We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 970
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[Image:51-TheCalciumPumps-calcium-pumps.jpg|400px|center|]] | [[Image:51-TheCalciumPumps-calcium-pumps.jpg|400px|center|]] | ||
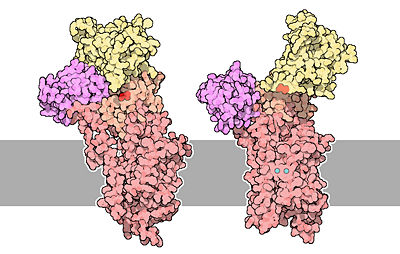
| - | The structure on the left is is the empty state. Two calcium ions are show in blue and Asp351 is show in red.<ref name="second"> David Goodsell, 2004 - Calcium pump molecul of the month - PDB, doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_3</ref> | + | The structure on the left is is the |
| + | <scene name='60/604489/E2_state_free_3w5c/2'>empty state</scene>. Two calcium ions are show in blue and Asp351 is show in red.<ref name="second"> David Goodsell, 2004 - Calcium pump molecul of the month - PDB, doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_3</ref> | ||
| - | To sum up, calcium pumps have two conformations, E1 and E2. These two conformations are characterized by different specificity for ion binding. When the pump is in the <scene name='60/604489/E1_state_3w5b/1'>E1 state</scene>, it has high calcium affinity and interacts with calcium at one side of the membrane. In the | + | To sum up, calcium pumps have two conformations, E1 and E2. These two conformations are characterized by different specificity for ion binding. When the pump is in the <scene name='60/604489/E1_state_3w5b/1'>E1 state</scene>, it has high calcium affinity and interacts with calcium at one side of the membrane. In the E2 state, the enzyme has a lower calcium affinity and that leads to the release of the ion at the opposite side. E1 has the calcium binding site oriented toward the cytoplasm. E2 has the calcium binding site oriented toward the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum or toward the extracellular background<ref name="third">"Thomas D.Pollard and William C. Earnshaw, - ''Membrane, structure and function'' - Cell Biology (second edition), p.133-136</ref>. The phosphorylated intermediate, E1 can phosphorylate ADP, whereas E2 can only react with water<ref>David H.MacLennan, William J.Rice and N. Michael Green, 1997 - ''The Mechanism of Ca2+ Transport by Sarco(Endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPases'' - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.272, 28815-28818, http://www.jbc.org/content/272/46/28815.full.html</ref>. |
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 11:50, 7 January 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 David Goodsell, 2004 - Calcium pump molecul of the month - PDB, doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_3
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Benjamin Lewin, 2007 - Cells - Jones & Bartlett Learning
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Thomas D.Pollard and William C. Earnshaw, - Membrane, structure and function - Cell Biology (second edition), p.133-136
- ↑ David H.MacLennan, William J.Rice and N. Michael Green, 1997 - The Mechanism of Ca2+ Transport by Sarco(Endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPases - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.272, 28815-28818, http://www.jbc.org/content/272/46/28815.full.html
- ↑ Marianela G.Dalghi, Marisa M.Fernández, Mariela Ferreira-Gomes, Irene C.Mangialavori, Emilio L.Malchiodi, Emanuel E.Strehler and Juan Pablo F.C.Rossi, 2013 - Plasma Membrane Calcium ATPase Activity Is Regulated by Actin Oligomers through Direct Interaction - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.288, 23380-23393, http://www.jbc.org/content/288/32/23380.full.
- ↑ Marisa Brini and Ernesto Carafoli, 2010 - The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase and the Plasma Membrane Sodium Calcium Exchanger Cooperate in the Regulation of Cell Calcium - Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, http://cshperspectives.cshlp.org/content/3/2/a004168.full