This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 970
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
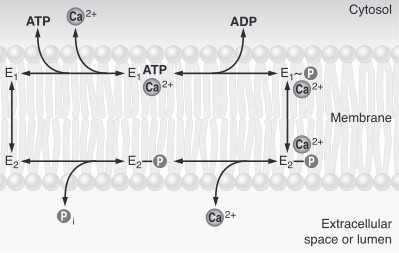
| - | All living organisms depend on P-type ATPase to pump | + | All living organisms depend on P-type ATPase to pump cations across membranes. They play a fundamental role in their metabolism and physiology. Ca2+ ATPase is a P-type ATPase which transport calcium ions across the membrane against a concentration gradient forming a phosphorylated intermediate state (P-type). These pumps clear cytoplasm of the second messenger, the calcium. It's very important to keep a low concentration of calcium in the cell for a good cell signaling. The hydrolysis of ATP is necessary for the pump's functioning. For each ATP hydrolysed, it transfers two calcium ions through the membrane, and two or three hydrogen ions in the opposite direction. |
<ref name="second"> David Goodsell, 2004 - Calcium pump molecul of the month - PDB, doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_3</ref> | <ref name="second"> David Goodsell, 2004 - Calcium pump molecul of the month - PDB, doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_3</ref> | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
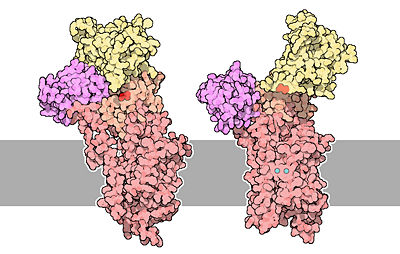
The calcium ATPase is a protein composed of 994 aminoacids. | The calcium ATPase is a protein composed of 994 aminoacids. | ||
| - | The | + | The <scene name='60/604489/Secondary_structure/1'>secondary structure</scene> of the protein is composed of helical regions (47%), beta sheet regions (16%) and loops. There are <scene name='60/604489/10_transmembrane_helices/1'>10 transmembrane alpha helices</scene>, and three of them line a channel that spans the lipid bilayer and that allows calcium to pass through membranes. It also contains too cytoplasmic loops between the transmembrane helices. When the protein is not phosphorylated, two of the transmembrane helices are disrupted and form a cavity that can bind two molecules of calcium. |
The protein is divided in <scene name='60/604489/The_4_domains_of_the_pump/1'>4 regions</scene>. The <scene name='60/604489/Transmembrane_domain/1'>transmembrane region</scene> of the protein contains the channel that span the lipid bilayer, and the calcium binding cavity. | The protein is divided in <scene name='60/604489/The_4_domains_of_the_pump/1'>4 regions</scene>. The <scene name='60/604489/Transmembrane_domain/1'>transmembrane region</scene> of the protein contains the channel that span the lipid bilayer, and the calcium binding cavity. | ||
Revision as of 15:56, 7 January 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 David Goodsell, 2004 - Calcium pump molecul of the month - PDB, doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2004_3
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Benjamin Lewin, 2007 - Cells - Jones & Bartlett Learning
- ↑ Marisa Brini , Ernesto Carafoli, 2009 - Calcium pumps in health and disease - Physiological Reviews
- ↑ Thomas D.Pollard and William C. Earnshaw, - Membrane, structure and function - Cell Biology (second edition), p.133-136
- ↑ David H.MacLennan, William J.Rice and N. Michael Green, 1997 - The Mechanism of Ca2+ Transport by Sarco(Endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPases - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.272, 28815-28818, http://www.jbc.org/content/272/46/28815.full.html
- ↑ Marianela G.Dalghi, Marisa M.Fernández, Mariela Ferreira-Gomes, Irene C.Mangialavori, Emilio L.Malchiodi, Emanuel E.Strehler and Juan Pablo F.C.Rossi, 2013 - Plasma Membrane Calcium ATPase Activity Is Regulated by Actin Oligomers through Direct Interaction - The Journal of Biological Chemistry, p.288, 23380-23393, http://www.jbc.org/content/288/32/23380.full.
- ↑ Marisa Brini and Ernesto Carafoli, 2010 - The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase and the Plasma Membrane Sodium Calcium Exchanger Cooperate in the Regulation of Cell Calcium - Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, http://cshperspectives.cshlp.org/content/3/2/a004168.full