This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 962
From Proteopedia
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[Image:Image_methyl_acceptor_specificity.png]] | [[Image:Image_methyl_acceptor_specificity.png]] | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| - | As we can see on the figure<ref name="Hausmann S, Zheng S, Fabrega C, Schneller SW, Lima CD, Shuman S. Encephalitozoon cuniculi mRNA cap (guanine N-7) methyltransferase: methyl acceptor specificity, inhibition BY S-adenosylmethionine analogs, and structure-guided mutational analysis. J Biol Chem. 2005 May 27;280(21):20404-12. Epub 2005 Mar 9.">PMID:15760890 </ref> , the enzyme specifically binds to guanine.{{clear}} | + | As we can see on the figure above<ref name="Hausmann S, Zheng S, Fabrega C, Schneller SW, Lima CD, Shuman S. Encephalitozoon cuniculi mRNA cap (guanine N-7) methyltransferase: methyl acceptor specificity, inhibition BY S-adenosylmethionine analogs, and structure-guided mutational analysis. J Biol Chem. 2005 May 27;280(21):20404-12. Epub 2005 Mar 9.">PMID:15760890 </ref> , the enzyme specifically binds to guanine.{{clear}} |
This specificity is achieved through the recognition by the enzyme residues through hydrogen bonds of the guanine N1, N3, and O6 atoms.{{clear}} | This specificity is achieved through the recognition by the enzyme residues through hydrogen bonds of the guanine N1, N3, and O6 atoms.{{clear}} | ||
We remark also that the methyltransferase is not able to discrminate between ribose and deoxyribose nucleoside sugars. | We remark also that the methyltransferase is not able to discrminate between ribose and deoxyribose nucleoside sugars. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
- An electrostatic interaction mediated by Gln140, Phe141{{clear}} | - An electrostatic interaction mediated by Gln140, Phe141{{clear}} | ||
- A water mediated contact mediated by Asp78. | - A water mediated contact mediated by Asp78. | ||
| - | |||
<ref name="Fabrega C, Hausmann S, Shen V, Shuman S, Lima CD. Structure and mechanism of mRNA cap (guanine-N7) methyltransferase. Mol Cell. 2004 Jan 16;13(1):77-89. ">PMID:14731396</ref> | <ref name="Fabrega C, Hausmann S, Shen V, Shuman S, Lima CD. Structure and mechanism of mRNA cap (guanine-N7) methyltransferase. Mol Cell. 2004 Jan 16;13(1):77-89. ">PMID:14731396</ref> | ||
Revision as of 10:22, 2 January 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/11/2014, through 15/05/2015 for use in the course "Biomolecule" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the Strasbourg University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 951 through Sandbox Reserved 975. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
mRNA Cap (Guanine-N7) Methyltransferase (Ecm1)
|
Contents |
Biological role
Structure
Interaction
Cap Analog Binding (7-Methylguanosine-5-Triphosphate-5-Guanosine)
binds to the enzyme in a pocket near the AdoHcy. (Tyr 145, Leu216, Leu217, Asp218, Ser219, Tyr284) are involded in the binding of the cap analog. The cap makes Van der Walls contacts with side chains from Leu216, Leu217, Asp218, Ser219.Tyr284 makes a hydrogen bond and Tyr145 a water mediated bond. [1]
Image:Image methyl acceptor specificity.png
As we can see on the figure above[2] , the enzyme specifically binds to guanine. This specificity is achieved through the recognition by the enzyme residues through hydrogen bonds of the guanine N1, N3, and O6 atoms.We remark also that the methyltransferase is not able to discrminate between ribose and deoxyribose nucleoside sugars.
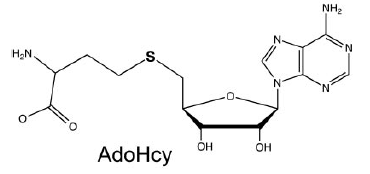
AdoHcy Binding (S-Adenosyl-L-Homocysteine)
The mRNA Cap Methyltransferase bind to which is the product of the methyl donor AdoMet after the methylation. AdoHcys is in a pocket formed by amino acids of segment 2.(Lys54, Gly72, Asp78, Asp94, Ile95, Asp122, Ser124, Gln140, Phe141, Ser142) are involved in the stabilisation of AdoHcys.
The interactions between AdoHcys and the enzyme are made of : - Hydrogen bonds mediated by Asp122, Asp 94, Gln140, Gly72, Lys54 - Van der Walls interactions mediated by Ser142, Tyr124 and Ile95 - An electrostatic interaction mediated by Gln140, Phe141- A water mediated contact mediated by Asp78. [1]
Mechanism
This enzyme catalyse N-methyl transfer from AdoMet (S-adenosylmethionine) to GpppRNA, this reaction produce 7-methyl-GpppRNA and AdoHcy. This reaction is made through a SN2 mechanism. We remark that there is no contact between the enzyme and the guanine N-7 nucleophile, the AdoMet methyl carbon, or the AdoHcy sulfur leaving group.Indeed the enzyme does not stabilize the transition state of the chemical reaction, does not promote the activation of the nucleophile or the expulsion of the leaving group. mRNA Cap Methyltransferase brings the two substrates closer and orientates the substrates to facilitate the methyl transfer.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Fabrega C, Hausmann S, Shen V, Shuman S, Lima CD. Structure and mechanism of mRNA cap (guanine-N7) methyltransferase. Mol Cell. 2004 Jan 16;13(1):77-89. PMID:14731396
- ↑ Hausmann S, Zheng S, Fabrega C, Schneller SW, Lima CD, Shuman S. Encephalitozoon cuniculi mRNA cap (guanine N-7) methyltransferase: methyl acceptor specificity, inhibition BY S-adenosylmethionine analogs, and structure-guided mutational analysis. J Biol Chem. 2005 May 27;280(21):20404-12. Epub 2005 Mar 9. PMID:15760890 doi:10.1074/jbc.M501073200