We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 959
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Biological role == | == Biological role == | ||
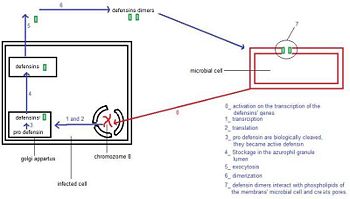
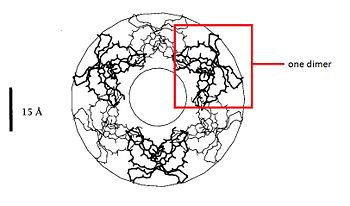
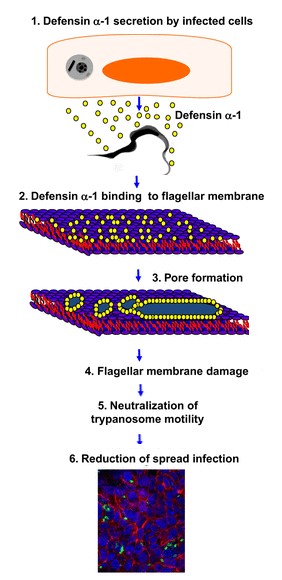
The presence of an unknown microbial cell active the transcription of the defensin-α-1 gene in the human neutrophil. When the RNAm is translated defensins-α-1 are not active. They became active in the Golgi apparatus, in which they are biologically cleaved. Then they are stock in the azurophil granule lumen. After the exocytosis, two defensins-α-1 create a dimere, which'll attack the membran of the microbial cell, by the formation of channel. This channels destabilize the membrane, which causes the destruction of the unknown microbial cell. | The presence of an unknown microbial cell active the transcription of the defensin-α-1 gene in the human neutrophil. When the RNAm is translated defensins-α-1 are not active. They became active in the Golgi apparatus, in which they are biologically cleaved. Then they are stock in the azurophil granule lumen. After the exocytosis, two defensins-α-1 create a dimere, which'll attack the membran of the microbial cell, by the formation of channel. This channels destabilize the membrane, which causes the destruction of the unknown microbial cell. | ||
| - | This mecanism is sum up in the following picture.<ref>http://www.reactome.org/PathwayBrowser/#DIAGRAM=1461973&PATH=168256,168249</ref> | + | This mecanism is sum up in the following picture.<ref name="reactome">http://www.reactome.org/PathwayBrowser/#DIAGRAM=1461973&PATH=168256,168249</ref> |
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| - | [[Image: schema1.jpg|350px|left|thumb| General pathway of defensins-α-1.<ref | + | [[Image: schema1.jpg|350px|left|thumb| General pathway of defensins-α-1.<ref name = "reactome"/>]] |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 20:30, 8 January 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Defensins-α-1
Introduction
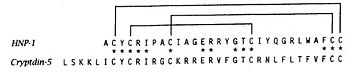
Defensins (DEF) are a family of proteins which are involved in host defense in the epithelia of mucosal surfaces such as those of the intestin, respiratory tract, urinary tract, and vagina. They are antimicrobial and cytotoxic. All the protein of the family are distinguished by a cystein motif and are encoded on the chromozome 8.[1]
There are many defensin but in this article we'll focus on the defensin-α-1. It is a polypeptide which is found in the microbicidal granules of neutrophils. It's syntetisize in the neutrophils, which plays a role in the defense process. defensin-α-1 plays a particular role in phagocite-mediated host defense.[2]
| |||||||||||