged Glu 161 and the positively charged Arg 162? Click on "F6P site". What influence would the absence of the positive charge of Arg 162 have on the binding of F6P? Does this explain, at least in part, why T state PFK has low affinity for F6P? Go to View 2: Closeup, for a closeup of the F6P-sidechain interactions. Center the molecules by choosing "pickcenter" from the "tools" menu and clicking on athe atom you'd like to be in the center. Slide the "zoom" slider to enlarge the view.
Site-Directed Mutagenesis
At one time, the negative charge of Glu 161 was thought to have a negative effect on F6P binding in the T state. This idea has not been supported by site-directed mutagenesis experiments[14].Several mutant PFKs have been made, including R162A, E161A and R162A/E161A. The R162A mutation caused a 30-fold decrease in F6P binding. The E161A mutation, however, had little effect on the ability of PEP to inhibit F6P binding.