This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Erythropoietin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Erythropoietin Structure, Function, and History== | ==Erythropoietin Structure, Function, and History== | ||
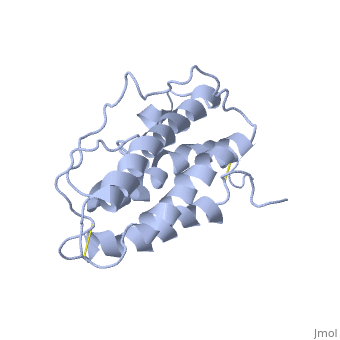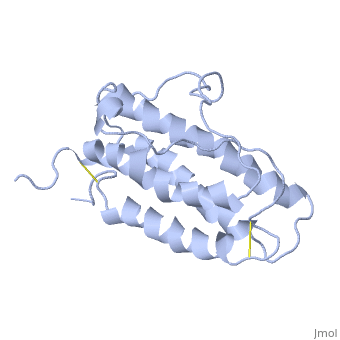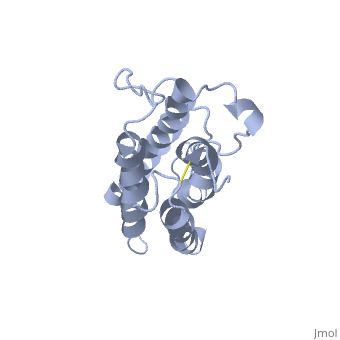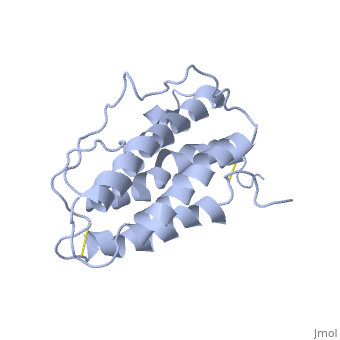
| - | <StructureSection load='1buy' size='450' side='right' scene=> | + | <StructureSection load='1buy' size='450' side='right' caption='Human erythropoietin NMR structure (PDB code [[1buy]]).' scene=> |
| - | + | ==Introduction== | |
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
'''Erythropoietin''' (EPO) is a hormone produced in the kidneys that stimulates the formation of red blood cells. EPO is a glycoprotein that is stimulated when the levels of O2 are abnormally low. This event signals more red blood cells to made from the erythrocytes. Abnormal levels of erythropoietin can be associated with bone marrow disorders, kidney disease, or a synthesized recombinant form that has been injected into the blood stream. Synthesized recombinant EPO has made many headlines in the past few years, due to its use to by Tour de France athletes. They used EPO to illegally dope their blood and increase the amount of oxygen that can be consumed by the body at the time of administration thus increasing endurance. They used EPO because there was no test at the time that could differentiate between naturally produced EPO and the form that was injected. | '''Erythropoietin''' (EPO) is a hormone produced in the kidneys that stimulates the formation of red blood cells. EPO is a glycoprotein that is stimulated when the levels of O2 are abnormally low. This event signals more red blood cells to made from the erythrocytes. Abnormal levels of erythropoietin can be associated with bone marrow disorders, kidney disease, or a synthesized recombinant form that has been injected into the blood stream. Synthesized recombinant EPO has made many headlines in the past few years, due to its use to by Tour de France athletes. They used EPO to illegally dope their blood and increase the amount of oxygen that can be consumed by the body at the time of administration thus increasing endurance. They used EPO because there was no test at the time that could differentiate between naturally produced EPO and the form that was injected. | ||
| - | + | ==History== | |
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
Miyake et al first purified a few milligrams of erythropoietin from 2500 L human urine in 1977 <ref>PMID: 6600633</ref>. This glycoprotein was first suspected as doctors observed anemia patients. Researchers noticed that patients with anemia had increased levels of erythropoiesis <ref>PMID:17253966</ref>. They noticed that the level of oxygen, seemed to be correlated with the amount of erythropoiesis, as well. After isolation, researchers worked to clone the gene so that they could produce the glycoprotein and treat hypoxia. The FDA approved this type of treatment in the 1990’s <ref>PMID:17253966</ref>. EPO works to stimulate the amount of red blood cells and the efficiency of hemoglobin, which increases oxygen library. This trait is what has led to many athletes to abuse this glycoprotein to improve their performance in their athletic sport, the most famous being Tour de France competitors (8). Most athletes involved in these scandal would intravenously inject themselves with this hormone (7). However, as medical techniques have advanced, some have started gene doping through in vivo and ex vivo gene transfer (7). | Miyake et al first purified a few milligrams of erythropoietin from 2500 L human urine in 1977 <ref>PMID: 6600633</ref>. This glycoprotein was first suspected as doctors observed anemia patients. Researchers noticed that patients with anemia had increased levels of erythropoiesis <ref>PMID:17253966</ref>. They noticed that the level of oxygen, seemed to be correlated with the amount of erythropoiesis, as well. After isolation, researchers worked to clone the gene so that they could produce the glycoprotein and treat hypoxia. The FDA approved this type of treatment in the 1990’s <ref>PMID:17253966</ref>. EPO works to stimulate the amount of red blood cells and the efficiency of hemoglobin, which increases oxygen library. This trait is what has led to many athletes to abuse this glycoprotein to improve their performance in their athletic sport, the most famous being Tour de France competitors (8). Most athletes involved in these scandal would intravenously inject themselves with this hormone (7). However, as medical techniques have advanced, some have started gene doping through in vivo and ex vivo gene transfer (7). | ||
| - | + | ==Structure== | |
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
The gene for EPO is found on chromosome 7 and is composed of five exons and four introns <ref>PMID: 1557429</ref>. The transcriptional product of this gene is an amino acid chain of 193 bases. During translation, the chain is modified to 166 amino acids <ref>PMID:17253966</ref>. The cleaved 27 amino acid leader sequence is made mostly of hydrophobic amino acids. After translation is complete, the C-terminus loses its final arginine residue to reach its final length of 165 amino acids residues <ref> Erslev, A. J., and J. Caro. "Physiologic and molecular biology of erythropoietin." Medical oncology and tumor pharmacotherapy 3.3-4 (1986): 159-164. </ref>. The total glycoprotein weighs 30 kDa with the peptide backbone weighing 18 kDa. EPO is a glycoprotein composed of only <scene name='12/128258/Epoalpha/1'>Alpha Helices</scene> <ref>Erslev, A. J., and J. Caro. "Physiologic and molecular biology of erythropoietin." Medical oncology and tumor pharmacotherapy 3.3-4 (1986): 159-164.</ref>. The sulfur of the cysteine residues links to form disulfide bonds. These disulfide bonds help keep EPO's structure. Helix A is connected to Helix D by <scene name='58/583377/Epocyslabels/1'>Cys7 and Cys161</scene>, while Helix A and Helix B are connected by <scene name='58/583377/Epocyslabels/1'>Cys29 and Cys33</scene> . EPO’s structure was determined in 1993. It is made up of four alpha helixes. EPO is produced mainly in the kidney, but further research has shown the brain and liver still produce small amounts <ref>Erslev, A. J., and J. Caro. "Physiologic and molecular biology of erythropoietin." Medical oncology and tumor pharmacotherapy 3.3-4 (1986): 159-164.</ref>. | The gene for EPO is found on chromosome 7 and is composed of five exons and four introns <ref>PMID: 1557429</ref>. The transcriptional product of this gene is an amino acid chain of 193 bases. During translation, the chain is modified to 166 amino acids <ref>PMID:17253966</ref>. The cleaved 27 amino acid leader sequence is made mostly of hydrophobic amino acids. After translation is complete, the C-terminus loses its final arginine residue to reach its final length of 165 amino acids residues <ref> Erslev, A. J., and J. Caro. "Physiologic and molecular biology of erythropoietin." Medical oncology and tumor pharmacotherapy 3.3-4 (1986): 159-164. </ref>. The total glycoprotein weighs 30 kDa with the peptide backbone weighing 18 kDa. EPO is a glycoprotein composed of only <scene name='12/128258/Epoalpha/1'>Alpha Helices</scene> <ref>Erslev, A. J., and J. Caro. "Physiologic and molecular biology of erythropoietin." Medical oncology and tumor pharmacotherapy 3.3-4 (1986): 159-164.</ref>. The sulfur of the cysteine residues links to form disulfide bonds. These disulfide bonds help keep EPO's structure. Helix A is connected to Helix D by <scene name='58/583377/Epocyslabels/1'>Cys7 and Cys161</scene>, while Helix A and Helix B are connected by <scene name='58/583377/Epocyslabels/1'>Cys29 and Cys33</scene> . EPO’s structure was determined in 1993. It is made up of four alpha helixes. EPO is produced mainly in the kidney, but further research has shown the brain and liver still produce small amounts <ref>Erslev, A. J., and J. Caro. "Physiologic and molecular biology of erythropoietin." Medical oncology and tumor pharmacotherapy 3.3-4 (1986): 159-164.</ref>. | ||
| - | + | ==Stimulus== | |
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
The levels of oxygen found in the blood moderate the process of erythropoiesis, which is the production of red blood cells. At low levels of oxygen, EPO released into the blood stream from the kidneys in adults humans. After release, the hormone travels to the bone marrow and binds to receptors, which starts the proliferation of red blood cells to increase the oxygen consumption. This increase in consumption will hopefully reestablish normal levels of blood in the system. | The levels of oxygen found in the blood moderate the process of erythropoiesis, which is the production of red blood cells. At low levels of oxygen, EPO released into the blood stream from the kidneys in adults humans. After release, the hormone travels to the bone marrow and binds to receptors, which starts the proliferation of red blood cells to increase the oxygen consumption. This increase in consumption will hopefully reestablish normal levels of blood in the system. | ||
| - | + | ==Receptors== | |
| - | + | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 37: | Line 36: | ||
| - | References | + | ==References== |
---- | ---- | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 12:08, 25 December 2014
Erythropoietin Structure, Function, and History
| |||||||||||