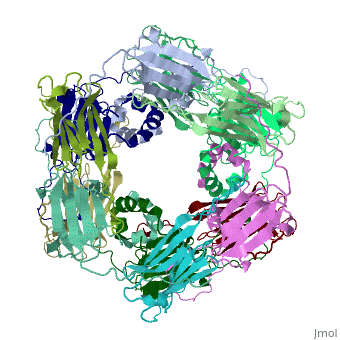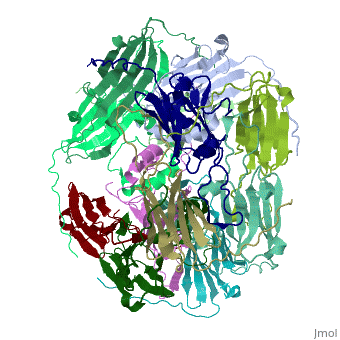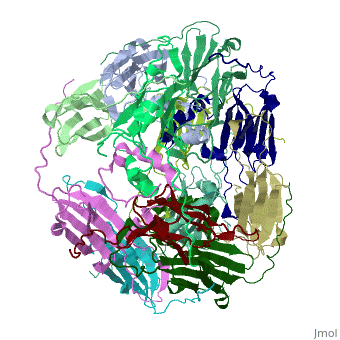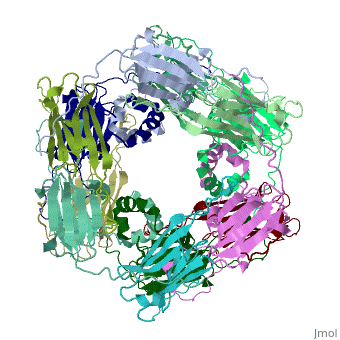We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Keithballard/sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Structure of Class I cytosolic sHSP== | ==Structure of Class I cytosolic sHSP== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1gme' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='1gme' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''><scene name='60/609774/Dimer_default/2'></scene> |
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Small heat shock proteins (sHSPs) and related α-crystallins are virtually ubiquitous, ATP-independent molecular chaperones linked to diseases of protein misfolding. They comprise a conserved core α-crystallin domain (ACD) flanked by an evolutionarily variable N-terminal arm (NTA) and semi-conserved C-terminal extension. They are capable of binding up to an equal mass of unfolding protein, forming large, heterogeneous sHSP-substrate complexes that make substrate available to the ATP-dependent chaperones for refolding. | Small heat shock proteins (sHSPs) and related α-crystallins are virtually ubiquitous, ATP-independent molecular chaperones linked to diseases of protein misfolding. They comprise a conserved core α-crystallin domain (ACD) flanked by an evolutionarily variable N-terminal arm (NTA) and semi-conserved C-terminal extension. They are capable of binding up to an equal mass of unfolding protein, forming large, heterogeneous sHSP-substrate complexes that make substrate available to the ATP-dependent chaperones for refolding. | ||
Revision as of 14:48, 3 December 2014
Structure of Class I cytosolic sHSP
| |||||||||||