We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
OhrR
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
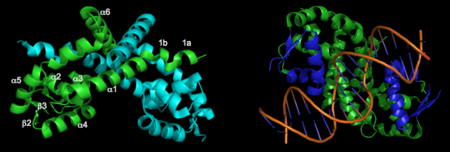
A winged Helix-Turn-Helix DNA-binding motiff is formed by α3, α4, β2, and β3. Superimposition of α4 with the same helix from 1Z9C (OhrR from Bs bound to DNA) reveals that the structure of these HTH regions are very well conserved. To illustrate how the HTH region of OhrR ''Xc'' interacts with the DNA to suppress Ohr and image of the alignment (with the protein component of 1Z9C hidden) is below (right). | A winged Helix-Turn-Helix DNA-binding motiff is formed by α3, α4, β2, and β3. Superimposition of α4 with the same helix from 1Z9C (OhrR from Bs bound to DNA) reveals that the structure of these HTH regions are very well conserved. To illustrate how the HTH region of OhrR ''Xc'' interacts with the DNA to suppress Ohr and image of the alignment (with the protein component of 1Z9C hidden) is below (right). | ||
| - | [[Image:2pexlabeledchains.png| | + | [[Image:2pexlabeledchains.png|left|450px]]<br /> |
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==Conserved Residues in OhrR ''Xc''== | ==Conserved Residues in OhrR ''Xc''== | ||
| - | <applet load='2pex' size='300' frame='true' align='left' caption='Conserved Residues in OhrR' scene='Sandbox1/2pex_conserved/1'/> | ||
The Consurf Server was used to predict which regions of OhrR ''Xc'' are most <scene name='User:David_Bruhn/Sandbox1/2pex_conserved/1'>highly conserved</scene>. Briefly, this freely-available tool performed a multiple sequence alignment of the input sequence and based on this alignment assigned residues a conservation score of 1 to 10. The structure of reduced OhrR (colored based on the output of this server) is available to the left with residues colored similar to output script files from ConSurf. Red spheres indicates the most highly conserved residues (10). Bright pink spheres indicate highly conserved residues (9). Light pink spheres indicate residues that are highly conserved but are more likely to substitution than those colored in bright pink. | The Consurf Server was used to predict which regions of OhrR ''Xc'' are most <scene name='User:David_Bruhn/Sandbox1/2pex_conserved/1'>highly conserved</scene>. Briefly, this freely-available tool performed a multiple sequence alignment of the input sequence and based on this alignment assigned residues a conservation score of 1 to 10. The structure of reduced OhrR (colored based on the output of this server) is available to the left with residues colored similar to output script files from ConSurf. Red spheres indicates the most highly conserved residues (10). Bright pink spheres indicate highly conserved residues (9). Light pink spheres indicate residues that are highly conserved but are more likely to substitution than those colored in bright pink. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 34: | ||
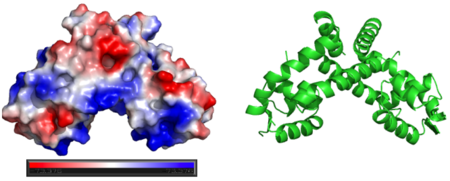
Generating vacuum electrostatics with PyMol shows significant positive charge distribution in the DNA-binding domain. The analysis also revealed a negative pocket in the center of the dimerization interface. The publishes of these OhrR structures have proposed that this region (which also included conserved hydrophobic residues) may serve as a binding pocket for hydroperoxide species. Positive charges have been colored in blue. Negative charges are indicated by red. The image below shows side-by-side views acquired from PyMol without changing the orientation of the molecule between images. | Generating vacuum electrostatics with PyMol shows significant positive charge distribution in the DNA-binding domain. The analysis also revealed a negative pocket in the center of the dimerization interface. The publishes of these OhrR structures have proposed that this region (which also included conserved hydrophobic residues) may serve as a binding pocket for hydroperoxide species. Positive charges have been colored in blue. Negative charges are indicated by red. The image below shows side-by-side views acquired from PyMol without changing the orientation of the molecule between images. | ||
| - | [[Image:ElectrostaticsOhrR.png|center| | + | [[Image:ElectrostaticsOhrR.png|center|450px]]<br /> |
== Presence of Additional Putative Functional Sites == | == Presence of Additional Putative Functional Sites == | ||
| Line 41: | Line 40: | ||
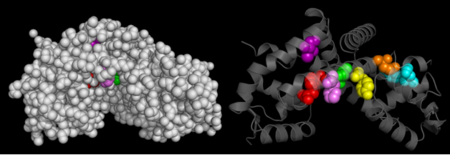
HotPatch (freely available from UCLA-DOE Institute for Genomics and Proteomics) was to search for additional sites of function importance for OhrR. Analysis of 2PEX (reduced OhrR) revealed several such patches. Most of these area were located along the DNA-binding domain of the protein. This raises the possibility that OhrR may not be the only protein bound to the Ohr gene. Additional analysis are required, however, to gain insight into the function relevance of any of these sites. | HotPatch (freely available from UCLA-DOE Institute for Genomics and Proteomics) was to search for additional sites of function importance for OhrR. Analysis of 2PEX (reduced OhrR) revealed several such patches. Most of these area were located along the DNA-binding domain of the protein. This raises the possibility that OhrR may not be the only protein bound to the Ohr gene. Additional analysis are required, however, to gain insight into the function relevance of any of these sites. | ||
| - | [[Image:HotPatchOhrR2.png|left| | + | [[Image:HotPatchOhrR2.png|left|450px]]<br /> |
==Transcription Regulation as a Mechanism to Evade Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)== | ==Transcription Regulation as a Mechanism to Evade Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)== | ||
Revision as of 12:01, 11 December 2014
| |||||||||||