We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 970
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
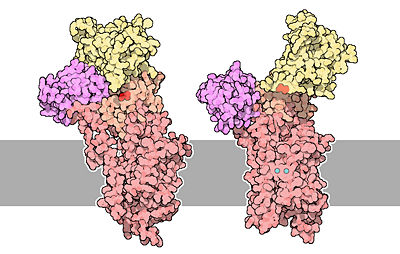
There are different kind of calcium ATPase regulations. For example, the phospholamban (PLN or PLB) is a membrane protein that regulates the calcium pump in cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle cells. This small phosphoprotein is a pentamer. The phospholamban can be phosphorylated at three distinct sites by various protein kinases (PKA, PKC, CamK...). The phosphorylation state is mediated through beta-adrenergic stimulation. In unphosphorylate state, the phospholamban inhibits the activity of calcium pump in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells by decreasing the apparent affinity of the ATPase for calcium. The phosphorylation of the protein results in the dissociation of the protein from the ATPase. The phosphoprotein binds just downstream of the active ATPase site (asp351). | There are different kind of calcium ATPase regulations. For example, the phospholamban (PLN or PLB) is a membrane protein that regulates the calcium pump in cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle cells. This small phosphoprotein is a pentamer. The phospholamban can be phosphorylated at three distinct sites by various protein kinases (PKA, PKC, CamK...). The phosphorylation state is mediated through beta-adrenergic stimulation. In unphosphorylate state, the phospholamban inhibits the activity of calcium pump in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells by decreasing the apparent affinity of the ATPase for calcium. The phosphorylation of the protein results in the dissociation of the protein from the ATPase. The phosphoprotein binds just downstream of the active ATPase site (asp351). | ||
Most of the activation mechanisms implicate the C-terminal region of the pump containing the high affinity calmodulin binding domain, which is involved in the autoinhibition of the pump<ref>Marianela G.Dalghi, Marisa M.Fernández, Mariela Ferreira-Gomes, Irene C.Mangialavori, Emilio L.Malchiodi, Emanuel E.Strehler and Juan Pablo F.C.Rossi, 2013 - ''Plasma Membrane Calcium ATPase Activity Is Regulated by Actin Oligomers through Direct Interaction'' - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.288, 23380-23393, http://www.jbc.org/content/288/32/23380.full.</ref>. | Most of the activation mechanisms implicate the C-terminal region of the pump containing the high affinity calmodulin binding domain, which is involved in the autoinhibition of the pump<ref>Marianela G.Dalghi, Marisa M.Fernández, Mariela Ferreira-Gomes, Irene C.Mangialavori, Emilio L.Malchiodi, Emanuel E.Strehler and Juan Pablo F.C.Rossi, 2013 - ''Plasma Membrane Calcium ATPase Activity Is Regulated by Actin Oligomers through Direct Interaction'' - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.288, 23380-23393, http://www.jbc.org/content/288/32/23380.full.</ref>. | ||
| - | Another example of regulation. The plasma membrane calcium pump carboxy-terminal tail contains the calmodulin binding domain (regulatory domain) which acts as an auto-inhibitory domain. The binding of the calmodulin frees the pump from autoinhibition. | + | Another example of regulation. The plasma membrane calcium pump carboxy-terminal tail contains the calmodulin binding domain (regulatory domain) which acts as an auto-inhibitory domain. The binding of the calmodulin frees the pump from autoinhibition<ref>Marisa Brini and Ernesto Carafoli, 2010 - ''The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase and the Plasma Membrane Sodium Calcium Exchanger Cooperate in the Regulation of Cell Calcium'' - Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, http://cshperspectives.cshlp.org/content/3/2/a004168.full</ref>. |
== Dysfunctions and Diseases == | == Dysfunctions and Diseases == | ||
Revision as of 17:36, 6 January 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 David Goodsell, 2004 - Calcium pump molecul of the month - PDB, doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_3
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Benjamin Lewin, 2007 - Cells - Jones & Bartlett Learning
- ↑ Thomas D.Pollard and William C. Earnshaw, - Membrane, structure and function - Cell Biology (second edition), p.133-136
- ↑ Thomas D.Pollard and William C. Earnshaw, - Membrane, structure and function - Cell Biology (second edition), p.133-136
- ↑ David H.MacLennan, William J.Rice and N. Michael Green, 1997 - The Mechanism of Ca2+ Transport by Sarco(Endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPases - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.272, 28815-28818, http://www.jbc.org/content/272/46/28815.full.html
- ↑ Marianela G.Dalghi, Marisa M.Fernández, Mariela Ferreira-Gomes, Irene C.Mangialavori, Emilio L.Malchiodi, Emanuel E.Strehler and Juan Pablo F.C.Rossi, 2013 - Plasma Membrane Calcium ATPase Activity Is Regulated by Actin Oligomers through Direct Interaction - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.288, 23380-23393, http://www.jbc.org/content/288/32/23380.full.
- ↑ Marisa Brini and Ernesto Carafoli, 2010 - The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase and the Plasma Membrane Sodium Calcium Exchanger Cooperate in the Regulation of Cell Calcium - Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, http://cshperspectives.cshlp.org/content/3/2/a004168.full