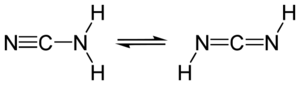This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 964
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
This enzyme is a lyase, which is able to break C-N links, and needs its cofactor, the zinc ion, to be activated. | This enzyme is a lyase, which is able to break C-N links, and needs its cofactor, the zinc ion, to be activated. | ||
| - | Carbonic anhydrase II is located in the cytosol, and normally catalyzes the reversible hydration of CO2 into bicarbonate | + | Carbonic anhydrase II is located in the cytosol, and normally catalyzes the reversible hydration of CO2 into bicarbonate: |
| - | + | [[Image:D7423ca6daa1149f361c10b977acad36.png]] | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
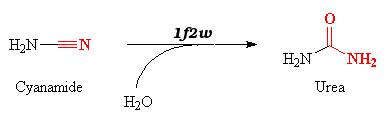
| + | But in this representation, we observe the carbonic anhydrase II bound to its suicide substrate, the cyanamide, which is hydrated by the enzyme, forming urea. The urea-carbonic anhydrase II complex leads to the inactivation of the enzyme. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cyanamide is an organic compound, which formula is : | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:620px-Cyanamide.svg.png|300px]] | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 36: | ||
| - | There | + | There are two binding sites for mercury : |
- <scene name='60/604483/Hg_binding_site/1'>Hg binding site</scene>. | - <scene name='60/604483/Hg_binding_site/1'>Hg binding site</scene>. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 58: | ||
[[Image:Cyanamide.png]] | [[Image:Cyanamide.png]] | ||
| - | Cyanamide is a toxic compound, and is an analog of CO2. It can thereby bind the active site of the carbonic anhydrase. | + | Cyanamide is a toxic compound, and is an analog of CO2. It can thereby bind the active site of the carbonic anhydrase II. |
The reaction is a '''suicide inhibition''': the enzyme binds an suicide substrate (here cyanamide), and this substrate is modified by the enzyme (here into urea) and produces a reactive group that forms a '''stable inhibitor-enzyme complex'''. | The reaction is a '''suicide inhibition''': the enzyme binds an suicide substrate (here cyanamide), and this substrate is modified by the enzyme (here into urea) and produces a reactive group that forms a '''stable inhibitor-enzyme complex'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The inactivation of the carbonic anhydrase II leads to health problems. In fact, it can cause several diseases, such as osteopetrosis autosomal recessive type 3 (also known as Guibaud-Vainsel syndrome). This syndrome is associated with renal tubular acidosis, cerebral calcification (marble brain disease) and in some cases with mental retardation. | ||
==Mechanism of Action== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
| Line 60: | Line 69: | ||
Urea is tightly linked to the carbonic anhydrase II, acting in this way as an inhibitor. | Urea is tightly linked to the carbonic anhydrase II, acting in this way as an inhibitor. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | == Disease == | ||
| - | |||
| - | Defects in CA2 are the cause of osteopetrosis autosomal recessive type 3 (OPTB3) [MIM:259730]; also known as osteopetrosis with renal tubular acidosis, carbonic anhydrase II deficiency syndrome, Guibaud-Vainsel syndrome or marble brain disease. Osteopetrosis is a rare genetic disease characterized by abnormally dense bone, due to defective resorption of immature bone. The disorder occurs in two forms: a severe autosomal recessive form occurring in utero, infancy, or childhood, and a benign autosomal dominant form occurring in adolescence or adulthood. Autosomal recessive osteopetrosis is usually associated with normal or elevated amount of non-functional osteoclasts. OPTB3 is associated with renal tubular acidosis, cerebral calcification (marble brain disease) and in some cases with mental retardation.[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] | ||
Revision as of 20:08, 8 January 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/11/2014, through 15/05/2015 for use in the course "Biomolecule" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the Strasbourg University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 951 through Sandbox Reserved 975. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
1f2w: Carbonic Anhydrase II
| |||||||||||