This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 971
From Proteopedia
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
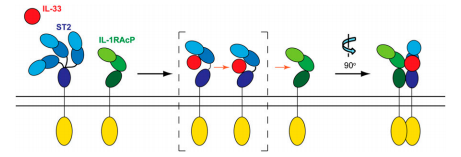
The understanding of the interaction of IL-33 with its receptors has been discovered thanks to the determination of the crystal structure of IL-33 in complex with ectodomain of ST2. | The understanding of the interaction of IL-33 with its receptors has been discovered thanks to the determination of the crystal structure of IL-33 in complex with ectodomain of ST2. | ||
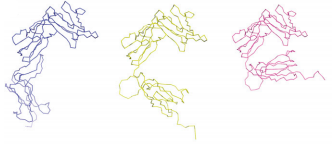
| - | Besides, the combination of crystallography and small-angle X-ray-scattering methods reveal that ST2 has a very flexible conformation, contrary to IL-1RAcP. In fact, ST2 is constituted of three IgG-like domains (<scene name='61/614056/Domains_d1d2d3_de_st2/1'>D1 to D3</scene>). D1 and D2 gather to form a single D1D2 module, connected through a linker with the D3 domain. ST2 | + | Besides, the combination of crystallography and small-angle X-ray-scattering methods reveal that ST2 has a very flexible conformation, contrary to IL-1RAcP. In fact, ST2 is constituted of three IgG-like domains (<scene name='61/614056/Domains_d1d2d3_de_st2/1'>D1 to D3</scene>). D1 and D2 gather to form a single D1D2 module, connected through a linker with the D3 domain. The flexibility of these domains allows ST2 to exist in three different conformers, as you can see on the image below. |
| + | [[Image:ST2_conformers.png ]] | ||
| + | On the left and on the right, there are respectively the open conformer and the close conformer of ST2. On the middle, the half-open conformer is shown. This conformer superimposes perfectly with the conformation of ST2 bound with IL-33. | ||
This conformational specificity provides a capactity of ligand-binding with IL-33. Moreover, the rigidity of IL-1RAcP explains that it can not bind the IL-33 ligand directly. | This conformational specificity provides a capactity of ligand-binding with IL-33. Moreover, the rigidity of IL-1RAcP explains that it can not bind the IL-33 ligand directly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ST2 contains also <scene name='61/614056/Three_residues_of_st2_with_nag/3'>three residues</scene> linked with NAG and an <scene name='61/614056/St2_hydrophobic_patch/1'>hydrophobic patch</scene> which is involved in the interaction with the other receptor, IL-1RAcP. | ||
In humans, IL-33 in its full length is composed of 270 residues and is biologically active. | In humans, IL-33 in its full length is composed of 270 residues and is biologically active. | ||
Revision as of 21:24, 8 January 2015
ST2/IL33 complex
| |||||||||||
References
1. Xi Liua, Michal Hammelb, Yanfeng Hea, John A. Tainerc,d, U-Ser Jenge, Linqi Zhangf, Shuying Wangg, and Xinquan Wanga Structural insights into the interaction of IL-33 with its receptors (2013) DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1308651110
2. Ananda S. Mirchandani, Robert J. Salmond, Foo Y. Interleukin-33 and the function of innate lymphoid cells (2012) DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2012.04.005
3. Rahul Kakkar & Richard T. Lee. The IL-33/ST2 pathway: therapeutic target and novel biomarker (2008) DOI: 10.1038/nrd2660
4. Lécart S, Lecointe N, Subramaniam A, Alkan S, Ni D, Chen R, Boulay V, Pène J, Kuroiwa K, Tominaga S, Yssel H. Activated, but not resting human Th2 cells, in contrast to Th1 and T regulatory cells, produce soluble ST2 and express low levels of ST2L at the cell surface. PMID: 12355452
5. Chia-Lin Hsu and Paul J Bryce. Inducible IL-33 expression by mast cells is regulated by a calcium-dependent pathway. PMCID: PMC3541686