Introduction
Carbonic anhydrase II (gene name CA2), is one of fourteen forms of human α carbonic anhydrases. Their locations are numerous : cytosol, membrane, mitochondrie or in the extra-cellular domain. Carbonic anhydrase II is located in the cytosol.
This enzyme is a lyase, which is able to break C-N links.
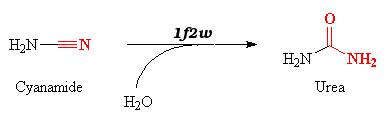
1f2w catalyzes reversible hydration of cyanamide into urea.
Structure
The carbonic anhydrase II is composed of 259 amino acids, and its dimensions are 42Å x 42Å x 72Å.
The protein is composed of :
- 5
- 15
The protein's active site is formed of (residues 94,96 and 119) that can bind a zinc ion. The active site is located in an hydrophobic hole :
Image:125.png
We can see here the conservation of the residues:

The most conserved residues are located in the active site's cavity.
.
.
.
Function
1f2w triggers the hydration of cyanamide into urea according to the equation :
Essential for bone resorption and osteoclast differentiation (By similarity). Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. Can hydrate cyanamide to urea. Involved in the regulation of fluid secretion into the anterior chamber of the eye
Image:D7423ca6daa1149f361c10b977acad36.jpg
Mechanism of Action
Changes in the spectrum of the Co(II)-hCA II derivative observed in the presence of cyanamide suggest that it likely binds the metal ion within the CA active site, adding to the coordination sphere, not substituting the metal-bound solvent molecule. It thereafter undergoes a nucleophilic attack from the metal-bound hydroxide ion, forming urea which remains bound to the metal, as observed in the X-ray crystal structure of hCA II soaked in cyanamide solutions for several hours. The urea molecule is directly coordinated to the active site Zn(II) ion through a protonated nitrogen atom. Several hydrogen bonds involving active site residues Thr199 and Thr200 as well as three water molecules (Wat99, Wat122, and Wat123) further stabilize the urea-hCA II adduct. Kinetic studies in solution further proved that urea acts as a tight binding inhibitor of the two isozymes hCA I and hCA II, with very slow binding kinetics (k(on) = 2.5 x 10(-5)s(-1)M(-1)). A mechanism to explain the hydration process of cyanamide by CAs, as well as the tight binding of urea in the active site, is also proposed based on the hypothesis that urea is deprotonated when bound to the enzyme. Cyanamide is thus the first true suicide substrate of this enzyme for which binding has been documented by means of X-ray crystallographic and spectroscopic studies.
The three-dimensional structure of a possible intermediate in the hydration reaction of cyanamide to urea catalyzed by human carbonic anhydrase II (hCAII) has been determined by cryocrystallographic techniques. The crystal structure shows that two different adducts are formed under the experimental conditions and that they have different occupancy in the crystal. The high occupancy form consists of a binary hCAII-cyanamide complex where the substrate has replaced the zinc-bound hydroxide anion present in the native enzyme, maintaining the tetrahedral geometry around the metal ion. The second, low-occupancy form consists of a hCAII-cyanamide-water ternary complex where the catalytic zinc ion, still being bound to cyanamide, is approached by a water molecule in a five-coordinate adduct. While the first form can be considered a nonproductive complex, the second form may represent an intermediate state of the catalyzed reaction where the water molecule is about to perform a nucleophilic attack on the zinc-activated cyanamide substrate. The structural evidence is consistent with the kinetic data previously reported about this recently described hydrolytic reaction catalyzed by hCAII, and indicates that a different mechanism with respect to that generally accepted for the physiologic carbon dioxide hydration reaction may be adopted by the enzyme, depending on the substrate chemical properties.
Disease
[CAH2_HUMAN] Defects in CA2 are the cause of osteopetrosis autosomal recessive type 3 (OPTB3) [MIM:259730]; also known as osteopetrosis with renal tubular acidosis, carbonic anhydrase II deficiency syndrome, Guibaud-Vainsel syndrome or marble brain disease. Osteopetrosis is a rare genetic disease characterized by abnormally dense bone, due to defective resorption of immature bone. The disorder occurs in two forms: a severe autosomal recessive form occurring in utero, infancy, or childhood, and a benign autosomal dominant form occurring in adolescence or adulthood. Autosomal recessive osteopetrosis is usually associated with normal or elevated amount of non-functional osteoclasts. OPTB3 is associated with renal tubular acidosis, cerebral calcification (marble brain disease) and in some cases with mental retardation.[1] [2] [3] [4] [5]
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.


