Tachyplesin I (TP-I) is an antimicrobial polypeptide originally detected in the leukocytes of Japanese Horse Shoe Crab. It has also been reported to inhibit the growth of gram positive bacteria, fungui and viruses suggesting its antimicrobial property.
The antimicrobial activity of the peptide is related to the composition of the pathogen membrane and ability of the peptide to permeabilize the cell membranes. Bacteria and fungi have negatively charged membranes, and the interaction of is mediated in large part by electrostatic interactions[1] (see the Hydrophobic and Polar amino acids).
Specifically, TP-I shows high affinity for lipopolysaccharides (LPS) of gram-negative bacteria, thus neutralizing its effects.
Structural highlights
Tachyplesine I is a 17-residue peptide containing six cationic residues with molecular weight 2,269 and isoelectric point (pI) of 9.93.[2]
The amino acid sequence of the TP-I is NH₂-Lys-Trp-Cys-Phe-Arg-Val-Cys-Tyr-Arg-Gly-Ile-Cys-Tyr-Arg-Arg-Cys-Arg-CONH₂.
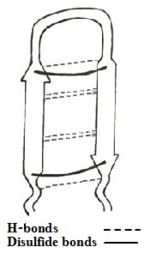
Figure 1: Simplefied model of Tachyplesin I.
The sequence adapts antiparallel β-sheet (hairpin) conformation in solution stabilized by two cross-strand between Cys³-Cys¹⁶ and Cys⁷-Cys¹²[3], and C-terminus amidation.[1][4].
Besides, there exists H-bonds and aromatic rings stacking interactions which helps stabilizing the hairpin loop structure of the peptide.
The β-hairpin structure is well characterized by a for the centrally located residues .[5]
Along with TP-I, there exists three linear derivatives: , TPF4 and TPA4 as shown below.
Image:Derivatives.jpg
Of those 3 linear derivatives of TP-I, TPA4 was inactive which was due to its incapability to form hairpin loop structure. This guided to the conclusion that linear Tachyplesin analogues do not show preferential affinity for LPS. Therefore, the hairpin properties of the peptide seems to be important for recognition of lipopolysaccharides and its biological activities.
TP-I undergoes confirmation change in . The backbone of the polypeptide becomes , making it more stable.
A Cys Deleted Linear Analog
(CDT) is a linear mutant lacking the cysteines and therefore lacking the disulfide bonds (NH₂-Lys-Trp-Phe-Arg-Val-Tyr-Arg-Gly-Ile-Tyr-Arg-Arg-Arg-CONH₂). It contains a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity with a reduced hemolytic property that stems from selective interactions with the negatively charged lipids including LPS.
CDT has been demonstrated to markedly inhibit the growth of Gram negative and Gram positive bacterial strains akin to TP-I. But, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values for CDT were found to be lower against Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes in comparison to the wild type TP-I peptide.
CDT Structure
CDT, like TP-1, has a β-turn in the in its LPS-bound structure.
The β-hairpin topology of CDT is sustained by the between the aromatic ring of Trp2 and the sidechain of nonpolar amino acid of Val5 and the cationic sidechain of residue Arg11.
There is a close proximity between residues , supported by the nuclear overhauser effects (NOEs) involving indole ring protons of Trp2 with sidechain proton of Ile9. These packing interactions have rendered an approximate anti-parallel orientation of the hairpin structure of CDT in presence of LPS.
The β-hairpin like structure of CDT displays an extended positively charged surface patch of . These basic residues would be interacting, salt bridges and/or hydrogen bonds, with the anionic phosphate groups of LPS.
The interactions between CDT and LPS may lead to a plausible disruption or fluidization of LPS structures facilitating traversal of the peptide through the LPS-outer membrane.[5]
Mode of action
TP-I has affinity to LPS and also has ability to permeabilize the cell membrane of pathogens. TP-I primary and critical target is the cell membrane.[6]Docking model suggests strong affinity between TP-I and LPS; gained by interaction between cationic residues of TP-I with phosphate group and sachharides of LPS. Furthermore, interaction between hydrophobic residues of TP-I with acyl chains of LPS strengthens the TP-I/LPS interaction. The binding of TP-I/LPS neutralizes LPS, which is widely considered as endotoxin, and disrupts membrane function.
In addition to LPS binding, footpriting analysis has revealed the binding of TP-I to DNA by interacting specifically in minor groove of DNA duplex. The interaction between TP-I and DNA is contributed by secondary structure of the peptide which contains an antiparallel beta-sheet constrained by two disulfide bridges and connected by β-turn [7].
By binding to DNA and RNA TP-I inhibits the synthesis of macromolecules.
There are three processes that can occur upon TP-I exposure: (1) Bacterial cell membranes are penetrated without disruption of the membrane and the peptide reaches the inner structures of the cell, damaging critical intracellular targets and interfering with intracellular functions and normal metabolism. (2) Pores are formed in the cell wall, causing leakage of intracellular content, leading to cell death. (3) DNA, RNA or protein synthesis are inhibited, killing the bacteria.[6]
Importance and relevance
Evidences suggest that TP-1 has ability to permeabilize the cell membranes of pathogens.[1]. Also, LPS and DNA being the potential biological targets of the peptide, its antimicrobial activity might be exploited. Eyeing the potential of TP-1, it has been insetred successfully in genome of Ornithogalum dubium and Ornithogalum thyrsoides. These ornamentals plants were originally sensitive to soft rot erwinias (SREs) and insertion of TPI in the plants has successfully protected them without affecting their normal physiology [8].
Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes are Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, respectively. They are the most common intestinal tract pathogenic bacteria in animals and humans.
Studying the effect of TP-I on E. coli and S. aureus will be valuable in guiding clinical practice.
The potential mechanism of E. coli membrane disruption by TP-I is the induction of macromolecule leakage into the cytoplasm and the release of potassium ions, leading to an increase in inner permeability, the formation of a toroidal pore, the neutralization of LPS, and the disruption of the permeability barrier of the outer membrane. TP-I killed E. coli mainly through cell membrane damage and intracellular esterase inactivation dependent on concentration.
In food production, requirements must be met for producing high quality food with minimal microbial contamination, and the determination of microbial viability based on different physiological and metabolic parameters is critical for acceptable sterilization. Therefore, the presence of injured, metabolically active bacteria is a very important aspect to consider in food production and for clinical applications. Sublethally injured cells might be repaired under suitable conditions. If TP-I is applied as a clinical treatment at a lower concentration than the MIC over a long period of time, drug resistance could develop.[6]
Possible Function as anti-tumor peptide
The cationic nature of Tachyplesin allows it to interact with anionic phospholipids present in the bacterial membrane and thereby disrupting membrane function. Besides this, the structural nature of Tachyplesin also highlights its antitumor properties. Since it can interact with the membrance of prokaryotic cell, it is likely that TP-I can also interact with the mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria are widely believed to have evolved from prokaryotic cells, that have established a symbiotic relationship with the primitive eukaryotic cell which signifies the structural similarity of mitrochondrial and prokaryotic membranes.
It was found that the synthetic tachyplesin conjugated to the integrin homing domain (RGD-tachyplesin) can inhibit the proliferation of TSU tumor cells prostate cancer and B16 melanoma cells as well as endothelial cells in a dose-dependent mannar in vitro and reduce tumor growth in vivo by inducing apoptosis.[2]. Besides this RGD-tachyplesin can activate caspases and induce Fas ligand, which are the markers for programmed cell death (PCD). Collectively, suppression of tumor associated cell and induction of programmed cell death will eventually act as therapy for cancer and tumor cells.

