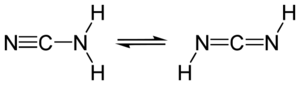This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 964
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sandbox_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | {{Sandbox_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| - | ==1f2w | + | |
| + | ==1f2w Cyanamide-Carbonic Anhydrase II EC 4.2.1.1== | ||
<StructureSection load='1f2w' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of carbonic anhydrase II' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1f2w' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of carbonic anhydrase II' scene=''> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | 1f2w is a protein from the Carbonic anhydrase II (gene name CA2) sub-sub-family, which is one of the fourteen isoforms of human α carbonic anhydrases. | + | 1f2w is a human protein from the Carbonic anhydrase II (gene name CA2) sub-sub-family, which is one of the fourteen isoforms of human α carbonic anhydrases. |
This enzyme is a lyase, which is able to break C-N links, and needs its cofactor, the zinc ion, to be activated. | This enzyme is a lyase, which is able to break C-N links, and needs its cofactor, the zinc ion, to be activated. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 57: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
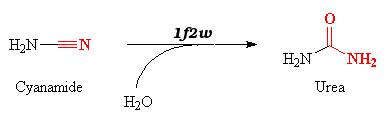
| - | 1f2w catalyzes the hydration of cyanamide into urea according to the equation : | + | In this complex, 1f2w catalyzes the hydration of cyanamide into urea according to the equation : |
[[Image:Cyanamide.png]] | [[Image:Cyanamide.png]] | ||
| - | Cyanamide is a toxic compound, and is an analog of CO2. It can thereby bind the active site of the carbonic anhydrase II. | + | Cyanamide is a toxic compound, and is an analog of CO2. It can thereby bind the active site of the carbonic anhydrase II thanks to the zinc ion. |
The reaction is a '''suicide inhibition''': the enzyme binds an suicide substrate (here cyanamide), and this substrate is modified by the enzyme (here into urea) and produces a reactive group that forms a '''stable inhibitor-enzyme complex'''. | The reaction is a '''suicide inhibition''': the enzyme binds an suicide substrate (here cyanamide), and this substrate is modified by the enzyme (here into urea) and produces a reactive group that forms a '''stable inhibitor-enzyme complex'''. | ||
| - | The inactivation of the carbonic anhydrase II leads to health | + | The inactivation of the carbonic anhydrase II leads to health issues. In fact, it can cause several diseases, such as osteopetrosis autosomal recessive type 3 (also known as Guibaud-Vainsel syndrome). This syndrome is associated with renal tubular acidosis, cerebral calcification (marble brain disease) and in some cases with mental retardation. |
==Mechanism of Action== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
| - | The <scene name='60/604483/Cnn_binding_site/2'>Cyanamide</scene> can bind the metal ion and two threonine residues (THR 199 and 200), it is thereby adding to the coordination sphere. The cyanamid attacks the zinc ion (nucleophilic attack). Afertwards the water molecule performs a nucleophilic attack on the zinc-activated cyanamide substrate forming urea which remains bound to the | + | The <scene name='60/604483/Cnn_binding_site/2'>Cyanamide</scene> can bind the metal ion and two threonine residues (THR 199 and 200), it is thereby adding to the coordination sphere. The cyanamid attacks the zinc ion (nucleophilic attack). Afertwards the water molecule performs a nucleophilic attack on the zinc-activated cyanamide substrate forming urea which remains bound to the zinc ion. |
Urea is tightly linked to the carbonic anhydrase II, acting in this way as an inhibitor. | Urea is tightly linked to the carbonic anhydrase II, acting in this way as an inhibitor. | ||
| Line 76: | Line 77: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| - | Briganti F, Mangani S, Scozzafava A, Vernaglione G, Supuran CT (1999) "Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes cyanamide hydration | + | 1. Briganti F, Mangani S, Scozzafava A, Vernaglione G, Supuran CT (1999) "Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes cyanamide hydration |
to urea: is it mimicking the physiological reaction?" J. Biol. Chem 528-36. | to urea: is it mimicking the physiological reaction?" J. Biol. Chem 528-36. | ||
| - | Guerri A, Briganti F, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT, Mangani S (2000) "Mechanism of cyanamide hydration catalyzed by carbonic | + | 2. Guerri A, Briganti F, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT, Mangani S (2000) "Mechanism of cyanamide hydration catalyzed by carbonic |
anhydrase II suggested by cryogenic X-ray diffraction" Biochemistry 12391-7 | anhydrase II suggested by cryogenic X-ray diffraction" Biochemistry 12391-7 | ||
| - | RCBS: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1f2w consulted the 2/01/2015 [online] | + | 3. RCBS: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1f2w consulted the 2/01/2015 [online] |
| - | PDJB: http://pdbj.org/mine/summary/1f2w consulted the 2/01/2014 [online] | + | 4. PDJB: http://pdbj.org/mine/summary/1f2w consulted the 2/01/2014 [online] |
| - | Jennalib: http://jenalib.fli-leibniz.de/cgi-bin/ImgLib.pl?CODE=1f2w consulted the 3/01/2015 [online] | + | 5. Jennalib: http://jenalib.fli-leibniz.de/cgi-bin/ImgLib.pl?CODE=1f2w consulted the 3/01/2015 [online] |
| - | Wikipedia "Carbonic anhydrase" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbonic_anhydrase consulted the 27/12/2014 [online] | + | 6. Wikipedia "Carbonic anhydrase" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbonic_anhydrase consulted the 27/12/2014 [online] |
| - | Wikipedia "Cyanamide" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyanamide consulted the 27/12/2014 [online] | + | 7. Wikipedia "Cyanamide" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyanamide consulted the 27/12/2014 [online] |
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 21:34, 8 January 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/11/2014, through 15/05/2015 for use in the course "Biomolecule" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the Strasbourg University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 951 through Sandbox Reserved 975. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
1f2w Cyanamide-Carbonic Anhydrase II EC 4.2.1.1
| |||||||||||
References
1. Briganti F, Mangani S, Scozzafava A, Vernaglione G, Supuran CT (1999) "Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes cyanamide hydration
to urea: is it mimicking the physiological reaction?" J. Biol. Chem 528-36.
2. Guerri A, Briganti F, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT, Mangani S (2000) "Mechanism of cyanamide hydration catalyzed by carbonic
anhydrase II suggested by cryogenic X-ray diffraction" Biochemistry 12391-7
3. RCBS: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1f2w consulted the 2/01/2015 [online]
4. PDJB: http://pdbj.org/mine/summary/1f2w consulted the 2/01/2014 [online]
5. Jennalib: http://jenalib.fli-leibniz.de/cgi-bin/ImgLib.pl?CODE=1f2w consulted the 3/01/2015 [online]
6. Wikipedia "Carbonic anhydrase" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbonic_anhydrase consulted the 27/12/2014 [online]
7. Wikipedia "Cyanamide" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyanamide consulted the 27/12/2014 [online]